Team:ETH Zurich/Project/Background
From 2008.igem.org
(→Current approaches) |
(→Current approaches) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
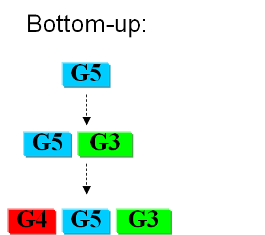
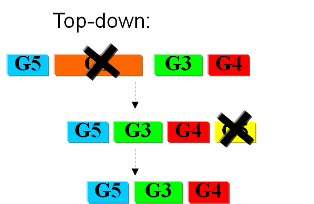
As usual when takling engineering projects, two main approaches can be followed: '''bottom-up''' and '''top-down'''. | As usual when takling engineering projects, two main approaches can be followed: '''bottom-up''' and '''top-down'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We start with a given set of genes and the goal is to find the subset that contains the minimal amount of genes necessary to support life. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:geneset.png]] | ||
In the first case we try to identify all the necessary functions for our system to work (in this case: to live). In this case we identify pathways to produce all necesary metabolites the cell needs, such as lipids, aminoacids, etc. A good example of this approach can be found in []. The following step is to sinthesize the complete chromosome with the identified genes into an "empty" cell. This approach is beeing followed e.g. by the Craig Venter Institute []. | In the first case we try to identify all the necessary functions for our system to work (in this case: to live). In this case we identify pathways to produce all necesary metabolites the cell needs, such as lipids, aminoacids, etc. A good example of this approach can be found in []. The following step is to sinthesize the complete chromosome with the identified genes into an "empty" cell. This approach is beeing followed e.g. by the Craig Venter Institute []. | ||
Revision as of 20:10, 25 October 2008
Current approachesAs usual when takling engineering projects, two main approaches can be followed: bottom-up and top-down. We start with a given set of genes and the goal is to find the subset that contains the minimal amount of genes necessary to support life. In the first case we try to identify all the necessary functions for our system to work (in this case: to live). In this case we identify pathways to produce all necesary metabolites the cell needs, such as lipids, aminoacids, etc. A good example of this approach can be found in []. The following step is to sinthesize the complete chromosome with the identified genes into an "empty" cell. This approach is beeing followed e.g. by the Craig Venter Institute []. The second approach starts from a working syspem (such as a well characterized strain like K12). By identifying non-essential parts of the metabolism and deleting them, we reduce the complexity of the cell. Many groups are working on this method, such as the Biofrontier Laboratories [] or Scarab Genomics []. |
 "
"