Cellular Communication Systems
From 2008.igem.org
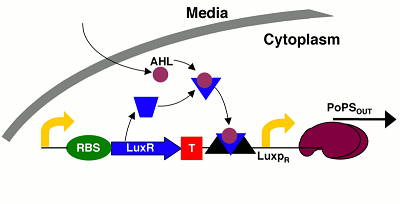
Lux cell signaling system
Responsible: Andrew Gordon and Pallavi Penumetcha
Signal molecule: N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) Generic term for a variety of species specific hormone-like molecules
Bacterial species: discovered in Vibrio fischeri known to work in E. coli
Receiver protein: LuxR protein receives signal from AHL; also has some control over transciption of luciferase
Signal molecule synthase: LuxI; also has some control over transciption of luciferase
Additional Information: "Quorum Quenching" aiiA (intracellular) lactonase reduces AHL concentration
Resources
AHL signaling molecules by species; some are specific to gram pos but may affect gram negs
Reducing Crosstalk in Lux System
References
Quorum Quenching to control Lux Pathway
[1] A Synthetic multicellular system for programmed pattern formation
Parts Needed:
LuxR + pro/term
RBS
LuxI + pro/term
LuxI sender
 "
"