Team:BCCS-Bristol/Notebook-Progress
From 2008.igem.org
JGSchenkel (Talk | contribs) (→Chambers for bacteria-moving-bead assay) |
JGSchenkel (Talk | contribs) (→23rd July - 29th July) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
- different inoculation depths | - different inoculation depths | ||
| - | {| {{table}} | + | {|align="center" {{table}} |
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Media for swimming agar assay plates''' | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Media for swimming agar assay plates''' | ||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''0.3% 400ml''' | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''0.3% 400ml''' | ||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
in addition did a streak out for master colonies of MG1655 in LB from table below overnight at 37oC | in addition did a streak out for master colonies of MG1655 in LB from table below overnight at 37oC | ||
| - | {| {{table}} | + | {|align="center" {{table}} |
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''10ml LB''' | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''10ml LB''' | ||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''''' | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''''' | ||
| Line 99: | Line 99: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| - | {| {{table}} | + | {|align="center" {{table}} |
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''LB Broth 100ml''' | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''LB Broth 100ml''' | ||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''weight (g)''' | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''weight (g)''' | ||
| Line 115: | Line 115: | ||
SOC medium in preparation for Biobrick transformation this consisted of | SOC medium in preparation for Biobrick transformation this consisted of | ||
| - | {| {{table}} | + | {|align="center" {{table}} |
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Trypton''' | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Trypton''' | ||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''2g''' | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''2g''' | ||
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
in 95ml of water, then autoclaved. after this add this: | in 95ml of water, then autoclaved. after this add this: | ||
| - | {| {{table}} | + | {|align="center" {{table}} |
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''MgCl2''' | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''MgCl2''' | ||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''0.5ml 2M solution''' | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''0.5ml 2M solution''' | ||
| Line 141: | Line 141: | ||
'''Swimming Medium''' | '''Swimming Medium''' | ||
| - | {| {{table}} | + | {|align="center" {{table}} |
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''In 100ml of water''' | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''In 100ml of water''' | ||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''weight (g)''' | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''weight (g)''' | ||
| Line 161: | Line 161: | ||
After an incubation overnight, we measured the diameter of the ''E. coli'' MG1655 swarms. Surprisingly, we observed two swarm layers: The lower one has a bigger diameter than the upper. | After an incubation overnight, we measured the diameter of the ''E. coli'' MG1655 swarms. Surprisingly, we observed two swarm layers: The lower one has a bigger diameter than the upper. | ||
| - | {| {{table}} | + | {|align="center" {{table}} |
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Agar (%)''' | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Agar (%)''' | ||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Temperature (<sup> o </sup> C)''' | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Temperature (<sup> o </sup> C)''' | ||
| Line 214: | Line 214: | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
===9th July - 15th July=== | ===9th July - 15th July=== | ||
| Line 318: | Line 316: | ||
===23rd July - 29th July=== | ===23rd July - 29th July=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====BioBrick Transformation==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The cells transformed with BioBrick were grown on ampicillin plates as if transformed are able to do so, however there was no growth of bacteria except when pUC19 was used. This highlights some problems with the DNA and not the actual transformation. The experiment was repeated with larger amounts of TE buffer around spot and with a different BioBrick. Results see weekly summary. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Bead experiment 1==== | ||
| + | The bead we had focused on overnight (see [[Team:BCCS-Bristol/Calendar-Notebook/22 July 2008 | 22 July 2008]]) had gone!! There were observed lots of beads clumping together, areas of dead/non-motile bacteria and also filamentous bacteria (possible conaminant). There were also areas of still motile bacteria. | ||
| + | The bacteria had travelled 40 % of way across bridge, thus a smaller bridge was suggested. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Swimming agar assay==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The experiment from [[Team:BCCS-Bristol/Calendar-Notebook/21 July 2008 | 21 July 2008]] was repeated. The aspartate solution was added eigth hours before the inoculation. The Results for showed that both strains were actually repelled by aspartate, possibly because the concentration was too high. Aspartate is the well on the right, and the control (water) is on the left. | ||
| + | {| align="center" | ||
| + | !align="center"|[[Image:BCCS-WetLabMC1000_25C_1.JPG | 200px]] | ||
| + | !align="center"|[[Image:BCCS-WetLabMC1000_30C_3.JPG | 200px]] | ||
| + | !align="center"|[[Image:BCCS-WetLabMG1655_25C_3.JPG | 200px]] | ||
| + | !align="center"|[[Image:BCCS-WetLabMG1655_30C_5.JPG | 200px]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | {| align="center" | ||
| + | !align="center" width="10%"|MC1000 25<sup>o</sup>C | ||
| + | !align="center" width="10%"|MC1000 30<sup>o</sup>C | ||
| + | !align="center" width="10%"|MG1655 25<sup>o</sup>C | ||
| + | !align="center" width="10%"|MG1655 30<sup>o</sup>C | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ====Results from different aspartate concentrations==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:BCCS-WETLAB-MG1655_ASP.JPG | 500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:BCCS-WETLAB-MC1000_ASP.JPG | 500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | As you can see there wasn't much difference between control and aspartate, possibly due to the chemtactic gradient not being set up. motility comparison gave much better results | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:BCCS-WETLAB-MOTILITY_COMPARISON.JPG | 500px]] | ||
===30th July - 6th August=== | ===30th July - 6th August=== | ||
Latest revision as of 14:36, 23 September 2008
Progress Reports
- 1st July - 8th July
- Swimming agar assay
- 31st July - 6th August
- BioBrick Transformation
- Heat shock transformations with BioBrick DNA resulted in zero, one or two colonies per attempt
- All colonies have been verified to possess the plasmids
- Electroporation is much more successful
- Agar plug assay
- E. coli MG1655 moved apparently some beads!!!
- but unfortunenately, no chemotaxis was observed
- BioBrick Transformation
- 7th August - 13th August
- BioBrick Transformation
- The self-made electro competent E. coli DH5α cells are working
- A longer incubation time of the punched paper disc in water seems to resolve more BioBrick DNA
- BioBrick Transformation
- 14th August - 20th August
- Agar plug assay
- Repulsion achieved to some degree in the agar-plug assay.
- BioBrick transformation
- DH5α transformed with pRZ1(pRS415 containing cpxR responsive promotor - sent to us by T.Silhavy, Princeton)
- Agar plug assay
- 2nd September - 9th September
- BioBrick transformation
Progress Report Details
1st July - 8th July
Swimming agar assay
We wanted to test different conditions for the swimming agar assay:
- different agar concentrations
- different incubation temperatures
- different inoculation depths
| Media for swimming agar assay plates | 0.3% 400ml | 0.15% 150ml | 0.5% 150ml |
| Bactotryptone | 4g | 1.5g | 1.5g |
| NaCl | 2g | 0.75g | 0.75g |
| BactoAgar | 1.2g | 0.225g | 0.75g |
in addition did a streak out for master colonies of MG1655 in LB from table below overnight at 37oC
| 10ml LB | ' |
| Yeast Extract | 0.05 |
| Tryptone | 0.1 |
| Nacl | 0.1 |
| LB Broth 100ml | weight (g) |
| Yeast Extract | 0.5 |
| Tryptone | 1 |
| NaCl | 1 |
SOC medium in preparation for Biobrick transformation this consisted of
| Trypton | 2g |
| Yeast Extract | 0.5g |
| NaCl | 0.05g |
in 95ml of water, then autoclaved. after this add this:
| MgCl2 | 0.5ml 2M solution |
| Glucose | 2ml 1M |
then freeze at -20oC. this solution is from Molecular Cloning 3 A.2 SOB/SOC Medium.
Swimming Medium
| In 100ml of water | weight (g) |
| Potassium Phosphate | 0.1742 |
| NaCl | 0.392 |
| Glucose | 0.18016 |
| EDTA | 0.003722 |
| Tween -20 aka polysorbate 20 | 0.2 µl |
After an incubation overnight, we measured the diameter of the E. coli MG1655 swarms. Surprisingly, we observed two swarm layers: The lower one has a bigger diameter than the upper.
| Agar (%) | Temperature ( o C) | Inoculation Depth | Number | JPG File | Inner Ring (cm) | Outer Ring (cm) |
| 0.3 | 30 | Deep | 1 | 4828 | 4.6 | 5.3 |
| 0.3 | 30 | Deep | 2 | 4827 | 4.6 | 5.3 |
| 0.3 | 30 | Deep | 3 | 4829 | 4.7 | 5.2 |
| 0.3 | 30 | Under Surface | 1 | 4830 | 4.6 | 5.2 |
| 0.3 | 30 | Under Surface | 2 | 4831 | 4.6 | 5.2 |
| 0.3 | 30 | Under Surface | 3 | 4832 | 4.6 | 5.1 |
| 0.3 | 30 | On Surface | 1 | 4833 | 2.9 | 3 |
| 0.3 | 30 | On Surface | 2 | 4834 | 3.8 | 4.4 |
| 0.3 | 30 | On Surface | 3 | 4835 | 4.4 | 4.9 |
| 0.3 | 37.5 | Under Surface | 1 | 4836 | 7.2 | 7.6 |
| 0.3 | 37.5 | Under Surface | 2 | 4837 | 7.4 | 7.7 |
| 0.3 | 37.5 | Under Surface | 3 | 4838 | 7.1 | 7.4 |
| 0.3 | 25 | Under Surface | 1 | 4840 | 2.8 | 3.5 |
| 0.3 | 25 | Under Surface | 2 | 4839 | 3 | 3.6 |
| 0.3 | 25 | Under Surface | 3 | 4841 | 3.1 | 3.7 |
| 0.2 | 30 | Under Surface | 1 | 4842 | 8.6 | 8.6 |
| 0.2 | 30 | Under Surface | 2 | 4843 | 8.6 | 8.6 |
| 0.2 | 30 | Under Surface | 3 | 4844 | 8.6 | 8.6 |
| 0.5 | 30 | Under Surface | 1 | 4847 | 2.3 | 2.3 |
| 0.5 | 30 | Under Surface | 2 | 4845 | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| 0.5 | 30 | Under Surface | 3 | 4846 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
9th July - 15th July
Swimming agar assay with L-aspartic acid
We conducted a second swimming agar assay with E. coli MG1655. This time, we added paper discs that were soaked with a L-aspartic acid solution. We wanted to observe whether the bacteria are attracted by the amino acid. We tested again different parameters:
- agar concentrations of 0.15 %, 0.3 % and 0.5 %
- incubation temperatures of 25 oC, 30 oC and 37 oC
- inoculations depths of "on the surface", "under the surface" and "deep in the medium"
- aspartic acid concentrations of 0.2 %, 0.1 % and 0.01 %
Photos of swiming agar were taken and travelled distances measured. 0.3% agar was found to be the best for an overnight culture and a temperature of 37oC was too high, since the swarms spread over the whole plate. All plates showed swarm spread at different levels giving inner and outer rings. Unfortunately, we observed no different movement/growth towards the L-aspartic acid compared with the control (water). It was assumed that this is due to the low concentration, but it wasn't possible to made a 0.4 % solution.
The swimming agar experiment was repeated. Since the OD600 of the bacteria culture for the inoculation was too low, the plates were inoculated the next day. More concentrated aspartic acid solution was made by reacting with NaOH to make aspartic acid salt. A concentration up to 7 % was reached. Also some salt was ordered to save doing this in future.
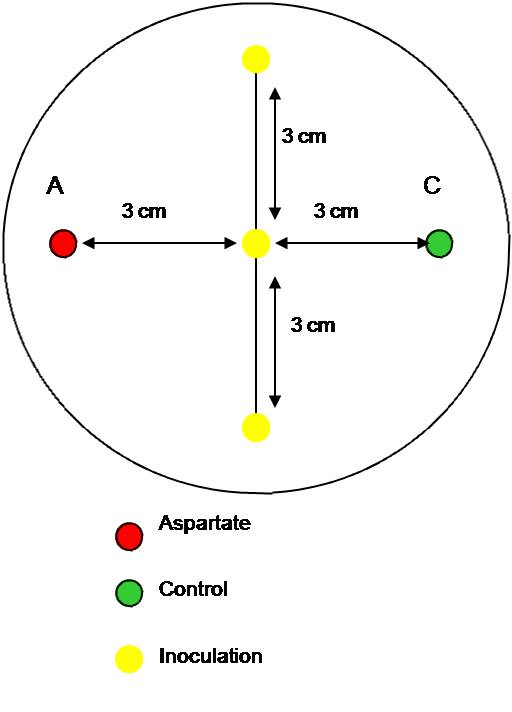
This time, only 0.3 % agar plates were used. Two wells were made using the thick end of a 1000 µl pipette tip. In the left hole some aspartate solution was put and on the right some water (control). To half of the plates the solutions were added in the morning to allow chemotactic gradient to set up, to the second half the solutions were added immediately before the inoculation in the afternoon (arond 5 hours later). The E. coli MG1655 strain was inoculated three times on a line in the centre between the two holes and incubated overnight at the different temperatures: 25oC, 30oC and 37oC.
Today, the plates were photographed and measured. There was some significant movement more towards the aspartate (chemoattractant), but the difference should be more visible. Thus, various conditions should be tested during the next experiments.
16th July - 22nd July
BioBrick Transformation
SOC medium was made in preparation for Biobrick transformation. This consisted of
| Component | Amount |
| Trypton | 2g |
| Yeast Extract | 0.5g |
| NaCl | 0.05g |
in 95ml of water, then autoclaved. After this the following was added:
| Component | Amount |
| MgCl2 (2 M) | 0.5ml |
| Glucose (1 M) | 2ml |
The medium is stored at -20oC. This solution is from Molecular Cloning 3 A.2 SOB/SOC Medium.
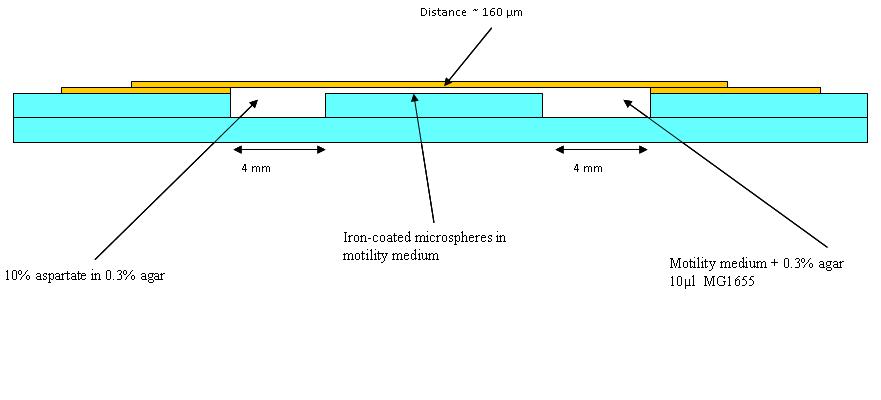
Chambers for bacteria-moving-bead assay
The first trial in making wells as in the diagram (See below) was made, but it was found that a different glue is needed. Nevertheless, in the first chambers a blue dye in 0.3% agar (to represent aspartate) and an orange dye in 0.1% agar to represent the bacteria was put (beads were added in later experiments). Pictures were taken at 30 minutes intervals. This was to see how long a chemotatic gradient would take to set up. However, after three hours no gradient was obvious, so the chambers were left overnight.
The dye plates were observed: They had dried out somewhat overnight, however the dyes had mixed well. The experiment was carried out again with whatman paper soaked in water in 15 cm petri dishes to make a humid environment. This time swimming medium (see table below) was also used instead of the 0.1% agar used before as this may be more like what we use in the final experiment.
Swimming Medium
| In 100ml of water | weight (g) |
| Potassium Phosphate | 0.1742 |
| NaCl | 0.392 |
| Glucose | 0.18016 |
| EDTA | 0.003722 |
| Tween -20 aka polysorbate 20 | 0.2 µl |
Comparision of motility between E. coli MG1655 and MC1000
The motility of both strains was tested under different conditions:
- agar concentration: 0.3 % and 0.5 %
- incubation temperatures: 25oC and 30oC
The OD600 was adjusted to 1.25 and the bacteria were inoculated in the middle of an LB-plate without yeast extract, but with streptomycin. After an incubation overnight there was no growth of MG1655 visible, because only MC1000 is resistant. Therefore, the experiment should be repeated.
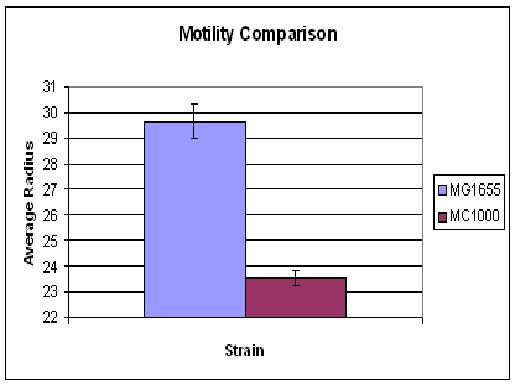
The motility comparison experiment was repeated, but this time only the plates for MC1000 contained streptomycin. None of the 0.5% agar showed growth. Overall MG1655 swarms were possibly slightly larger than MC1000 (in Cambridge 06' MC1000 had much greater motility than MG1655). The growth/motility of MC1000 might be disturbed because, in contrast to MG1655, the bacteria had to deal with an antibiotic. Thus, the experiment will be repeated without any antibiotics in the agar.
23rd July - 29th July
BioBrick Transformation
The cells transformed with BioBrick were grown on ampicillin plates as if transformed are able to do so, however there was no growth of bacteria except when pUC19 was used. This highlights some problems with the DNA and not the actual transformation. The experiment was repeated with larger amounts of TE buffer around spot and with a different BioBrick. Results see weekly summary.
Bead experiment 1
The bead we had focused on overnight (see 22 July 2008) had gone!! There were observed lots of beads clumping together, areas of dead/non-motile bacteria and also filamentous bacteria (possible conaminant). There were also areas of still motile bacteria. The bacteria had travelled 40 % of way across bridge, thus a smaller bridge was suggested.
Swimming agar assay
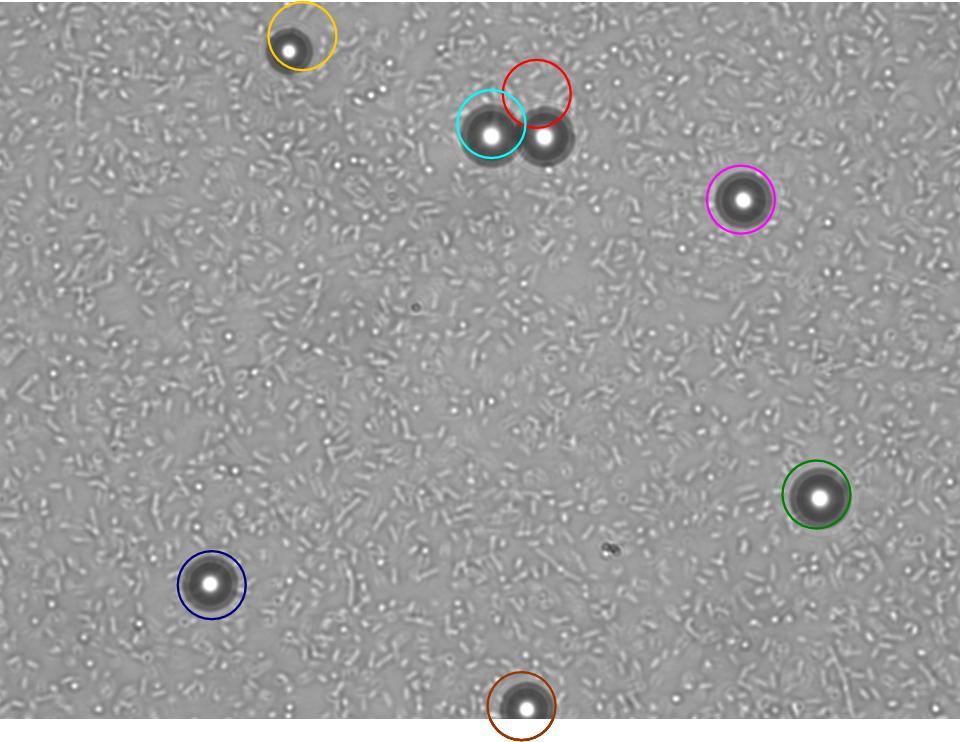
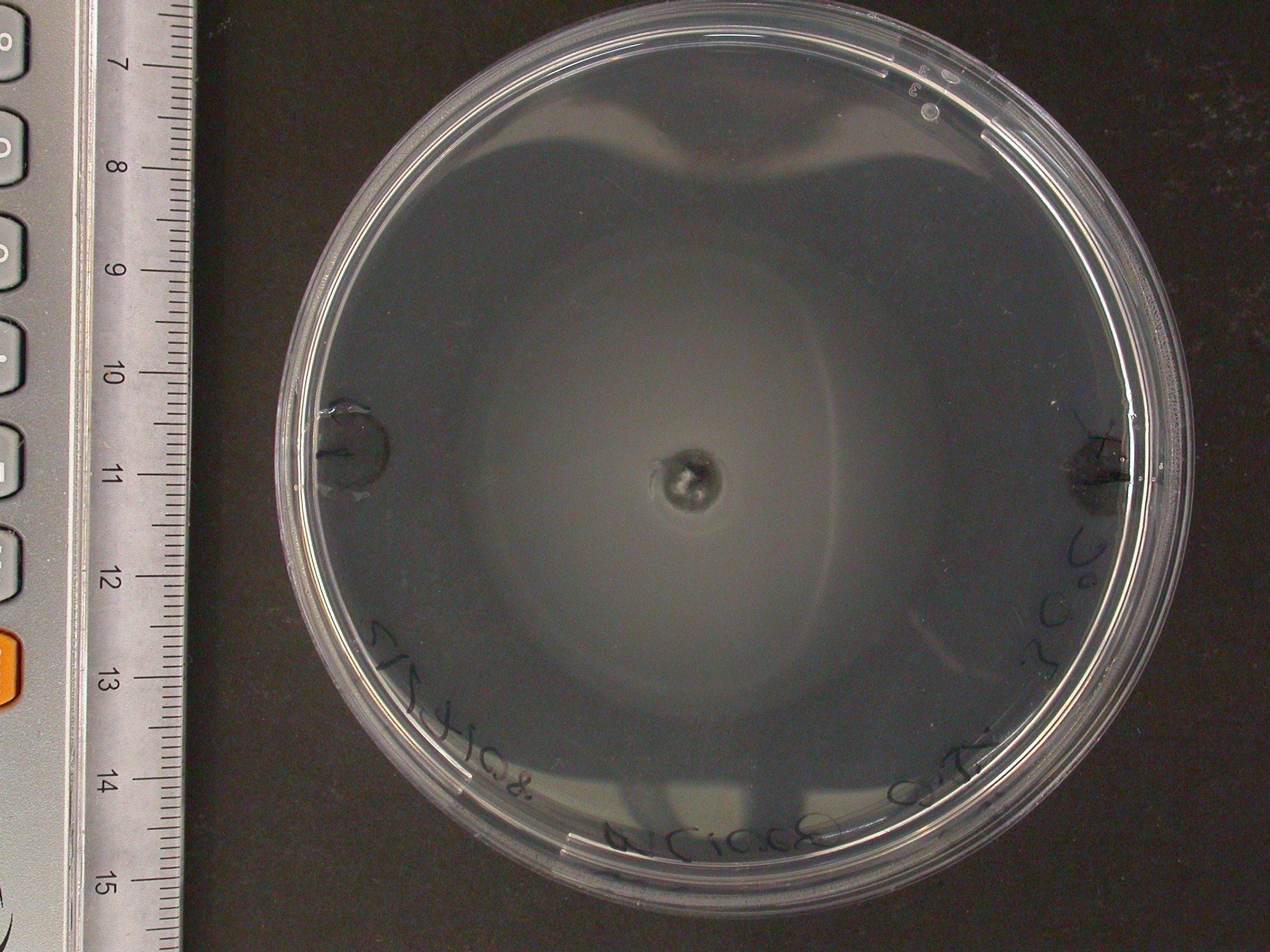
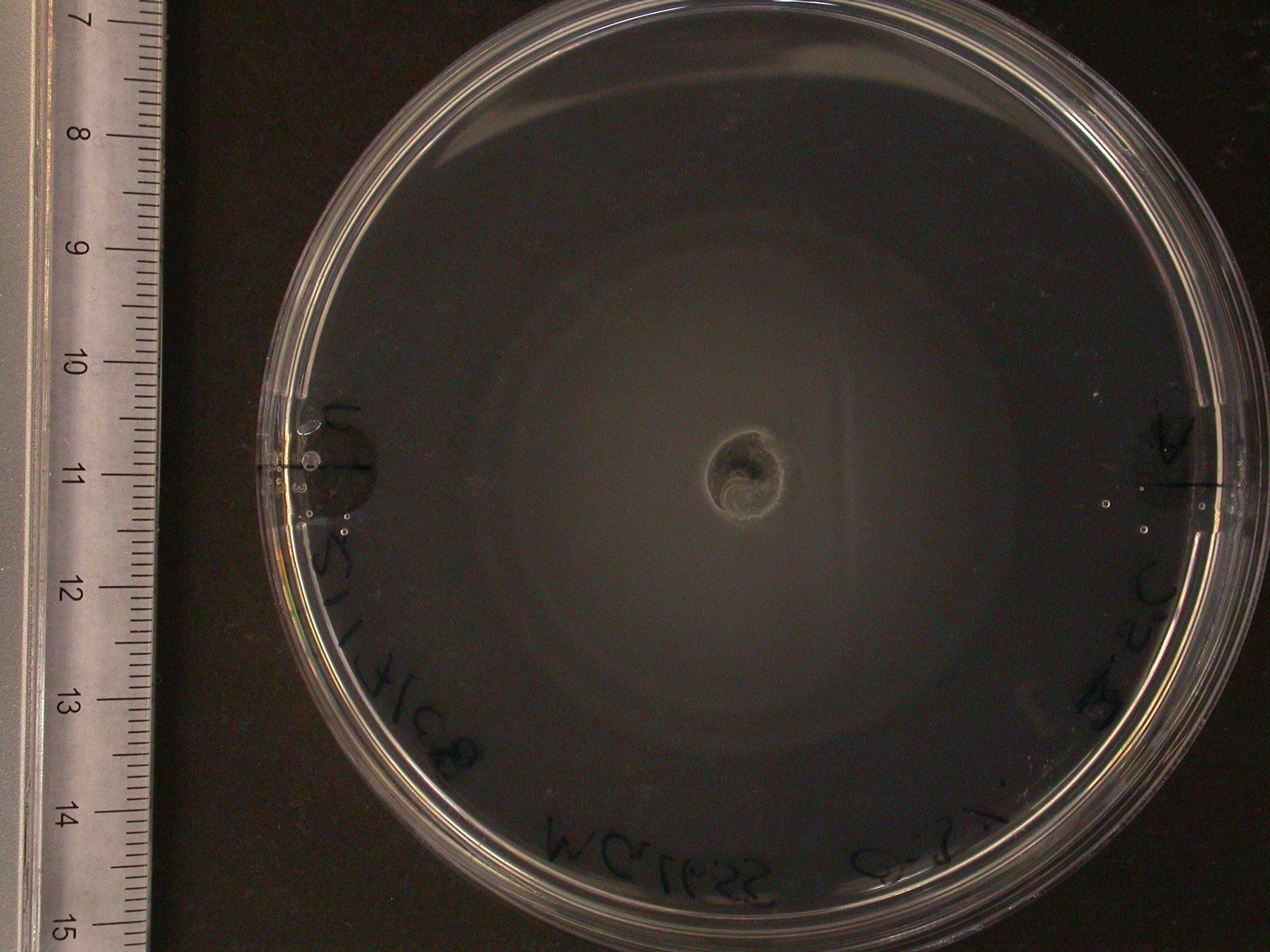
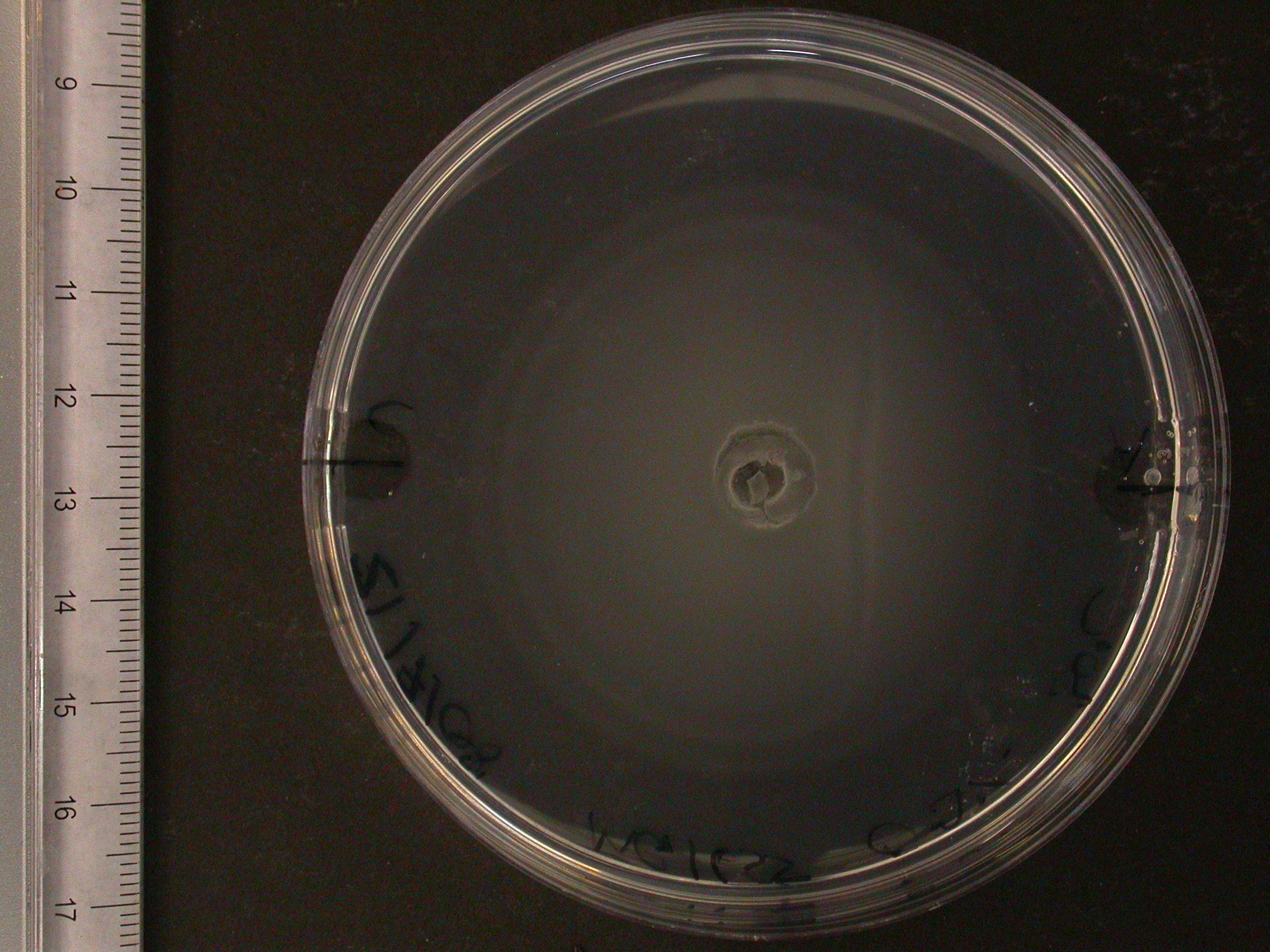
The experiment from 21 July 2008 was repeated. The aspartate solution was added eigth hours before the inoculation. The Results for showed that both strains were actually repelled by aspartate, possibly because the concentration was too high. Aspartate is the well on the right, and the control (water) is on the left.
| 
| 
| 
|
|---|
| MC1000 25oC | MC1000 30oC | MG1655 25oC | MG1655 30oC |
|---|
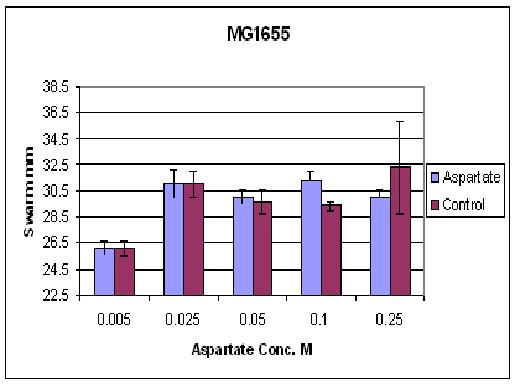
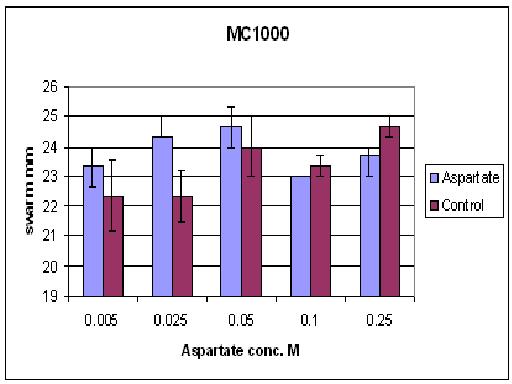
Results from different aspartate concentrations
As you can see there wasn't much difference between control and aspartate, possibly due to the chemtactic gradient not being set up. motility comparison gave much better results
30th July - 6th August
BioBrick Transformation
Last Thursday, the primers [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php/Part:BBa_G00100 VF2] and [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_G00101 VR] arrived. These primers allow a confirmation of a succesful transformation of most BioBrick parts by means of PCR. The resulting fragment length depends on the specific BioBrick DNA.
Using VF2 and VR, a colony PCR are was conducted with all colonies that were obtained with chemical competent cells so far. Two colonies with the [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J63005 yeast ADH1 promoter] (No. 1 and 2, see left photo) and three colonies with a [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_E0240 GFP generator] (No. 3-5, see left photo) were identified as positive. Thus, all colonies are positive, but the transformation efficiency is too low, since the result was only one or zero colonies per transformation attempt.
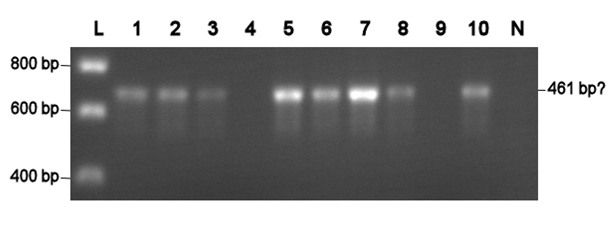
Electroporation should give higher efficiencies. An attempt with a new BioBrick ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J63002 ADH1 terminator]) resulted in 69 colonies! Ten of them were analysed using PCR. The resulting fragment should have a length of 461 bp, but from the eigth positive colonies fragments between 650-750 bp were obtained (see right photo). This is probably due to a mutation which might result in a different binding location for one of the primers. Another explanation might be that the denoted length is wrong. Since this BioBrick is not important for our project, it will be disregarded.
|
L= HyperLadder I (BIOLINE) N= Negative control Numbers= See text |
The transformation efficiency of the electroportation was significant higher than of the chemical competent cells. Therefore, an own stock of electric competent cells was made.
Agar plug assay
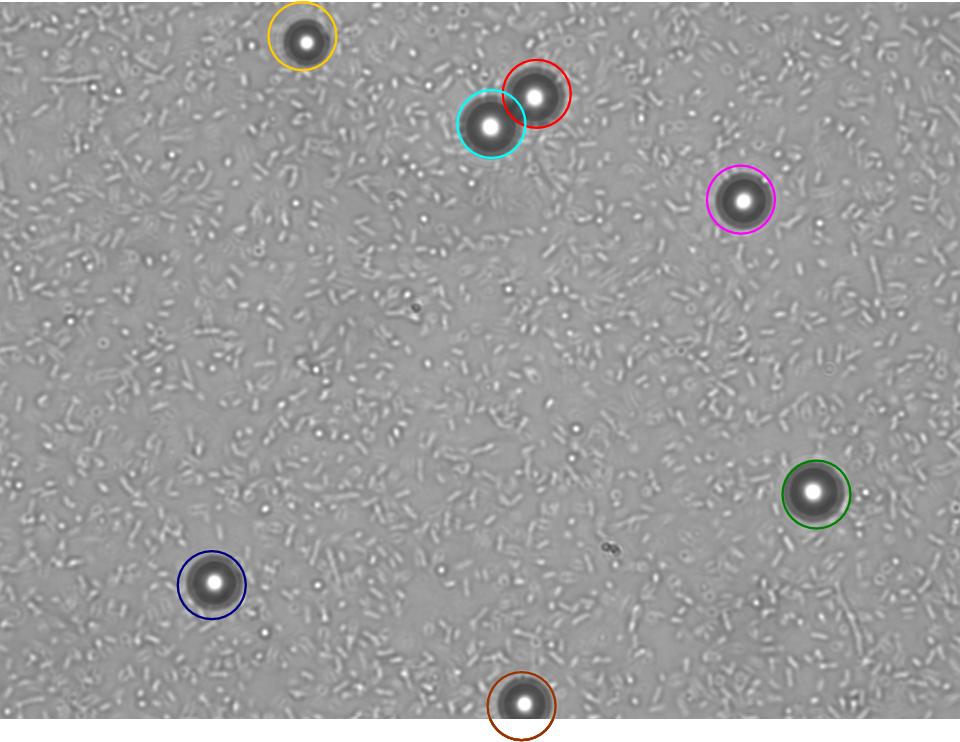
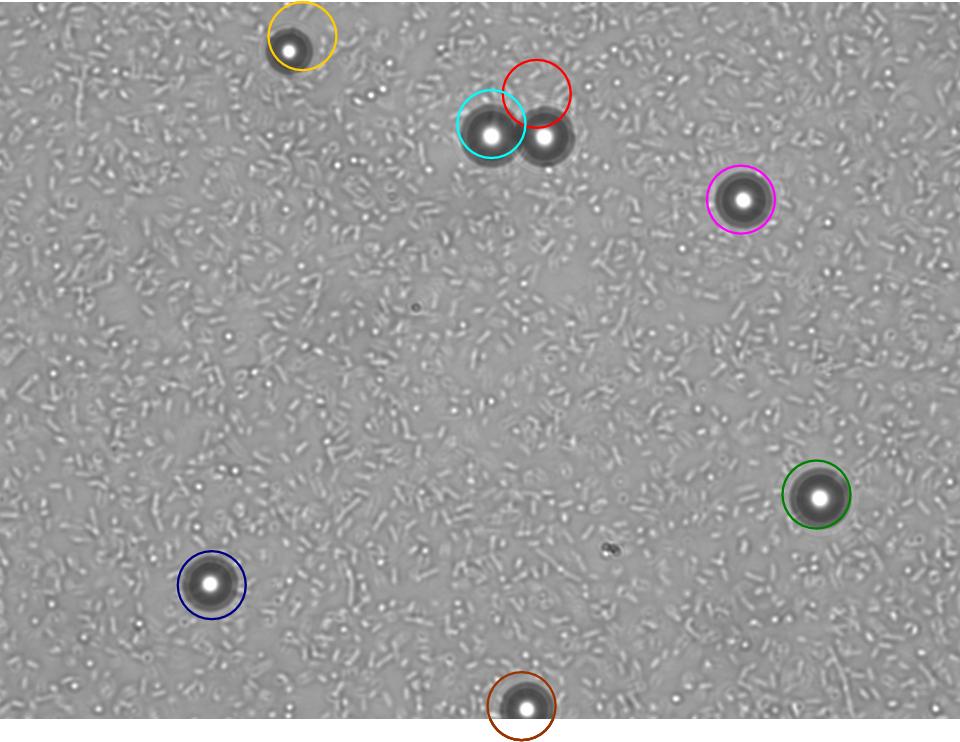
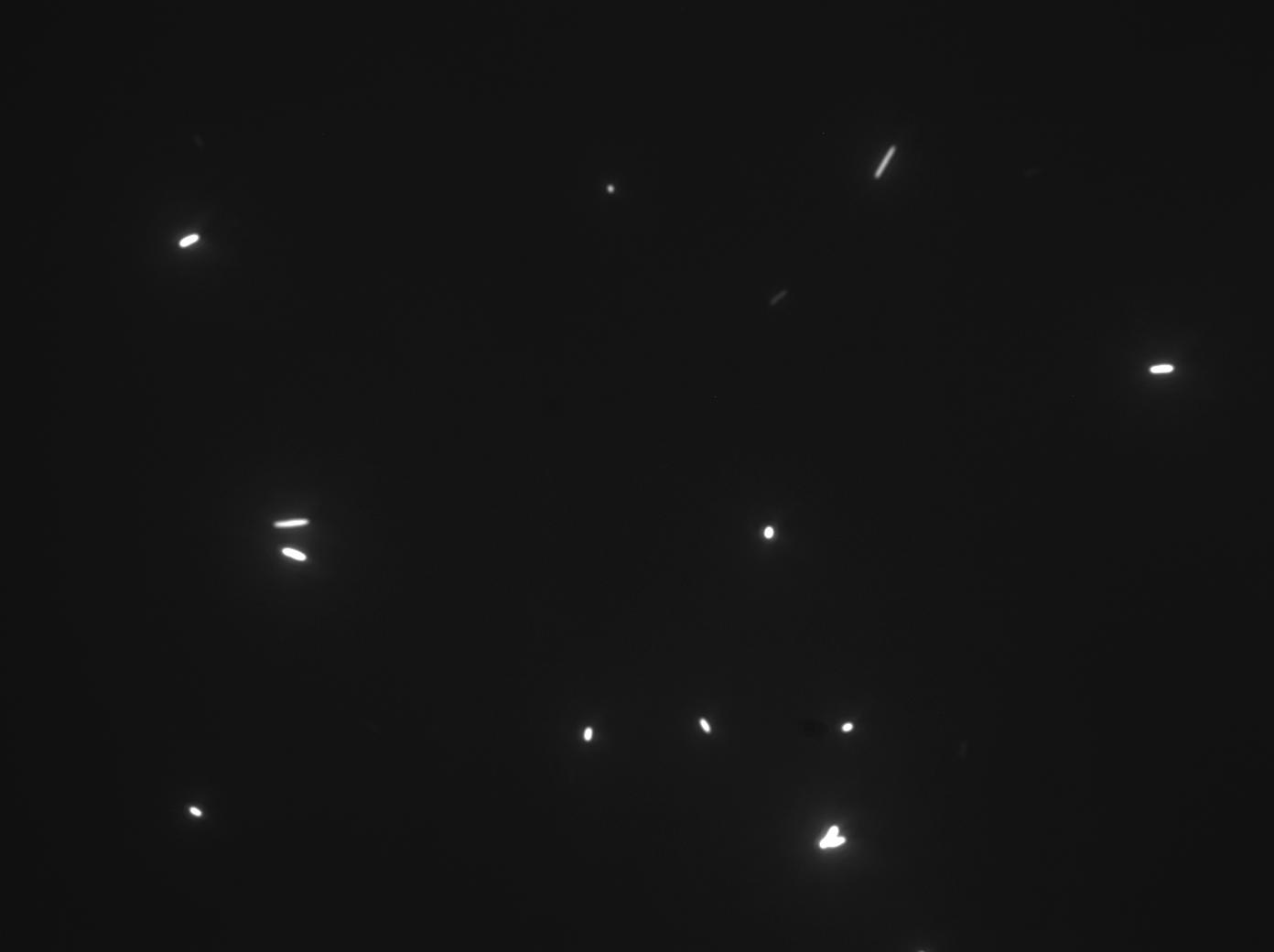
TR235 (E. coli with construct to detect adhesion to hydrophobic surfaces) arrived from Princeton (Thomas J. Silhavy). Cells are viable, growth curve done. 11µm PS beads shown to be moved by bacteria (MG1655); we observed ‘jiggling’ of beads when bacteria present (not seen in no-bacteria control). Also, we observed significant movement in different directions (distances of approx 1x to 5x length of the beads by eye) of beads that were close together, suggesting that movement was not due to currents in the medium. We saw no distance covered in almost all the control beads, a few moved small distances, so some currents are present. Bacteria and beads were left together for ~30mins to allow time for adhesion. No movement has yet been seen when the bacteria and beads are not left to adhere. We will look again at this, as we may have not previously looked closely enough (photographing over a time course of a few minutes).
| 0 mins | 1 min | 2 mins |
|---|
| Circles represent position at 0 mins, one colour for each bead. For example, the bead that starts in red circle moves down and right, while that in the yellow circle moves left. |
|---|
Chemotaxis assay (Yu, H.S. et al. (1997) FEMS Microbiology Letters, 156, 265-269.) has not worked so far. Currents can be seen flowing from the aspartate plug, pushing bacteria away. The focus of this week will be on getting this fixed, with a view to combining chemotaxis and the ability to move beads, allowing us to move beads in a particular direction.
The GRN for switching on the chemotactic response by binding to a bead, and signaling to nearby bacteria that a particle is in the vicinity, is almost finalised.
7th August - 13th August
BioBrick Transformation
The self-made electro competent E. coli DH5α cells were tested twice. The transformation efficiency with pUC19 was 4.45 x 108 cfu/µg and 5.67 x 108 cfu/µg. The first attempt with BioBrick DNA failed, but this might be due to a too low cell amount compared to all the other decanted tubes. In the following transformations, the incubation of the punched paper disc with the DNA was varied in time (3 h and 5.5 h). It seems that a longer incubation increases the transformation efficiency. This has to be confirmed, since the transformations were conducted by different persons. Thereby, next to the [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J63005 yeast ADH1 promoter] another BioBrick ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J63001 enhanced version of EYFP, yeast-optimized YFP]) was tested because the VF2-VR value of [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J63005 yeast ADH1 promoter] we got didn't coincide with the value given on the iGEM page.
Agar Plug Assay
Evaporation and currents that were occurring in previous attempts at the agarose-in-plug assay were eliminated by ensuring water potentials of plug and chemotaxis buffer were as similar as possible. Both the beads and the bacteria were found to sink to the bottom of the chamber shortly after inoculation. This makes the model much simpler, as everything can be modelled in 2D. We showed that beads need to be left in bacteria for around 30mins in order for significant bead movement to occur. We currently have not determined if this is because the bacteria form a layer under the beads which stops them sticking to the slide, or if adherence itself is needed for bead movement. We determined the diffusion speed of bromophenol blue dye (which is three times larger than aspartate), and concluded that by 30mins aspartate would have diffused throughout the slide.
14th August - 20th August
Agar Plug Assay
We repeated the chemotaxis assays and found that the bacterial density surrounding the plug varied and therefore we obtained more valid results by using lower magnification and scanning around the whole plug (as opposed to focussing on one area for the whole time course). This gave a much better overview of changes in bacterial density.
We tried testing bacterial chemotaxis to 1% serine and 1% aspartate in the plug. Bacterial density around the plug was monitored for 1hr. Bacteria appeared to be repelled by both the serine (see below)and aspartate at this concentration compared with the control where no chemoattractant was present in the plug. Research group page (Professor Jong Yoon, Micro/nanofluidic Bio MEMS group) indicates that serine becomes chemorepellent 1M concentration (the same may be true of aspartate).

| 
|
|---|
| Control | 1%Serine in plug |
|---|
We have been attempting a 'dead bacteria' control, but have been unable to successfully kill our bacteria without using a method that physically alters them. We have tried sodium azide (bacteriostatic)- but resuspension allows them to recover. Kanamycin and chloramphenicol were also used, but only for a few hours. We might try leaving a culture overnightin these two antibiotics - this should be sufficient to kill them!
BioBrick Transformation
The transformation efficiency should be increased. It was assumed that the quality of the BioBrick DNA is the most important factor to improve. Thus, two punched paper discs of the same BioBrick were incubated overnight at two different temperatures: 37oC and room temperature. The room temparature DNA resulted in 63 colonies (compared to 14 colonies with the 37oC-DNA), but it was not comparable since the 63 colonies were a result from a double electro shock. This may enhance the transformation efficiency. Thus, further tests should be conducted considering different incubation times and temperatures of the paper disc in water and as well single and double electroporation.
Electro competent cell of E. coli MG1655 were made and tested with pUC19. This resulted in zero colonies and may due to the high OD600 of the cells when they were prepared. New cells should be made.
DH5α cells were transformed with pRZ1 (pRS415 containing cpxR responsive promotor). The efficiency was very high and 15 colonies were isolated.
21st August - 1st September
Change to a proof-of-concept
Unfortunately it was discovered that the Cpx response (activated by adhesion to hydrophobic surfaces) actually downregulates, via CpxR, chemotaxis through a number of genes. This means that our initial plan of using the Cpx system to detect adhesion to the beads will not work in its current form as the bacteria adhered to the bead will stop chemotaxing. Indeed, bacteria that adhere to the bead because of short or long-range co-ordination will also stop chemotaxing soon after they reach and adhere to the bead. There would be two ways around this problem: either we stop CpxR switching off chemotaxis by knocking-out the two binding regions that allow CpxR to downregulate the two operons downregulating the chemotactic genes, or we place these genes (eight of them) under the control of an activating CpxR region. In the time remaining, neither of these are achievable. Furthermore, it is likely that there are additional unknown genes required for chemotaxis, that are also downreguated by CpxR upon adhesion, therefore there is a good chance that neither strategy would work initially. As our experimental work has not yet confirmed whether bacteria adhered to beads, and able to chemotax, can actually direct bead movement towards a goal chemoattractant, at the least we would require the modelling work to suggest that this was indeed possible before any effort was made to maintain chemotaxis upon adhesion by either of the above strategies.
In light of this, the focus of the lab work will move towards producing proof-of-concept BioBricks that will allow us to demonstrate the communication of an adhesion event from an adhered to an unadhered bacteria. This can be achieved making extensive use of the available BioBricks. Specifically, sender cells (cells that have adhered to beads and are trying to communicate with unadhered cells), will contain the LuxI-GFP portion of BBa_J37015, fused downstream of a CpxR responsive promoter (modified from current version fused to LacZ provided courtesy of T.Silhavy, Princeton). Upon adhesion to beads, LuxI will produce AHL, which will diffuse into the medium, while GFP will give confirmation that the transcript is working. For receiver cells we will test both BBa_T9002 and BBa_I731014, which produce GFP and mCherry respectively upon activation by AHL. We will also BioBrick the CpxR responsive promoter itself, and aim to fuse BBa_E0840 (GFP) to the CxpR responsive promoter, creating a nice visual assay for adhesion (the CpxR-LuxI-GFP BioBrick will also do this, but producing AHL in addition may not be ideal for certain future applications). Therefore in total we aim to produce 3 BioBricks in total.
2nd September - 9th September
Biobrick transformations
A series of biobrick transformations (J37015, T9002, E0840 and I731014) were performed using electro-competent DH5α cells. After several attempts, only J37015 and T9002 appeared to work, but after carrying out colony PCR on the transformed bacteria we found that the J37015 part doesn’t appear to be in its plasmid (pSB1A3). The T9002 transformation, however, was successful, and this was verified by plasmid mini-prep and subsequent test digestion. Its activity as a luxR GFP receiver construct was also confirmed, by testing the fluorescence of the transformed bacteria when incubated with two different concentrations of AHL. (No GFP was produced in the control, un-transformed, bacteria). Since we have tried several times, unsuccessfully, to transform the other biobricks, strains already transformed with these biobricks were requested from iGEM HQ.
| 
|
|---|
| DH5α T9002, 10E-6M AHL, Bright Field | DH5α T9002, 10E-6M AHL, GFP |
|---|
10th September - 16th September
We received strains from iGEM HQ transformed with the following biobricks: J37015, pSB1A3, I731014, T9002, E0840.
The AHL test used to verify the activity of our T9002-transformed DH5α cells was repeated (see protocols page) to test the I731014 and T9002 strains provided by iGEM. We used pSB1A3-transformed strains as our control. Both test strains displayed fluorescence at both 10-6M and 10-8M AHL, whilst no fluorescence was detected in the negative control. The proportion of total I731014-transformed bacteria that actually fluoresced was quite low however. (T9002 fluorescence, in contrast, was near to 100% of total bacteria in the sample that was viewed).
Plasmid mini-preps and restriction digests were performed to test the identity of the plasmids. Single and double digests were carried out for each biobrick. The results for T9002 and E0840 were as expected and corresponded to the part sequence data. Both the single and double digests for J37015, however, produced only one band – all running just above the 2000bp marker. SpeI was used in both the single and double digest and according to the sequence data cuts once in the plasmid containing the J37015 part (pSB1A2). HindIII was the second restriction enzyme used in the double digests and should cut once in the J37015 part. We concluded from this information that the J37015 part is not in the plasmid – and the resulting single band corresponds to the linearised pSB1A2 plasmid! The digests for pSB1A3 and I731014 were rather confusing. We don’t know what went wrong here, especially as we had shown previously in the AHL test that the I731014 part appears to be functioning.
This week we also started on the road to making our first biobricks. The CpxR promoter was cloned out of the TR235 and MG1655 genomes, and was verified on a gel after restriction digest. The results of the digest of pSB1A3, however, did not make sense again, and doesn’t appear to correspond to what it is meant to be. We have now decided to obtain this plasmid by using the T9002 biobrick, cutting out the T9002 part, and inserting our CpxR promoter.
The second biobrick we want to make is luxI and GFP under the control of our CpxR promoter. Originally the LuxI and GFP portion were to be obtained from the J37015 biobrick, but since this doesn’t appear to be in the plasmid, we have started on building it ourselves using the separate LuxI (I15030) and GFP (E0840) parts. Transformations of electro-competent DH5α with the I15030 part were carried out.
 "
"