Team:Newcastle University/Notebook
From 2008.igem.org
Riachalder (Talk | contribs) |
Riachalder (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
Fig 1 shows the construct which contains: | Fig 1 shows the construct which contains: | ||
| - | * spaR (subtilin peptide antibiotic Regulation) - the 220 amino acid product of this gene usually regulates the downstream production of subtilin antibiotic. It has an N-terminal domain that can be phosphorylated and a C-terminal domian that has DNA binding properties | + | * spaR (subtilin peptide antibiotic Regulation) - the 220 amino acid product of this gene usually regulates the downstream production of subtilin antibiotic. It has an N-terminal domain that can be phosphorylated and a C-terminal domian that has DNA binding properties [http://http://aem.asm.org/cgi/reprint/59/1/296.pdf] |
| - | * spaK (subtilin peptide antibiotic Kinase) - this gene codes for a 325 amino acid histadine kinase peptide that phosphorylates the N-terminus of spaR. This activates the DNA binding ability of spaR's C-terminus, which in turn initiates transcription of the downstream gene. In the case of our construct, this gene is GFP. | + | * spaK (subtilin peptide antibiotic Kinase) - this gene codes for a 325 amino acid histadine kinase peptide that phosphorylates the N-terminus of spaR [http://http://aem.asm.org/cgi/reprint/59/1/296.pdf]. This activates the DNA binding ability of spaR's C-terminus, which in turn initiates transcription of the downstream gene. In the case of our construct, this gene is GFP. |
* GFP (green fluorescence protein) - the marker being used to show activation of the spaRK system and therefore diagnosis of gram-positive bacteria by ''B. Subtilis'' | * GFP (green fluorescence protein) - the marker being used to show activation of the spaRK system and therefore diagnosis of gram-positive bacteria by ''B. Subtilis'' | ||
Revision as of 16:20, 19 August 2008
Newcastle University
GOLD MEDAL WINNER 2008
| Home | Team | Original Aims | Software | Modelling | Proof of Concept Brick | Wet Lab | Conclusions |
|---|
Lab Notebook
Meetings The team meets at least once a week on thursday afternoons. Details of each meeting can be found through the calendar links.
Ria and Jess finally started in the labs on Monday the 4th August. So we will start updating the wiki with what's been happening and the progress we are making.
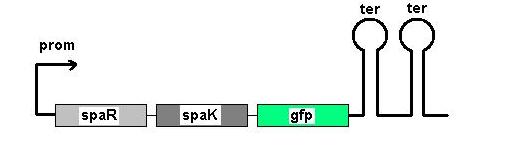
Fig 1: Newcastle iGEM team's construct
Fig 1 shows the construct which contains:
- spaR (subtilin peptide antibiotic Regulation) - the 220 amino acid product of this gene usually regulates the downstream production of subtilin antibiotic. It has an N-terminal domain that can be phosphorylated and a C-terminal domian that has DNA binding properties [1]
- spaK (subtilin peptide antibiotic Kinase) - this gene codes for a 325 amino acid histadine kinase peptide that phosphorylates the N-terminus of spaR [2]. This activates the DNA binding ability of spaR's C-terminus, which in turn initiates transcription of the downstream gene. In the case of our construct, this gene is GFP.
- GFP (green fluorescence protein) - the marker being used to show activation of the spaRK system and therefore diagnosis of gram-positive bacteria by B. Subtilis
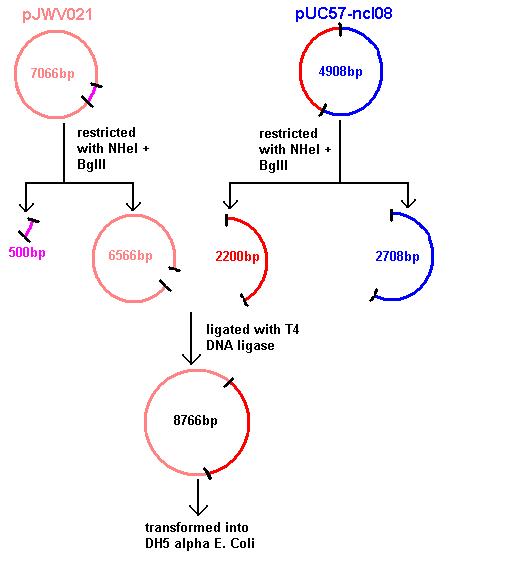
Aim 1: clone the spaRK system from pUC57 into pJWV021 and transform into DH5 alpha competent E. coli
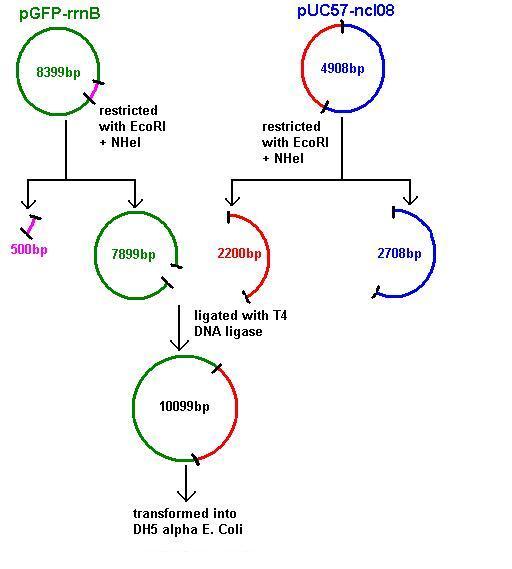
Aim 2: clone the spaRK system from pUC57 into pGFP-rrnB and transform into TOP10 competent E. coli
The 2.2kb fragment (ncl08) contains the spaRK system and a promotor-less GFP gene linked to this. This means that when spaR is activated, its positive regulatory effect on spaK will in turn activate GFP.
Monday 4th August
All 5 of us (Megan, Mark, Nina, Ria and Jess) went into the lab today to decide on a plan of action for the weeks to come.
- We used electrophoresis to check for the presence of plasmids (pGFPrrnB- our plasmid with the GFP gene, and pJWV021- with the mCherry gene). Our gel was inconclusive, so we decided to re-run it the following day to confirm our results.
- In the afternoon we attempted to transform DH5 Alpha competent cells with DNA from the registry (from source plate 1010 well 4A and 1018 7A).
- We followed the extraction method outlined in the green folder and for each DNA spot we plated two petri dishes: one with a larger volume of DNA (4μl) and one with a smaller volume (2μl) to make colony counting easier. We plated the following and incubated at 37˚C overnight:
Plate 1: +ve control (isolated plasmid plus TOP10 cells)
Plate 2: -ve control (TOP10 cells only, no plasmid)
Plate 3: Large 1010 4A
Plate 4: Small 1010 4A
Plate 5: Large 1018 7A
Plate 6: Small 1018 7A
Tuesday 5th August
Today we re-ran the gel electrophoresis of pGFP-rrnB and pJWV021 to check correct plasmid size and sufficient plasmid quantity. Results showed this to be true and the expected plasmid sizes of 8399bp for pGFP-rrnB and 7066bp for pJWV021.
Wednesday 6th August
Analyses of results from Monday’s transformation showed no colony growth except for the positive control. We decided to try another transformation into TOP10 E. coli using different spots from the registry. This time we used 1018 7A and 1004 6G.
We noticed that Cambridge, who had also been having problems, had adapted the extraction method. So we tried their improved method, with a couple of minor differences:
1) Warm 50μl of H20 in an Eppendorf tube at 50˚C
2) Add 4 punched-out spots from the registry
3) Keep at 50˚C for 20 minutes
4) Centrifuge at 13,300g for 3 minutes
5) Warm for a further 10 minutes at 50˚C
6) Centrifuge at 13,300g for 3 minutes
7) Pipette out the supernatant which should (hopefully!) contain the DNA
To see the original modified method, go to Cambridge’s OpenWetWare page:
http://openwetware.org/wiki/IGEM:Cambridge/2008/Protocols
| May | ||||||
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | |
| June | ||||||
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 | ||||||
| July | ||||||
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | |||
| August | ||||||
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
 "
"