Team:Rice University/CONSTRUCTS
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
StevensonT (Talk | contribs) (→Constructs) |
|||
| (14 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==='''Constructs'''=== | ==='''Constructs'''=== | ||
| - | <p>''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' is widely used for baking and brewing, a versatile eukaryotic model system, and | + | <p>''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' is widely used for baking and brewing, a versatile eukaryotic model system, and particularly useful for synthesizing metabolites under fermentation conditions. The microaerobic conditions of fermentation impede the oxidation of sensitive bioreactive compounds and are optimal for the ''de novo'' synthesis of resveratrol. To achieve our project goals and expand the yeast synthetic biology toolbox, we have constructed BioBricks encoding 3 yeast promoters, 3 yeast terminators, a 2-micron origin of replication, 2 selectable markers, 2 metabolic enzymes, and a yeast integration plasmid. We have also submitted two additional parts representing foundational tools, including a gene encoding an amber suppressed RFP biobrick for screening of SupF+ (Amber suppressor) genotype and an amber suppressor tRNA biobrick. <br /> |
</p> | </p> | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
<td width="120">[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122000 BBa_K122000]</td> | <td width="120">[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122000 BBa_K122000]</td> | ||
<td width="118">pPGK1</td> | <td width="118">pPGK1</td> | ||
| - | <td width="466"> | + | <td width="466">~1500 bp upstream of the PGK1 coding region. Strongly induced during fermentation. </td> |
| - | <td width="24"> | + | <td width="24">1497bp</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122002 BBa_K122002]</td> | <td>[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122002 BBa_K122002]</td> | ||
<td>pADH1</td> | <td>pADH1</td> | ||
| - | <td>700bp upstream of ADH1 promoter region | + | <td>700bp upstream of ADH1 promoter region. Constitutive promoter under aerobic and anaerobic conditions.</td> |
| - | <td> | + | <td>701bp</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122001 BBa_K122017]</td> | <td>[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122001 BBa_K122017]</td> | ||
<td>pGAL1 + tetO</td> | <td>pGAL1 + tetO</td> | ||
| - | <td> | + | <td>Glucose repressible / galactose inducible GAL1 promoter. An additional TetR operator site was included to allow repression by TetR.</td> |
| - | <td> | + | <td>484bp</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
<td width="74">tCYC1</td> | <td width="74">tCYC1</td> | ||
<td width="493">300bp downstream the CYC1 coding region in a standard yeast strain.</td> | <td width="493">300bp downstream the CYC1 coding region in a standard yeast strain.</td> | ||
| - | <td width="46"> | + | <td width="46">300bp</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
<td>tADH1</td> | <td>tADH1</td> | ||
<td>300bp downstream the ADH1 coding region in a standard yeast strain.</td> | <td>300bp downstream the ADH1 coding region in a standard yeast strain.</td> | ||
| - | <td> | + | <td>300bp</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
<td>tPGK1</td> | <td>tPGK1</td> | ||
<td>1000bp downstream the PGK1 coding region in an industrial yeast strain.</td> | <td>1000bp downstream the PGK1 coding region in an industrial yeast strain.</td> | ||
| - | <td> | + | <td>1000bp</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
<td width="115">[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122001 BBa_K122018]</td> | <td width="115">[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122001 BBa_K122018]</td> | ||
<td width="74">ZeoR</td> | <td width="74">ZeoR</td> | ||
| - | <td width="493">Zeocin Resistance Gene</td> | + | <td width="493">Zeocin/Bleocin Resistance Gene</td> |
| - | <td width="46"> | + | <td width="46">300bp</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
<td>BleoR</td> | <td>BleoR</td> | ||
<td>Bleocin Resistance Gene under pTet promoter</td> | <td>Bleocin Resistance Gene under pTet promoter</td> | ||
| - | <td> | + | <td>80bp-ish</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122014 BBa_K122014]</td> | <td>[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122014 BBa_K122014]</td> | ||
<td>ORI+HisTag</td> | <td>ORI+HisTag</td> | ||
| - | <td>2 Micron ORI and | + | <td>2 Micron ORI and auxotrophic histidine marker </td> |
| - | <td>< | + | <td><9000bp</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
<td width="451">[pGAL1][tetO][ZeoR]</td> | <td width="451">[pGAL1][tetO][ZeoR]</td> | ||
<td width="74">[[Image:C2.jpg|120px]]</td> | <td width="74">[[Image:C2.jpg|120px]]</td> | ||
| - | <td width="90"> | + | <td width="90">874bp</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
<td>Tyrosine Ammonia Lyase</td> | <td>Tyrosine Ammonia Lyase</td> | ||
<td>[[Image:TAL.jpg|50px]]</td> | <td>[[Image:TAL.jpg|50px]]</td> | ||
| - | <td> | + | <td>1933bp</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122010 BBa_K122010]</td> | <td>[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122010 BBa_K122010]</td> | ||
| - | <td> | + | <td>4-coumarate CoA ligase :: Stilbene Synthase Fusion Protein</td> |
<td>[[Image:4CL.jpg|50px]]</td> | <td>[[Image:4CL.jpg|50px]]</td> | ||
| - | <td> | + | <td>4000bp</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
<td>[pPGK1][4CL:STS][tCYC1]</td> | <td>[pPGK1][4CL:STS][tCYC1]</td> | ||
<td>[[Image:C1.jpg|150px]]</td> | <td>[[Image:C1.jpg|150px]]</td> | ||
| - | <td> | + | <td>5497bp</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 126: | Line 126: | ||
<td>[pGAL1][tetO][ZeoR][tADH1]</td> | <td>[pGAL1][tetO][ZeoR][tADH1]</td> | ||
<td>[[Image:C2full.jpg|150px]]</td> | <td>[[Image:C2full.jpg|150px]]</td> | ||
| - | <td> | + | <td>1175bp</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 132: | Line 132: | ||
<td>[pADH1][TAL][tPGK1]</td> | <td>[pADH1][TAL][tPGK1]</td> | ||
<td>[[Image:C3.jpg|150px]]</td> | <td>[[Image:C3.jpg|150px]]</td> | ||
| - | <td> | + | <td>2651bp</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| - | <td>[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part: | + | <td>[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122019 BBa_K122019]</td> |
<td>[pPGK1][4CL:STS][tCYC1][pGAL1][tetO][ZeoR][tADH1]</td> | <td>[pPGK1][4CL:STS][tCYC1][pGAL1][tetO][ZeoR][tADH1]</td> | ||
<td>[[Image:C1C2C3.jpg|350px]]</td> | <td>[[Image:C1C2C3.jpg|350px]]</td> | ||
| - | <td> | + | <td>1824bp</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 150: | Line 150: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td width="71">[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122007 K122007]</td> | <td width="71">[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122007 K122007]</td> | ||
| - | <td width="354">The supF construct, an amber suppressor tRNA, allows for read-through at native amber (TAG) stop codons.</td> | + | <td width="354">The supF construct, an amber suppressor tRNA, allows for read-through at native amber (TAG) stop codons. Charges with tyrosine.</td> |
| - | <td width="30"> | + | <td width="30">211bp</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td height="54">[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122006 K122006]</td> | <td height="54">[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122006 K122006]</td> | ||
| - | <td>Point Mutation of RFP(13521) with incorporation of an amber stop codon at the | + | <td>Point Mutation of RFP(13521) with incorporation of an amber stop codon at the native tyrosine required for fluorophore maturation.</td> |
| - | <td> | + | <td>923bp</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 162: | Line 162: | ||
<BR><BR> | <BR><BR> | ||
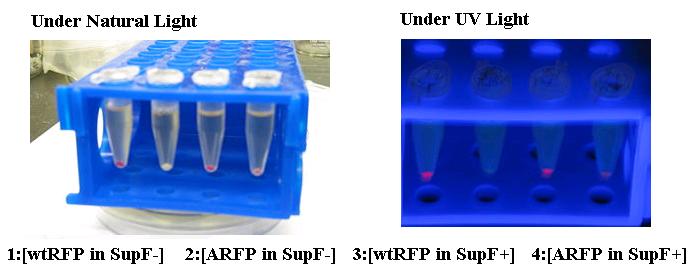
| - | Through incorporation of amber stop codons or point mutations of tyrosine codons (TAC) to TAG within the coding region, a genetic circuit can be used to add an additional level of regulation and determine whether a full protein or partial peptide with be synthesized. This design has | + | Through incorporation of amber stop codons or point mutations of tyrosine codons (TAC) to TAG within the coding region, a genetic circuit can be used to add an additional level of regulation and determine whether a full protein or partial peptide with be synthesized. This design has high signal-to-noise ratio, with virtually no leaky expression. |
<BR><BR><BR> | <BR><BR><BR> | ||
[[Image:arfp.jpg|center]] | [[Image:arfp.jpg|center]] | ||
| + | The Amber suppressed Red Florescent Protein (ARFP) has no virtually expression in SupF- (2) cells while visually apparent levels of red pigment is present in SupF+ cells (4). ARFP expression was compared against wtRFP expression in both cell types (1 and 3). | ||
Latest revision as of 19:41, 16 January 2009
|
|
 "
"