Materials and Methods
From 2008.igem.org
(→Materials and Methods) |
(→Materials and Methods) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
'''1. Cloning''' | '''1. Cloning''' | ||
| - | Constructs were cloned by the AarI method. This a multi-part/combinatorial cloning method that is particularly well suited to shuffling protein domains with various promoters and terminators. The key to this approach is | + | Constructs were cloned by the AarI method. This a multi-part/combinatorial cloning method that is particularly well suited to shuffling protein domains with various promoters and terminators. The key to this approach is the Type II-S restriction enzyme, AarI, arare (7-cutter) that cuts 4bp offset from its binding site. Thus, '''AarI can generate four base overhangs of any sequence'''. |
[[Image:AarI fig1.png]] | [[Image:AarI fig1.png]] | ||
| - | Since the user can specify the overhangs, this method can be used to "stitch-together" fragments '''without a scar'''. | + | Since the user can specify the overhangs, this method can be used to "stitch-together" fragments '''without a scar''', which is sometimes necessary to preserve protein function. |
| - | + | Most importantly, these overhangs can be '''non-palindromic''', which solves the biggest problem faced when trying to do multipart ligations using standard restriction enzymes, illustrated here: | |
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:AarI fig2.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 21:55, 21 October 2008
Materials and Methods
1. Cloning
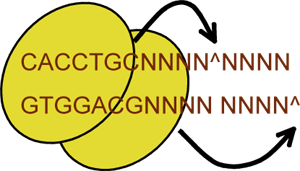
Constructs were cloned by the AarI method. This a multi-part/combinatorial cloning method that is particularly well suited to shuffling protein domains with various promoters and terminators. The key to this approach is the Type II-S restriction enzyme, AarI, arare (7-cutter) that cuts 4bp offset from its binding site. Thus, AarI can generate four base overhangs of any sequence.
Since the user can specify the overhangs, this method can be used to "stitch-together" fragments without a scar, which is sometimes necessary to preserve protein function.
Most importantly, these overhangs can be non-palindromic, which solves the biggest problem faced when trying to do multipart ligations using standard restriction enzymes, illustrated here:
Digestion yields parts with standard, non-palindromic, overhangs.
AarI Shuttle Vector To facilitate exchange of parts between AarI users and the biobricks community, we are offering a Shuttle Vector. This vector accepts AarI parts in the AB or BD format (as were used in our 2008 project). These parts can then be cut out of the vector, with in-frame biobrick ends.
 "
"