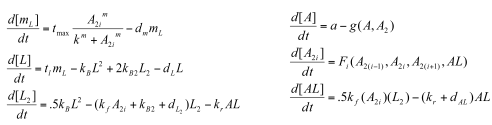Team:Michigan/Project/Modeling/Model2.html
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
*A= NifA protein | *A= NifA protein | ||
*A2i= NifA complex, where i=1 is a dimer, i=4 is a tetramer, and i=6 is a hexamer | *A2i= NifA complex, where i=1 is a dimer, i=4 is a tetramer, and i=6 is a hexamer | ||
| - | |||
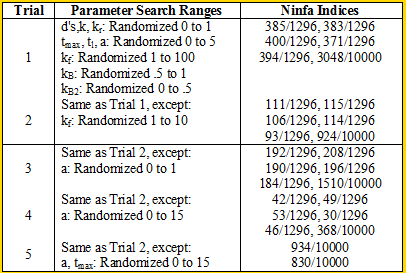
| + | We ran some Ninfa Index simulations on the i=1 model (the other models were too complex to run the simulations on [my MacBook lacks computing power]): | ||
| + | <div align='center'> [[Image: Table2.png]]</div> | ||
| + | Overall, we see smaller indices than the ones we saw in Model 1. Nonetheless,we see that the clock has at least some chance of oscillating. | ||
| + | <br> When we decrease the randomization range of kf to in between 0 and 10 for trial 2, we see an almost threefold decrease in the Ninfa index. | ||
[https://2008.igem.org/Team:Michigan/Project/Modeling Back to Modeling] | [https://2008.igem.org/Team:Michigan/Project/Modeling Back to Modeling] | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 02:30, 30 October 2008
|
|---|
|
Sequestillator Model 2: A More Complicated ModelWhile Model 1 gave us some important results (mainly: need a low Kd for oscillations to occur) , we decided to look at more complete model that accounted for some of the dimerizations the proteins undergo: Parameters
Functions
Variables
We ran some Ninfa Index simulations on the i=1 model (the other models were too complex to run the simulations on [my MacBook lacks computing power]): Overall, we see smaller indices than the ones we saw in Model 1. Nonetheless,we see that the clock has at least some chance of oscillating.
|
|---|
 "
"