Team:Rice University/STRATEGY
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
DavidOuyang (Talk | contribs) (→Selection of Brewing Strain) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision not shown) | |||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
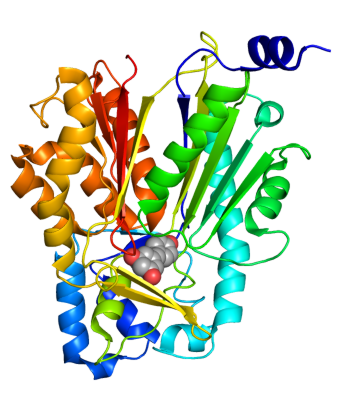
[[Image:STS.png|right|190px|thumb|[http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1Z1F Peanut STS] monomer bound to resveratrol.]] | [[Image:STS.png|right|190px|thumb|[http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1Z1F Peanut STS] monomer bound to resveratrol.]] | ||
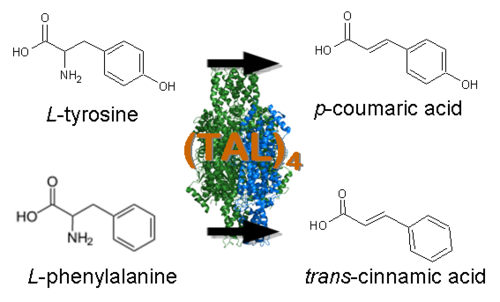
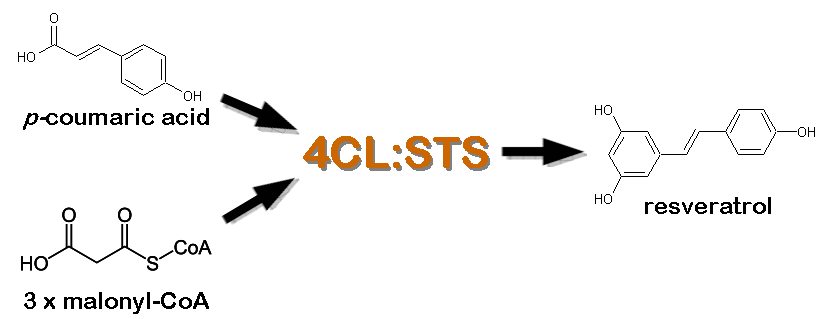
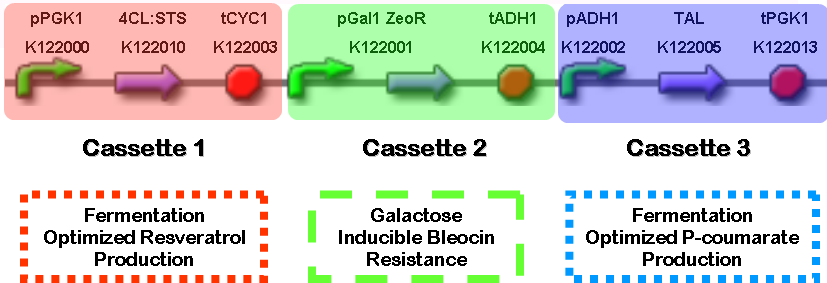
| - | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/viewer.fcgi?val=NM_001084228.1 4-coumarate CoA ligase] :: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/viewer.fcgi?tool=portal&db=nuccore&term=&query_key=18&dopt=gb&dispmax=20&page=1&qty=1&WebEnv=1BAyWdNufvUWxpNM-oKD-9JoRgEPTXzU_kF02A2hfcePWB3nxyPvHO3gqlDJksRdZq9GmTDHNDmKEFuabzP4VKB%40263F5D1B8F754EA0_0062SID&WebEnvRq=1 Stilbene Synthase] Fusion Protein (4CL:STS, [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122005 BBa_K122005]) - This enzyme fusion is comprised of ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL), which catalyzes the conversion of ''p''-coumaric acid to 4-coumaroyl-CoA, and ''Vitis vinifera'' Stilbene Synthase, which catalyzes the condensation of resveratrol from 4-coumaroyl-CoA and three malonyl-CoA molecules. This 4CL:STS fusion protein was selected for our project because it has been shown to more efficiently produce resveratrol than coexpression of the proteins separately (possibly due to substrate channeling). | + | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/viewer.fcgi?val=NM_001084228.1 4-coumarate CoA ligase] :: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/viewer.fcgi?tool=portal&db=nuccore&term=&query_key=18&dopt=gb&dispmax=20&page=1&qty=1&WebEnv=1BAyWdNufvUWxpNM-oKD-9JoRgEPTXzU_kF02A2hfcePWB3nxyPvHO3gqlDJksRdZq9GmTDHNDmKEFuabzP4VKB%40263F5D1B8F754EA0_0062SID&WebEnvRq=1 Stilbene Synthase] Fusion Protein (4CL:STS, [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122005 BBa_K122005]) - This enzyme fusion is comprised of ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL), which catalyzes the conversion of ''p''-coumaric acid to 4-coumaroyl-CoA, and ''Vitis vinifera'' Stilbene Synthase, which catalyzes the condensation of resveratrol from 4-coumaroyl-CoA and three malonyl-CoA molecules. This 4CL:STS fusion protein was selected for our project because it has been shown to more efficiently produce resveratrol than coexpression of the proteins separately (possibly due to substrate channeling), see Zhang Y, et al. (2006) Using unnatural protein fusions to engineer resveratrol biosynthesis in yeast and Mammalian cells. ''J Am Chem Soc.'' '''128'''(40):13030-1. |
| + | . | ||
[[Image:4CL_STS catalysis.png|left|550px]] | [[Image:4CL_STS catalysis.png|left|550px]] | ||
Latest revision as of 05:09, 30 October 2008
| OUR TEAM ::: SUMMARY ::: BACKGROUND ::: STRATEGY ::: CONSTRUCTS ::: RESULTS ::: ONGOING WORK
OUR TEAM ::: SUMMARY ::: INTRODUCTION ::: STRATEGY ::: RESULTS ::: ONGOING WORK |
 "
"