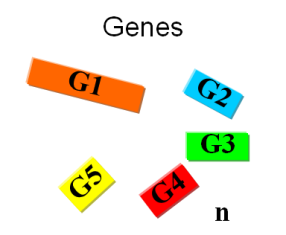Team:ETH Zurich/Project/Background
From 2008.igem.org
(→Current approaches) |
(→Current approaches) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
[[Image:geneset.png]] | [[Image:geneset.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Bottom-up == | ||
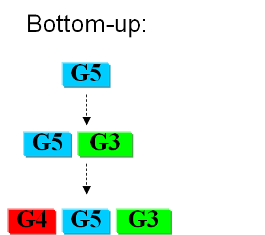
In the first case we try to identify all the necessary functions for our system to work (in this case: to live). In this case we identify pathways to produce all necesary metabolites the cell needs, such as lipids, aminoacids, etc. A good example of this approach can be found in []. The following step is to sinthesize the complete chromosome with the identified genes into an "empty" cell. This approach is beeing followed e.g. by the Craig Venter Institute []. | In the first case we try to identify all the necessary functions for our system to work (in this case: to live). In this case we identify pathways to produce all necesary metabolites the cell needs, such as lipids, aminoacids, etc. A good example of this approach can be found in []. The following step is to sinthesize the complete chromosome with the identified genes into an "empty" cell. This approach is beeing followed e.g. by the Craig Venter Institute []. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 25: | ||
[[Image:bottomup.png]] | [[Image:bottomup.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Bottom-up == | ||
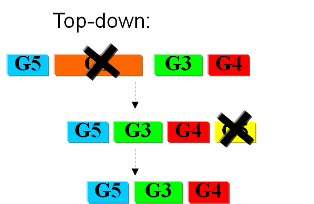
The second approach starts from a working syspem (such as a well characterized strain like K12). By identifying non-essential parts of the metabolism and deleting them, we reduce the complexity of the cell. Many groups are working on this method, such as the Biofrontier Laboratories [] or Scarab Genomics []. | The second approach starts from a working syspem (such as a well characterized strain like K12). By identifying non-essential parts of the metabolism and deleting them, we reduce the complexity of the cell. Many groups are working on this method, such as the Biofrontier Laboratories [] or Scarab Genomics []. | ||
Revision as of 20:16, 25 October 2008
Current approachesAs usual when takling engineering projects, two main approaches can be followed: bottom-up and top-down. We start with a given set of genes and the goal is to find the subset that contains the minimal amount of genes necessary to support life.
Bottom-upIn the first case we try to identify all the necessary functions for our system to work (in this case: to live). In this case we identify pathways to produce all necesary metabolites the cell needs, such as lipids, aminoacids, etc. A good example of this approach can be found in []. The following step is to sinthesize the complete chromosome with the identified genes into an "empty" cell. This approach is beeing followed e.g. by the Craig Venter Institute [].
Bottom-upThe second approach starts from a working syspem (such as a well characterized strain like K12). By identifying non-essential parts of the metabolism and deleting them, we reduce the complexity of the cell. Many groups are working on this method, such as the Biofrontier Laboratories [] or Scarab Genomics []. |
 "
"