Team:Guelph/Results
From 2008.igem.org
m |
m |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
{|align="center" | {|align="center" | ||
|[[Image:PSBAinpSB1A2-E0240.jpg|300px]] | |[[Image:PSBAinpSB1A2-E0240.jpg|300px]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
Knowing we had at least this biobricked strong promoter to work with, we went on building the synthetic operon in the pSB1A2 biobrick plasmid. Using the Phusion proofreading taq kindly provided to us by NEB and primers from IDT, we PCR amplified the crtE, B, and Y genes from Erwinia uredevora that were shared with us by members of iGEM Minnesota. Biobricked crt I was sent to us by iGEM Edinburgh. These were sequenced and test digested to confirm insert size. The gel photo showing Eco/Pst digests of the constructs in pSB1A2 is below. | Knowing we had at least this biobricked strong promoter to work with, we went on building the synthetic operon in the pSB1A2 biobrick plasmid. Using the Phusion proofreading taq kindly provided to us by NEB and primers from IDT, we PCR amplified the crtE, B, and Y genes from Erwinia uredevora that were shared with us by members of iGEM Minnesota. Biobricked crt I was sent to us by iGEM Edinburgh. These were sequenced and test digested to confirm insert size. The gel photo showing Eco/Pst digests of the constructs in pSB1A2 is below. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 30: | ||
{|align="center" | {|align="center" | ||
|[[Image:CrtTest]] | |[[Image:CrtTest]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
Next, we ligated crt B to E, and crt Y to I. E and I were cut with SpeI and Pst, while B and Y were cut with XbaI and PstI. This is illustrated below using gels. | Next, we ligated crt B to E, and crt Y to I. E and I were cut with SpeI and Pst, while B and Y were cut with XbaI and PstI. This is illustrated below using gels. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 38: | ||
{|align="center" | {|align="center" | ||
|[[Image:halfoperon]] | |[[Image:halfoperon]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
To cap off the operon, we used the same strategy and to restrict and ligate on the biobrick GFP (plus terminators and rbs) from E0240. We also ligated the 1.5 kb frdBCD operon to this GFP in vitro, then PCR fished for the frdBCD plus GFP using a frdBCD fwd primer and VR. This PCR product was cut with XbaI and PstI and put onto the end of the CrtE,B,I,Y operon. The gel results are shown below. | To cap off the operon, we used the same strategy and to restrict and ligate on the biobrick GFP (plus terminators and rbs) from E0240. We also ligated the 1.5 kb frdBCD operon to this GFP in vitro, then PCR fished for the frdBCD plus GFP using a frdBCD fwd primer and VR. This PCR product was cut with XbaI and PstI and put onto the end of the CrtE,B,I,Y operon. The gel results are shown below. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 46: | ||
{|align="center" | {|align="center" | ||
|[[Image:Operon Caps]] | |[[Image:Operon Caps]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
The last cloning steps were to put promoters onto the constructs, test them for carotenoid production and GFP fluorescence, but this website will be frozen before we could show that. Likewise, we intend to do a quick intestinal simulation to include in our presentation and poster, but the website won't show it. Talk to us at the Jamboree to see if we made it or not! | The last cloning steps were to put promoters onto the constructs, test them for carotenoid production and GFP fluorescence, but this website will be frozen before we could show that. Likewise, we intend to do a quick intestinal simulation to include in our presentation and poster, but the website won't show it. Talk to us at the Jamboree to see if we made it or not! | ||
| Line 45: | Line 53: | ||
{|align="center" | {|align="center" | ||
|[[Image:guelph intestine.jpg|300px]] | |[[Image:guelph intestine.jpg|300px]] | ||
| - | + | | | |
| + | |} | ||
| Line 62: | Line 71: | ||
{|align="center" | {|align="center" | ||
|[[Image:KP342 GFP assay in corn.jpg|700px]] | |[[Image:KP342 GFP assay in corn.jpg|700px]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
We injected 20 ul of a bacterial OD of 0.85 we estimated to amount to be 1.07 million microbes based on colony forming unit counts (CFU). The above plates show a one fold dilution of homogenized plant tissue. That is to say, 100 mg of plant was ground in 100 ul of sodium phoshpate buffer (1:1 dilution) and 50 ul of this plated on half a kanamycin filled plate. This suggests that corn leaf tissue was harbouring 12 microbes per milligram of tissue (both root types had a similar number), while stem tissue near the site of injection had a number closer to 500. It is difficult to extrapolate accurately how many microbes might exist in the plant, but at the very least this suggests the microbes we injected spread systematically and are stabily transcribing a transgene on a plasmid inside this plant for a significant period of time. | We injected 20 ul of a bacterial OD of 0.85 we estimated to amount to be 1.07 million microbes based on colony forming unit counts (CFU). The above plates show a one fold dilution of homogenized plant tissue. That is to say, 100 mg of plant was ground in 100 ul of sodium phoshpate buffer (1:1 dilution) and 50 ul of this plated on half a kanamycin filled plate. This suggests that corn leaf tissue was harbouring 12 microbes per milligram of tissue (both root types had a similar number), while stem tissue near the site of injection had a number closer to 500. It is difficult to extrapolate accurately how many microbes might exist in the plant, but at the very least this suggests the microbes we injected spread systematically and are stabily transcribing a transgene on a plasmid inside this plant for a significant period of time. | ||
| Line 69: | Line 80: | ||
{|align="center" | {|align="center" | ||
| - | [[Image:arab342.jpg|400px]] | + | |[[Image:arab342.jpg|400px]] |
| + | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 04:28, 29 October 2008
| Home | The Team | The Project | Parts | Notebook | Results | Links |
|---|
Synthetic Operon
We got the pDSK-GFPuv plasmid from the Noble Foundation and signed an MTA for its use in the iGEM competition. We PCRed the strong 250 bp consitutive promoter from this plasmid (its the 16S ribosomal promoter from the chloroplast of an herbicide resistant type of Amaranthus weed) and put it into the promoter testing device, pSB1A2-E0240 and it does indeed prove to be a strong promoter:
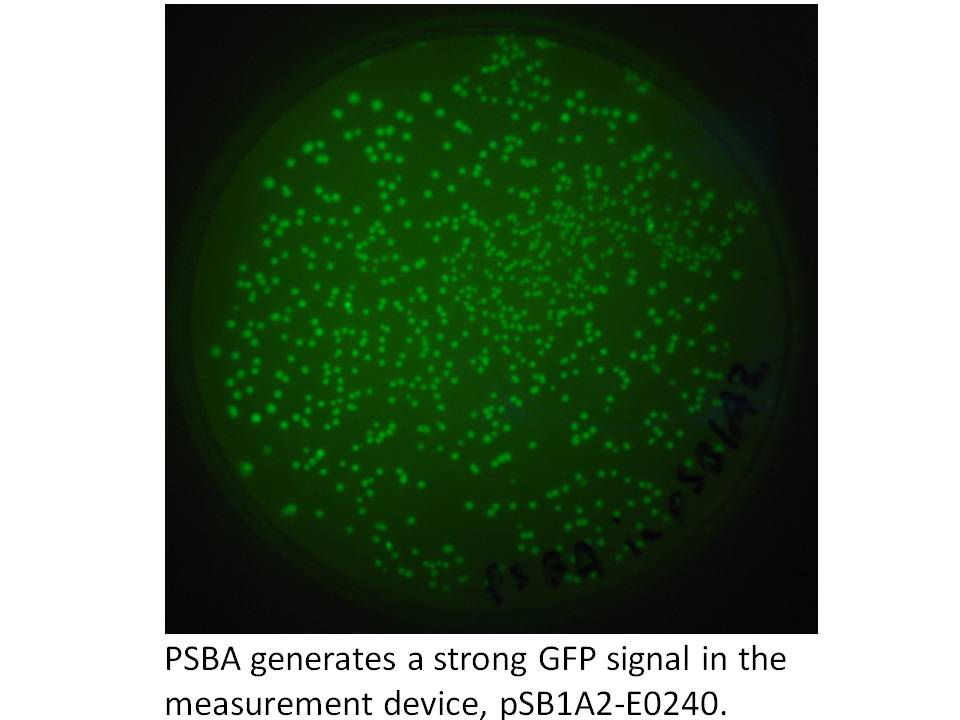
|
Knowing we had at least this biobricked strong promoter to work with, we went on building the synthetic operon in the pSB1A2 biobrick plasmid. Using the Phusion proofreading taq kindly provided to us by NEB and primers from IDT, we PCR amplified the crtE, B, and Y genes from Erwinia uredevora that were shared with us by members of iGEM Minnesota. Biobricked crt I was sent to us by iGEM Edinburgh. These were sequenced and test digested to confirm insert size. The gel photo showing Eco/Pst digests of the constructs in pSB1A2 is below.
| File:CrtTest |
Next, we ligated crt B to E, and crt Y to I. E and I were cut with SpeI and Pst, while B and Y were cut with XbaI and PstI. This is illustrated below using gels.
| File:Halfoperon |
To cap off the operon, we used the same strategy and to restrict and ligate on the biobrick GFP (plus terminators and rbs) from E0240. We also ligated the 1.5 kb frdBCD operon to this GFP in vitro, then PCR fished for the frdBCD plus GFP using a frdBCD fwd primer and VR. This PCR product was cut with XbaI and PstI and put onto the end of the CrtE,B,I,Y operon. The gel results are shown below.
| File:Operon Caps |
The last cloning steps were to put promoters onto the constructs, test them for carotenoid production and GFP fluorescence, but this website will be frozen before we could show that. Likewise, we intend to do a quick intestinal simulation to include in our presentation and poster, but the website won't show it. Talk to us at the Jamboree to see if we made it or not!
|
RNAi inducing corn endophytes (BIGS)
Making projections based on measurements on endosymbiont and endophyte numbers within a functioning biological system using GFP
We plan to do wet lab modelling. By tagging our microbes with simple GFP constructs and counting colony forming units per set sample fresh weight, we hope to be able to observe microbial survival with our construct and predict how much beta carotene or RNAi might be produced and released.
In corn, we are doing this using a corn endophyte called Klebsiella pneumonii. Plants were either injected with 5 ul of bacterial suspension or dipped in it at an early stage. Two weeks later (a month for the dipped plants) 500 mg of tissue were harvested, ground in sterilized mortars, resuspended in 500 ul of sodium phosphate buffer, and 50 ul of the dilution was spread on half of a kanamycin LB plate. The results are depicted graphically below.
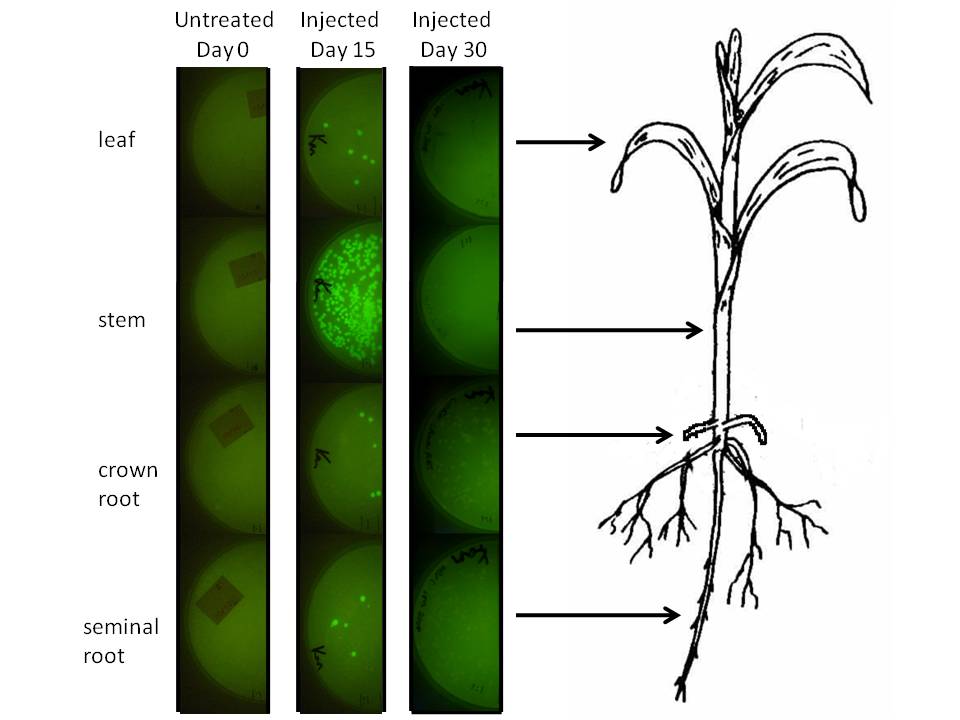
|
We injected 20 ul of a bacterial OD of 0.85 we estimated to amount to be 1.07 million microbes based on colony forming unit counts (CFU). The above plates show a one fold dilution of homogenized plant tissue. That is to say, 100 mg of plant was ground in 100 ul of sodium phoshpate buffer (1:1 dilution) and 50 ul of this plated on half a kanamycin filled plate. This suggests that corn leaf tissue was harbouring 12 microbes per milligram of tissue (both root types had a similar number), while stem tissue near the site of injection had a number closer to 500. It is difficult to extrapolate accurately how many microbes might exist in the plant, but at the very least this suggests the microbes we injected spread systematically and are stabily transcribing a transgene on a plasmid inside this plant for a significant period of time.
We observed similar result in Arabidopsis thaliana, which may indicate this would be a useful transgene delivery tool for Arabidopsis research.
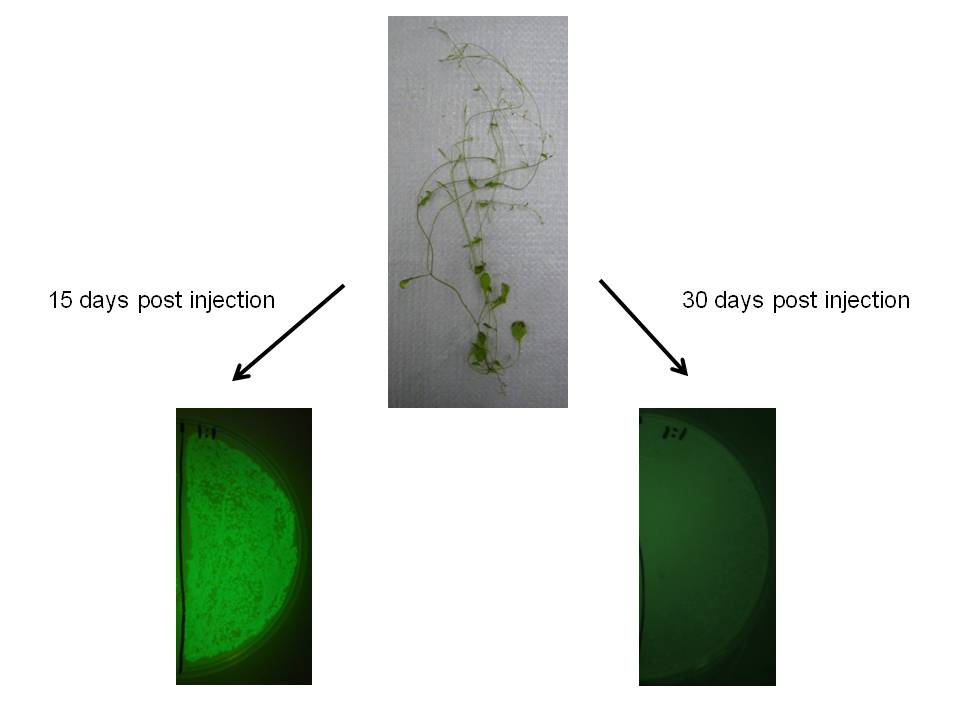
|
 "
"