Team:NTU-Singapore/Wetlab/Protocols
From 2008.igem.org
Lalala8585 (Talk | contribs) (→Creation of New Biobrick parts) |
Lalala8585 (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
<div id="maincontent" style="margin-top:200px;"> | <div id="maincontent" style="margin-top:200px;"> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ==Creation of New Biobrick parts== | + | |
| + | ='''Protocols'''= | ||
| + | =='''Creation of New Biobrick parts'''== | ||
To create a new biobrick part, the first step is to identify the gene of interest. In this project, our genes of interest are the E7 production gene, Immunity gene, and Lysis gene that is obtainable from the plasmid ColE7-K317 in BW Escherichia Coli strain. Another gene of interest is the LsrA promoter that is obtained from MG1655 Escherichia Coli strain. Information on the genome of interests is extracted from relevant publications and websites such as NCBI net. <br> | To create a new biobrick part, the first step is to identify the gene of interest. In this project, our genes of interest are the E7 production gene, Immunity gene, and Lysis gene that is obtainable from the plasmid ColE7-K317 in BW Escherichia Coli strain. Another gene of interest is the LsrA promoter that is obtained from MG1655 Escherichia Coli strain. Information on the genome of interests is extracted from relevant publications and websites such as NCBI net. <br> | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
4. Next, the purified DNA is digested using EcoRI and PstI restriction enzymes to generate a standard Biobrick part with the gene sequence:<br> | 4. Next, the purified DNA is digested using EcoRI and PstI restriction enzymes to generate a standard Biobrick part with the gene sequence:<br> | ||
| - | EcoRI – XbaI - Lysis gene – SpeI – PstI<br><br> | + | '''EcoRI – XbaI - Lysis gene – SpeI – PstI'''<br><br> |
| - | ==Digestion and Ligation of NTU@iGEM System== | + | [[Image:Cycle_mindmap.jpg|thumb|600px|center|Creation of New BioBricks]] |
| + | |||
| + | =='''Digestion and Ligation of NTU@iGEM System'''== | ||
To ligate 2 Biobrick parts together, firstly we identify one part to be "vector" and the second part to be "insert". There are 2 possibility of ligation:<br> | To ligate 2 Biobrick parts together, firstly we identify one part to be "vector" and the second part to be "insert". There are 2 possibility of ligation:<br> | ||
*Case I: Insert in front – Vector behind <br> | *Case I: Insert in front – Vector behind <br> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 44: | ||
2. Repeat Step 2 ~ 5 as from Case I<br> | 2. Repeat Step 2 ~ 5 as from Case I<br> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | ==OD600 measurement of pLsrA-Lysis-containing LuxS mutant upon addition of AI-2== | + | [[Image:Mindmap_expt.JPG|thumb|800px|center|Summary of Digestion and Ligation Procedures]] |
| + | |||
| + | =='''OD600 measurement of pLsrA-Lysis-containing LuxS mutant upon addition of AI-2'''== | ||
1) One colony of LuxS(-) W3110 strain containing pLsrA-lysis plasmid was inoculated overnight in 50ml LB inside 250ml flask at 37 degrees C and 225rpm. <br><br> | 1) One colony of LuxS(-) W3110 strain containing pLsrA-lysis plasmid was inoculated overnight in 50ml LB inside 250ml flask at 37 degrees C and 225rpm. <br><br> | ||
2) After 16 hour inoculation, 0.5 ml of cell sample was diluted in 50ml fresh LB.<br><br> | 2) After 16 hour inoculation, 0.5 ml of cell sample was diluted in 50ml fresh LB.<br><br> | ||
| Line 64: | Line 53: | ||
4) 50µl AI-2-containing supernatant was added into corresponding wells initially (set 1) and 1 hour after incubated inside absorbance-meter (set 2). <br><br> | 4) 50µl AI-2-containing supernatant was added into corresponding wells initially (set 1) and 1 hour after incubated inside absorbance-meter (set 2). <br><br> | ||
5) Five different supernatant solutions used, which correspond to the time points when they had been obtained during AI-2 preparation: 3, 4, 5, 6, 8 hours.<br><br> | 5) Five different supernatant solutions used, which correspond to the time points when they had been obtained during AI-2 preparation: 3, 4, 5, 6, 8 hours.<br><br> | ||
| - | 6) Control samples included | + | 6) Control samples included |
| - | + | i) cell suspension alone | |
| - | + | ii) cell suspension with 50µl LB added initially (set 1) | |
| - | + | iii) cell suspension with 50µl LB after 1 hour incubation (set 2) | |
| - | + | iv) cell suspension with 50µl water added initially (set 1) | |
| - | + | v) cell suspension with 50µl water added after 1 hour incubation (set 2) | |
| + | <br> | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <script language=Javascript1.2> | ||
| + | <!-- | ||
| - | == | + | var tags_before_clock = "<b>It is now " |
| - | < | + | var tags_middle_clock = "on" |
| - | == | + | var tags_after_clock = "</b>" |
| - | < | + | |
| + | if(navigator.appName == "Netscape") { | ||
| + | document.write('<layer id="clock"></layer><br>'); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (navigator.appVersion.indexOf("MSIE") != -1){ | ||
| + | document.write('<span id="clock"></span>'); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | DaysofWeek = new Array() | ||
| + | DaysofWeek[0]="Sunday" | ||
| + | DaysofWeek[1]="Monday" | ||
| + | DaysofWeek[2]="Tuesday" | ||
| + | DaysofWeek[3]="Wednesday" | ||
| + | DaysofWeek[4]="Thursday" | ||
| + | DaysofWeek[5]="Friday" | ||
| + | DaysofWeek[6]="Saturday" | ||
| + | |||
| + | Months = new Array() | ||
| + | Months[0]="January" | ||
| + | Months[1]="February" | ||
| + | Months[2]="March" | ||
| + | Months[3]="April" | ||
| + | Months[4]="May" | ||
| + | Months[5]="June" | ||
| + | Months[6]="July" | ||
| + | Months[7]="August" | ||
| + | Months[8]="September" | ||
| + | Months[9]="October" | ||
| + | Months[10]="November" | ||
| + | Months[11]="December" | ||
| + | |||
| + | function upclock(){ | ||
| + | var dte = new Date(); | ||
| + | var hrs = dte.getHours(); | ||
| + | var min = dte.getMinutes(); | ||
| + | var sec = dte.getSeconds(); | ||
| + | var day = DaysofWeek[dte.getDay()] | ||
| + | var date = dte.getDate() | ||
| + | var month = Months[dte.getMonth()] | ||
| + | var year = dte.getFullYear() | ||
| + | |||
| + | var col = ":"; | ||
| + | var spc = " "; | ||
| + | var com = ","; | ||
| + | var apm; | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (date == 1 || date == 21 || date == 31) | ||
| + | {ender = "<sup>st</sup>"} | ||
| + | else | ||
| + | if (date == 2 || date == 22) | ||
| + | {ender = "<sup>nd</sup>"} | ||
| + | else | ||
| + | if (date == 3 || date == 23) | ||
| + | {ender = "<sup>rd</sup>"} | ||
| + | |||
| + | else | ||
| + | {ender = "<sup>th</sup>"} | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (12 < hrs) { | ||
| + | apm="<font size='-1'>pm</font>"; | ||
| + | hrs-=12; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | else { | ||
| + | apm="<font size='-1'>am</font>"; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (hrs == 0) hrs=12; | ||
| + | if (hrs<=9) hrs="0"+hrs; | ||
| + | if (min<=9) min="0"+min; | ||
| + | if (sec<=9) sec="0"+sec; | ||
| + | |||
| + | if(navigator.appName == "Netscape") { | ||
| + | document.clock.document.write(tags_before_clock+hrs+col+min+col+sec+apm+spc+tags_middle_clock+spc+day+com+spc+date+ender+spc+month+com+spc+year+tags_after_clock); | ||
| + | document.clock.document.close(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (navigator.appVersion.indexOf("MSIE") != -1){ | ||
| + | clock.innerHTML = tags_before_clock+hrs+col+min+col+sec+apm+spc+tags_middle_clock+spc+day+com+spc+date+ender+spc+month+com+spc+year+tags_after_clock; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | setInterval("upclock()",1000); | ||
| + | //--> | ||
| + | </script> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
Latest revision as of 05:47, 27 October 2008
|
Contents |
Protocols
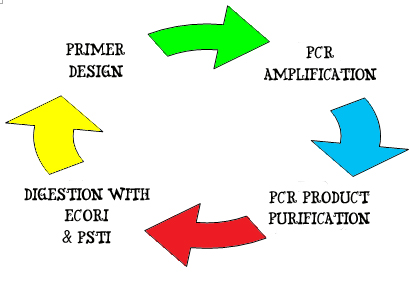
Creation of New Biobrick parts
To create a new biobrick part, the first step is to identify the gene of interest. In this project, our genes of interest are the E7 production gene, Immunity gene, and Lysis gene that is obtainable from the plasmid ColE7-K317 in BW Escherichia Coli strain. Another gene of interest is the LsrA promoter that is obtained from MG1655 Escherichia Coli strain. Information on the genome of interests is extracted from relevant publications and websites such as NCBI net.
For example the gene of interest – Lysis gene:
1. A pair of DNA primers, 10 ~ 15 nucleotides in length are designed and synthesized to flank the forward 3' – 5' end and reverse 5' – 3' end of the gene of interests. The primers also contain blunt ends of the EcoRI, XbaI, SpeI & PstI restriction sites. These primers will hook on to the double strand DNA by complementary pairing and serve as initiation and termination site of DNA amplification.
2. Amplification of the lysis gene occurs by PCR amplification. A gel electrophoresis is run, followed by a gel extraction of the specific interest.
3. The lysis gene is then purified using the PCR purification kit. Purified DNA is tested for concentration and purity using NanoDrop.
4. Next, the purified DNA is digested using EcoRI and PstI restriction enzymes to generate a standard Biobrick part with the gene sequence:
EcoRI – XbaI - Lysis gene – SpeI – PstI
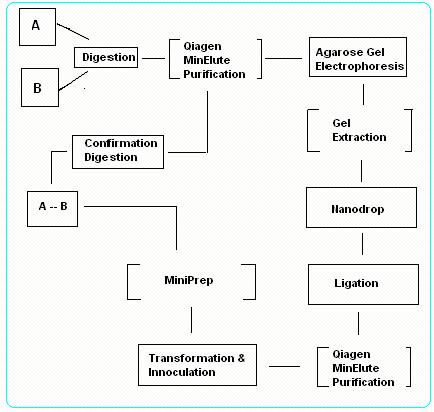
Digestion and Ligation of NTU@iGEM System
To ligate 2 Biobrick parts together, firstly we identify one part to be "vector" and the second part to be "insert". There are 2 possibility of ligation:
- Case I: Insert in front – Vector behind
- Case II: Vector in front – Insert behind
Case I: Insert in front – Vector behind
1.Digest Insert gene with EcoRI & SpeI and Vector gene with SpeI & PstI.
Purify the digested products with PCR Purification Kit and test for concentration and purity using NanoDrop.
2.Perform a gel electrophoresis of the purified products, followed by a gel extraction using PCR Gel Extraction Kit.
3.Fuse the Insert gene to the Vector gene to form a circular plasmid DNA using T4 DNA Quick Ligase.
Transform the DNA plasmid into Top 10 Competent Cells and select using appropriate antibiotic treatment.
Vector gene contain antibiotic resistant gene that confers resistance to the cells that are successfully transformed.
4.Extract the ligated DNA using MiniPrep Kit and digest the resultant DNA using EcoRI & PstI.
5.Lastly, perform a gel electrophoresis for confirmation. Check if the nucleotide length from the gel run matches the hypothetical nucleotide length of the digested product. If the result matches, ligation is successful.
Case II: Vector in front – Insert behind
1. Digest Insert gene with XbaI & PstI and Vector gene with EcoRI & XbaI. Purify the digested products with PCR Purification Kit and test for concentration and purity using NanoDrop.
2. Repeat Step 2 ~ 5 as from Case I
OD600 measurement of pLsrA-Lysis-containing LuxS mutant upon addition of AI-2
1) One colony of LuxS(-) W3110 strain containing pLsrA-lysis plasmid was inoculated overnight in 50ml LB inside 250ml flask at 37 degrees C and 225rpm.
2) After 16 hour inoculation, 0.5 ml of cell sample was diluted in 50ml fresh LB.
3) Diluted cell sample was distributed into the wells of the black-96-well microplate with an amount of 200 µL per well.
4) 50µl AI-2-containing supernatant was added into corresponding wells initially (set 1) and 1 hour after incubated inside absorbance-meter (set 2).
5) Five different supernatant solutions used, which correspond to the time points when they had been obtained during AI-2 preparation: 3, 4, 5, 6, 8 hours.
6) Control samples included
i) cell suspension alone ii) cell suspension with 50µl LB added initially (set 1) iii) cell suspension with 50µl LB after 1 hour incubation (set 2) iv) cell suspension with 50µl water added initially (set 1) v) cell suspension with 50µl water added after 1 hour incubation (set 2)
 "
"