Team:Paris/Modeling/f2
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[Image:f2.png]] | [[Image:f2.png]] | ||
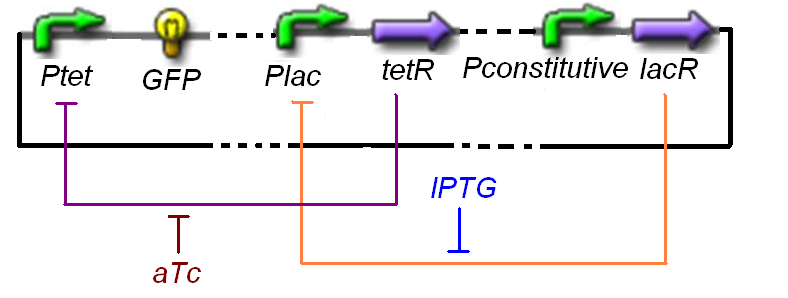
| - | Exactly as for the binding of IPTG on LacR, leading to a lowered inhibition of p-lac, aTc binds to TetR. So, after having determinated the Hill function [expr.p-tet] = | + | Exactly as for the binding of IPTG on LacR, leading to a lowered inhibition of p-lac, aTc binds to TetR. So, after having determinated the Hill function [expr.p-tet] = ƒ2(TetR) = ƒ2aux(IPTG), we can study [expr.''Ptet''] = ƒ2ter([TetR],[aTc]), and determine by calcul [TetR<sub>active<sub>] = ƒ2bis(aTc) = f2<sup>-1</sup>([expr.''Ptet'']), to endly give an analytical expression of ƒ2ter = ƒ2ºƒ2bis |
Revision as of 15:50, 1 August 2008
No particular strain.
Exactly as for the binding of IPTG on LacR, leading to a lowered inhibition of p-lac, aTc binds to TetR. So, after having determinated the Hill function [expr.p-tet] = ƒ2(TetR) = ƒ2aux(IPTG), we can study [expr.Ptet] = ƒ2ter([TetR],[aTc]), and determine by calcul [TetRactive] = ƒ2bis(aTc) = f2-1([expr.Ptet]), to endly give an analytical expression of ƒ2ter = ƒ2ºƒ2bis
 "
"