History of Resveratrol
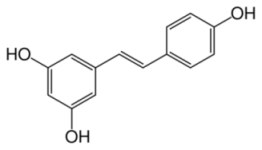 trans-Resveratrol In 1940, Resveratrol was identified as the active component in Cassia quniquangulata (cinnamon) extract and was shown to be responsible for the anti-inflammatory properties of Polygonum cuspidatum roots, used in traditional Chinese and Japanese medicine (Takaoka). Since then, studies have shown that resveratrol is a member of a class of compounds called phytoalexins, which are used as a defense mechanism in plants in response to pathogens. Grapes, blueberries, and bilberries produce appreciable levels of resveratraol, and thus the main sources of resveratrol in the human diet are red wine, grape juice, peanuts, and cranberry juice. The discovery of Resveratrol in wine (1992), implicated a role for this compound in underlying the “French Paradox”, i.e., the observation that French exhibit a relatively low risk of cardiovascular disease even though they exhibit a diet that is high in saturated fats (Reference here).
Health Benefits of Resveratrol
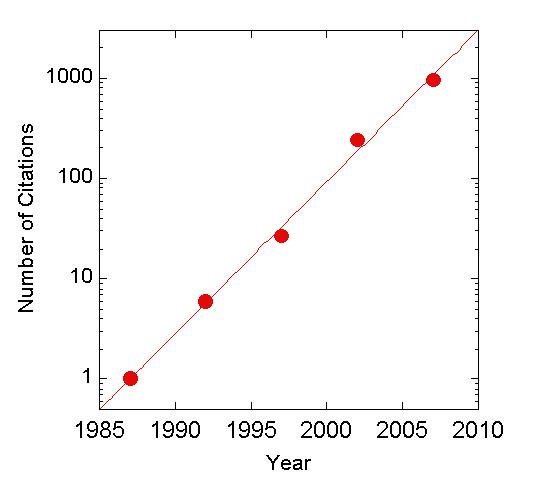 History of Resveratrol Citatitions on PubMed Notice Semilog Plot A PubMed search for “resveratrol”, indicates that scientific interest in the health benefits of resveratrol is growing exponentially. To date, a diverse array of health benefits have been associated with resveratrol, including:
1. Improved insulin sensitivity. Resveratrol has been shown as a potent therapeutic for type 2 diabetes [27]. Pharmaceuticals based on resveratrol-like compounds for the treatment of diabetes are currently in Phase I clinical trials [28].
2. Inhibits carcinogenesis. Resveratrol induces cell death specifically in cancerous cells. This property has been demonstrated for a variety of cancers, including colon [5-7], pancreatic [8], prostate [9,10], breast [11,12], and skin [13,14] cancer. Several ongoing phase I human clinical trials are investigating resveratrol as a cancer therapy [15,16]
3. Extended lifespan. Resveratrol mimics the effects of caloric restriction in mammals and has been shown to extend lifespans in invertebrates [29,30], anda fish model [31]. In addition, resveratrol reduces the genetic changes associated with aging in a mammalian mouse model [4,18,32]. PGC-1alpha levels was decreased threefold by induction of genes for oxidative phosphorylation and mitochondrial biogenesis in wt SIRT1 mice but no change in SIRT1(-/-) MEFs [33].
4. Improved cardiovascular function. Resveratrol exhibits cardioprotective effects, such as the suppression of atherosclerosis, inhibition of platelet aggregation, vasorelaxation promotion, and modulation of triglyceride blood levels [1-4].
5. Reduced Neurodegeneration. Mouse models of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease have provided evidence that resveratrol functions as a protective agent against degenerative neural diseases[22,23]. In addition, Experiments with rats, mice, and gerbils show that resveratrol administration protects against brain damage following isochemic stroke [24-26].
6. Decreases inflammation. NEED A SENTENCE OR TWO SUMMARIZING THESE CITATIONS [18-21].
Our understanding of Resveratrol effects on cellular function is currently too limited to explain the biochemical origin of the diverse pharmacological effects that have been observed to date.
Rationale for Creating Resveratrol-Enriched Beer
ONE OF THE BEST SOURCES OF RESVERATROL IS WINE, WITH RED WINE HAVING CONCENTRATIONS RANGING FROM X TO Y MG/L AND WHITE WINE HAVING CONCENTRATIONS RANGING FROM Z TO ZZ (REFERENCES). Unfortunately, THE ABUNDANCE OF RESVERATROL IN this beverage is thought to be TOO LOW TO ALLOW FOR ALL OF THE HEALTH BENEFITS THAT HAVE BEEN DEMONSTRATED IN MODEL ORGANISMS (REFERENCES). In fact, a recent study has suggested that one must consume LIST AMOUNT to gain all of the health benefits of resveratrol that have been observed in rats, such as XX, YY, and ZZ.
BEER is also expected to contain resveratrol. Hops that is used to flavor beer contains 0.5 to 1 µg resveratrol/g (reference), and BEER IS PRODUCED UNDER FERMENTATIVE CONDITION, which is likely to prevent the AIR OXIDATION AND INACTIVATION OF RESVERATROL from the Hops. While the levels of resveratrol in beer are less than that of wine, beer REPRESENTs >85% OF ALL ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES CONSUMED in the US?? (REFERENCE), and thus a better vehicle for widespread delivery of air-sensitive prophylactics like resveratrol. To increase the level of resveratrol present in beer, we are working to engineer a brewers yeast that synthesizes resveratrol from tyrosine.
-Beer made up 85.8% of all alcoholic beverage consumption (in total volume) in 2005.
-->Annual per capita consumption of Beer (2005) = ~20 gallons
-->Annual per capita consumption of Wine (2005) = ~2.5 gallons
-If resveratrol can be produced during fermentation, it provides an additional health benefit at no additional cost.
-->The resveratrol is produced in a ready-to-consume format!
-->Dark and anaerobic conditions required for fermentation improve resveratrol stability.
-->P-coumaric acid is a natural component of wood. Synergistic function with the wooden barrels used for aging.
References
1: Samuel SM, et al. Akt/FOXO3a/SIRT1-mediated cardioprotection by n-tyrosol against ischemic stress in rat in vivo model of myocardial infarction: switching gears toward survival and longevity. J Agric Food Chem. 2008 Oct 22;56(20):9692-8. Epub 2008 Oct 1. PMID: 18826227 [PubMed - in process].
2: Hwang JT, et al. Resveratrol protects ROS-induced cell death by activating AMPK in H9c2 cardiac
muscle cells.
Genes Nutr. 2008 Feb;2(4):323-6.
PMID: 18850225 [PubMed - in process]
3: Gresele P, et al. Resveratrol, at concentrations attainable with moderate wine consumption,
stimulates human platelet nitric oxide production.
J Nutr. 2008 Sep;138(9):1602-8.
PMID: 18716157 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
4: Barger JL, et al. A low dose of dietary resveratrol partially mimics caloric restriction and
retards aging parameters in mice.
PLoS ONE. 2008 Jun 4;3(6):e2264.
PMID: 18523577 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
5: Juan ME, et al. Resveratrol induces apoptosis through ROS-dependent mitochondria pathway in HT-29 human colorectal carcinoma cells.
J Agric Food Chem. 2008 Jun 25;56(12):4813-8. Epub 2008 Jun 4.
PMID: 18522405 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
6: Saiko P, et al. Novel resveratrol analogs induce apoptosis and cause cell cycle arrest in HT29
human colon cancer cells: inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase activity.
Oncol Rep. 2008 Jun;19(6):1621-6.
PMID: 18497974 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
7: Marel AK, et al. Inhibitory effects of trans-resveratrol analogs molecules on the proliferation and the cell cycle progression of human colon tumoral cells.
Mol Nutr Food Res. 2008 May;52(5):538-48.
PMID: 18384089 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
8: Bernhaus A, et al. Antitumor effects of KITC, a new resveratrol derivative, in AsPC-1 and BxPC-3 human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Invest New Drugs. 2008 Oct 8. [Epub ahead of print]
PMID: 18841326 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
9: Seeni A, et al. Suppression of Prostate Cancer Growth by Resveratrol in The Transgenic Rat for Adenocarcinoma of Prostate (TRAP) Model.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2008 Jan-Mar;9(1):7-14.
PMID: 18439064 [PubMed - in process]
10: Horvath Z, et al. Novel resveratrol derivatives induce apoptosis and cause cell cycle arrest in prostate cancer cell lines.
Anticancer Res. 2007 Sep-Oct;27(5A):3459-64.
PMID: 17970095 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
11: Filomeni G, et al. trans-Resveratrol induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells MCF-7 by the activation of MAP kinases pathways.
Genes Nutr. 2007 Dec;2(3):295-305. Epub 2007 Oct 18.
PMID: 18850184 [PubMed - in process]
12: Schlachterman A, et al. Combined resveratrol, quercetin, and catechin treatment reduces breast tumor growth in a nude mouse model.
Transl Oncol. 2008 Mar;1(1):19-27.
PMID: 18607509 [PubMed - in process]
13: Jang M, Cai L, et al. Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol, a natural product derived from grapes.
Science. 1997 Jan 10;275(5297):218-20.
PMID: 8985016 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
14: van Ginkel PR, et al. Resveratrol inhibits uveal melanoma tumor growth via early mitochondrial dysfunction.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 Apr;49(4):1299-306.
PMID: 18385041 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
15: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct/show/NCT00256334
16: http://www.cancer.gov/clinicaltrials/CCUM-2004-0535
17: Ellen L. Robb, et al. Molecular mechanisms of oxidative stress resistance induced by resveratrol: Specific and progressive induction of MnSOD, Biocehm and Biophys Res Comm, 2008
18: Kode A, et al. (2007). "Resveratrol induces glutathione synthesis by activation of Nrf2 and protects against cigarette smoke-mediated oxidative stress in human lung epithelial cells". Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.. doi:10.1152 (inactive 2008-06-20). PMID 18162601.
19: Venkatachalam K, et al. Resveratrol inhibits high glucose-induced PI3K/Akt/ERK-dependent interleukin-17 expression in primary mouse cardiac fibroblasts.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 May;294(5):H2078-87. Epub 2008 Feb 29.
PMID: 18310510 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
20: Zhu J, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of resveratrol on TNF-alpha-induced MCP-1 expression in adipocytes.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 May 2;369(2):471-7. Epub 2008 Feb 20.
PMID: 18291098 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
21: Kennedy A, et al. Conjugated linoleic acid-mediated inflammation and insulin resistance in human adipocytes are attenuated by resveratrol.
J Lipid Res. 2008 Sep 5. [Epub ahead of print]
PMID: 18776171 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
22: Kim D, et al. SIRT1 deacetylase protects against neurodegeneration in models for Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
EMBO J. 2007 Jul 11;26(13):3169-79. Epub 2007 Jun 21.
PMID: 17581637 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
23: Jin F, et al. Neuroprotective effect of resveratrol on 6-OHDA-induced Parkinson's disease in rats.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Oct 10. [Epub ahead of print]
PMID: 18940189 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
24: Sinha K, et al. Protective effect of resveratrol against oxidative stress in middle cerebral
artery occlusion model of stroke in rats.
Life Sci. 2002 Jun 28;71(6):655-65.
PMID: 12072154 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
25: Inoue H, et al. Brain protection by resveratrol and fenofibrate against stroke requires
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha in mice.
Neurosci Lett. 2003 Dec 11;352(3):203-6.
PMID: 14625020 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
26: Wang Q, et al. Resveratrol protects against global cerebral ischemic injury in gerbils.
Brain Res. 2002 Dec 27;958(2):439-47.
PMID: 12470882 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
27: Milne JC, et al. Small molecule activators of SIRT1 as therapeutics for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Nature. 2007 Nov 29;450(7170):712-6.
PMID: 18046409 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
28: http://www.sirtrispharma.com/pipeline-SRT501.html
29: Howitz KT, et al. Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan.
Nature. 2003 Sep 11;425(6954):191-6. Epub 2003 Aug 24.
PMID: 12939617 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
30: Wood JG, et al. Sirtuin activators mimic caloric restriction and delay ageing in metazoans.
Nature. 2004 Aug 5;430(7000):686-9.
PMID: 15254550 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
31: Valenzano DR, et al. Resveratrol prolongs lifespan and retards the onset of age-related markers in a short-lived vertebrate.
Curr Biol. 2006 Feb 7;16(3):296-300.
PMID: 16461283 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
32: Baur JA, et al. Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet. Nature. 2006 Nov 16;444(7117):337-42. Epub 2006 Nov 1.
PMID: 17086191 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
33: Resveratrol Improves Mitochondrial Function and Protects against Metabolic Disease by Activating SIRT1 and PGC-1α . Cell , Volume 127 , Issue 6 , Pages 1109 - 1122 M . Lagouge , C . Argmann , Z . Gerhart-Hines , H . Meziane , C . Lerin , F . Daussin , N . Messadeq , J . Milne , P . Lambert , P . Elliott
|  "
"





