Team:ETH Zurich/Modeling/Overview
From 2008.igem.org
Luca.Gerosa (Talk | contribs) |
Luca.Gerosa (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
* Which are the predicted quantitative differences in terms of growth rate and genome size of strains on which has been applied the selection procedure? <br><br> | * Which are the predicted quantitative differences in terms of growth rate and genome size of strains on which has been applied the selection procedure? <br><br> | ||
'''Method:''' <br> | '''Method:''' <br> | ||
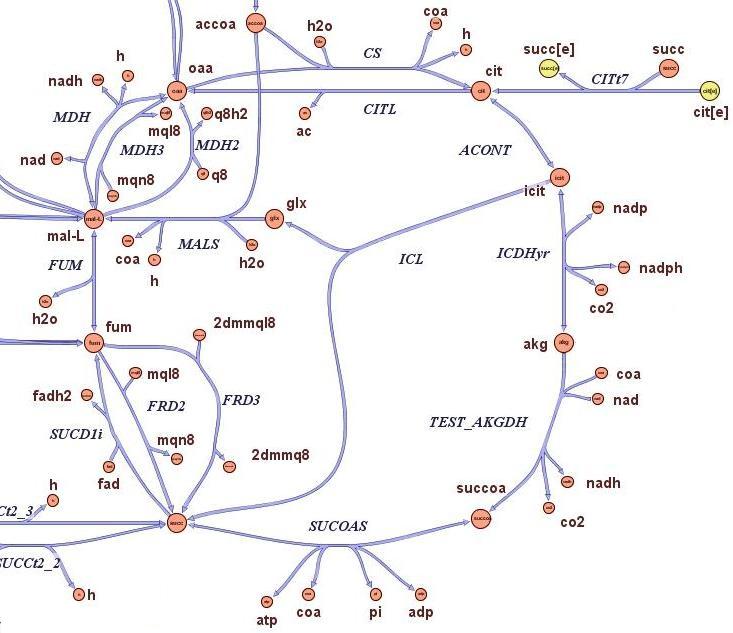
| - | The state-of-the-art genome scale model for E.Coli iAF1260 (1260 genes included) | + | The state-of-the-art genome scale model for E.Coli iAF1260 (1260 genes included) was modified in order to account for thymidine auxotrophycity, thymidine uptaking limitation, genome reduction and growth on different medium. Stochastic algorithm and flux balance analysis were applied to predict growth rates.<br><br> |
'''Results:''' <br> | '''Results:''' <br> | ||
It is indeed possible to select reduced genome strains using thymidine limitation. The quantification shows that the method is at the border line with the sensitivity of chemostat machinery setup. Predictions shows the possibility of reducing 4% of genes for a minimal medium growing strains and 8% of genese for rich medium growing strains. | It is indeed possible to select reduced genome strains using thymidine limitation. The quantification shows that the method is at the border line with the sensitivity of chemostat machinery setup. Predictions shows the possibility of reducing 4% of genes for a minimal medium growing strains and 8% of genese for rich medium growing strains. | ||
Revision as of 16:12, 11 October 2008
Overview on the modelling frameworkThis page is meant to give an introduction to the the overall modelling framework we have constructed in order to asses feasibility analysis, temporal scale details and other parameter estimations that regard our project setup. As introduced in the project overview section, four main components can be identified in the deviced mechanism. Accordingly, we divided the modelling framework in four modules that tackles the relative problematics.
|
 "
"