Team:NYMU-Taipei/Project/Phosphate
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Circuit Design) |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
== Circuit Design == | == Circuit Design == | ||
| - | {| border=1 width= | + | {| border=1 width=1000px | |
! colspan=2 | | ! colspan=2 | | ||
NYMU iGEM08 phosphate removal device v 1.0 | NYMU iGEM08 phosphate removal device v 1.0 | ||
Revision as of 08:08, 3 August 2008
| Home | Project Overview: | pH Sensor | Attachment | Time Regulation | Waste Removal | Experiments and Parts | About Us |
Contents |
Motivation
- When the phosphate level in blood exceeds 6.5 mg/dl, a patient kidney failure has a high risk of death.
- A high serum concentration of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphate phosphate (pi)] is clearly related to pruritus (搔癢症) and hyperparathyroidism (甲狀旁腺功能亢進症), both manifestations of the uremic syndrome.
- Phosphorus excess also inhibits 1 alpha-hydroxylase and hence the production of [http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/medmaster/a682335.html calcitriol], the active vitamin D metabolite.
- Phosphorus retention also alters polyamine metabolism by causing decreases in intestinal function and proliferation of intestinal villi.
Goal
- Enhance and regulate the phosphate absorption of E.coli to balance phosphate concentration to a normal level in patients with kidney failure.
- This device operates when:
- external pH is high.
- external phosphate level is high.
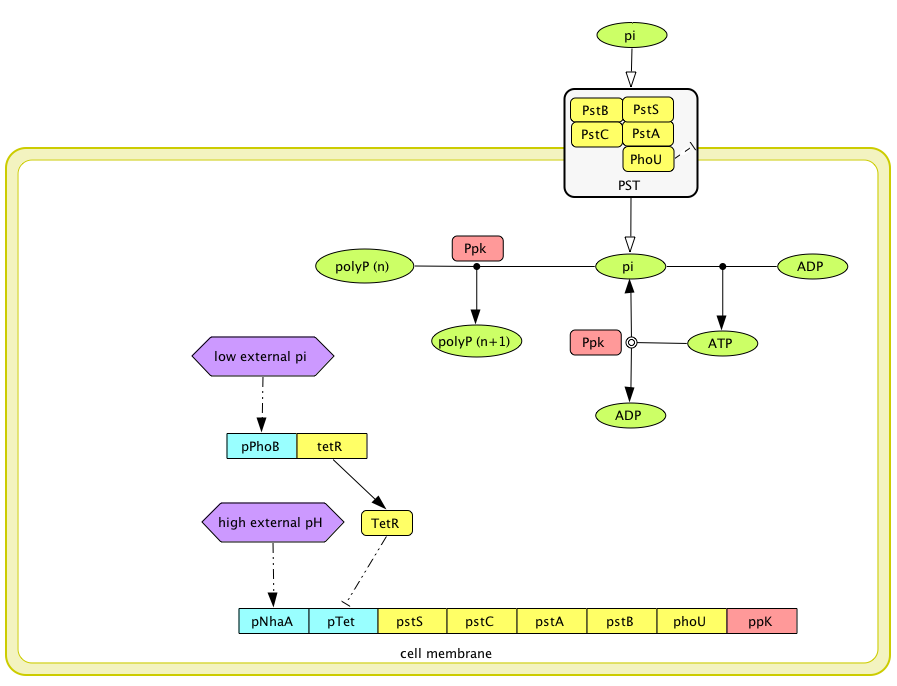
Circuit Design
|
NYMU iGEM08 phosphate removal device v 1.0 | |
|---|---|
| |
References
Phosphate Metabolism and Regulation in E.coli
- [http://jb.asm.org/cgi/content/abstract/183/17/5008 Characterization of PitA and PitB from Escherichia coli, JB 2001]
- [http://aem.asm.org/cgi/content/full/68/8/4107?view=long&pmid=12147514 Accumulation of Inorganic Polyphosphate in phoU Mutants of Escherichia coli and Synechocystis sp. Strain PCC6803, AEM 2002]
- [http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00101.x The phosphate regulon and bacterial virulence: a regulatory network connecting phosphate homeostasis and pathogenesis, FEMS Microbiology Reviews 2008]
Phosphate removal by Microbe
- [http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=182526 Genetic improvement of Escherichia coli for enhanced biological removal of phosphate from wastewater, AEM 1993]
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10448683 Genetic improvement of bacteria for enhanced biological removal of phosphate from wastewater, Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 1999]
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12964240 Microbial phosphate removal and polyphosphate production from wastewaters, Adv Appl Microbiol. 2003]
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12187377 Enhanced phosphate uptake and polyphosphate accumulation in Burkholderia cepacia grown under low pH conditions, Microb Ecol. 2002] and abstract
- [http://www.springerlink.com/content/t6qkt5214pqncmjd/ Intelligent yeast strains with the ability to self-monitor the concentrations of intra- and extracellular phosphate or ammonium ion by emission of fluorescence from the cell surface, AMB 2004]
- [http://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jbb/95/6/95_637/_article/-char/en A method for screening polyphosphate-accumulating mutants which remove phosphate efficiently from synthetic wastewater, Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering 2005]
 "
"