Team:Imperial College/Biocouture
From 2008.igem.org
m |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Imperial/StartPage2}} | {{Imperial/StartPage2}} | ||
| + | === Example Application: ''Biocouture'' === | ||
| + | {{Imperial/Box2|Biomaterial| | ||
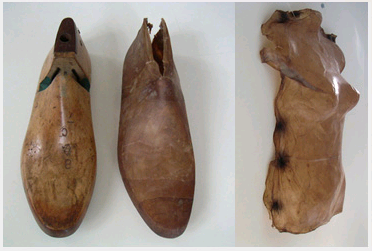
| + | To explore the use of synthetic biology for biomaterial we collaborated with Suzanne Lee, a Senior Research Fellow at St Martins School of Art & Design. She has been focusing on the use of a particular biomaterial called bacterial cellulose for the production of clothes in her project BioCouture (for more information please see the [http://www.biocouture.co.uk BioCouture website]. Drying the gel-like bacterial cellulose produces a dry sheet that can be cut and manipulated to produce clothes ranging from jackets to shoes (see pictures below). From our discussions with Ms. Lee it became apparent that there were a number of potential advantages for taking a synthetic biology approach to BioCouture. This page summarises the use of bacterial cellulose and the potential advantages for a synthetic biology approach. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[Image:Biocouture.PNG |200px]][[Image:Biocouture2.PNG |200px]]</center> | ||
| + | |}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Imperial/Box1|Structure of Bacterial Cellulose| | ||
| + | Although bacterial cellulose has been known and used for many years, its structure was not revealed until X-ray crystallography studies were carried out in the 1980s. On the molecular level, chains of glucose join together in repeating units that build up to form microfibers. These microfibers randomly assemble into fibers of about 130nm in width. During the drying process of bacterial cellulose, these fibres arrange parallel to each others and form layered sheets. These give the dried cellulose sheets high stability and strength. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | + | Traditionally, bacterial cellulose has been collected and used in nata-de-coca, an indigenous desert food of the Philippines. Recently a number of new applications have been proposed, ranging from paper production to skin patches for the treatment of skin damage. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
|}} | |}} | ||
| - | {| | + | {{Imperial/Box1|Genetics of bacterial cellulose| |
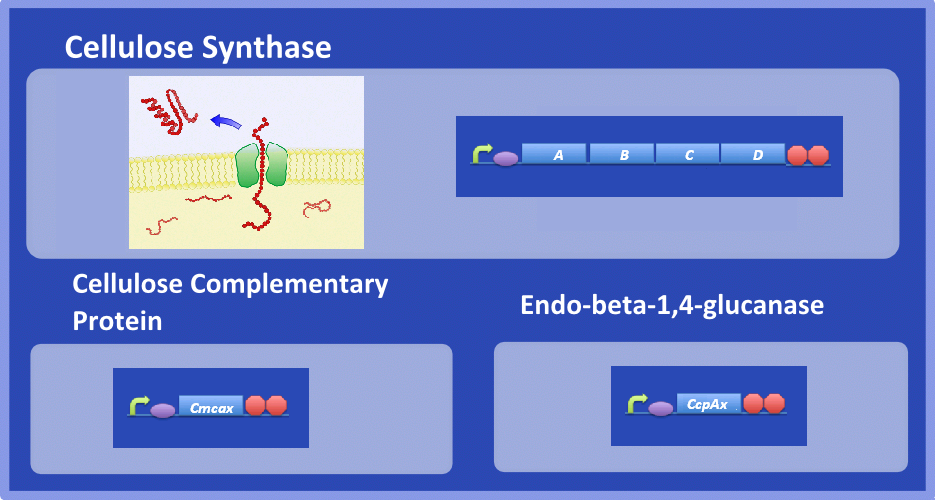
| - | + | ''Acetobacter xylinum'' is a Gram-negative bacterium that produces bacterial cellulose (BC). Central to BC production is cellulose synthase, which synthesizes cellulose from the sugar precursor, UDP-glucose. Cellulose synthase is thought to consist of four subunits known as A, B, C and D. A and B are thought to form a glycosyltransferase that catalyses a β-glycosyltransferase reaction to join two sugar molecules together to create chains of glucose progressively. It is hypothesised that the C subunit forms a pore for the transport of cellulose and D helps to crystallize cellulose into larger fibers. In addition two complementary enzymes appear to be essential for BC production, an endo-beta-1,4-glucanase (Cmcax) and cellulose complementary protein (CcpAx). Cmcax causes hydrolysis of cellulose, but has been shown to be essential for BC production. The function of CcpAx has yet to be elucidated. | |
| - | | | + | |[[Image:CELLULOSE GENES.PNG|500px|center]]}} |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | |[[Image:CELLULOSE GENES.PNG|500px|center]] | + | |
| - | + | ||
| + | {{Imperial/Box1|The Potential of Synthetic Biology| | ||
| + | The potential of synthetic biology for biomaterials lies in controlling synthesis. For example, in our Biofabricator subtilis we use a light input to drive the synthesis of biomaterial and halt movement. Using the biofabricator subtilis would allow a greater control of the '''''Microscopic properties''''' (i.e the layout of fibers) and '''''Macroscopic properties''''' (i.e. the overall shape) of the BioCouture. Furthermore, changing the inputs into our biofabricator subtilis could allow more specific control. For example, shaping cellulose around a mold to produce seamless clothes is technically challanging. However, adaption of the biofabrictor subtilis could allow binding and sensing of the mold to allow cellulose synthesis only when the bacteria is bound. | ||
| + | |[[Image:Blackbox cellulose.PNG|center|500px]]}} | ||
| - | + | <hr><br> | |
| - | + | {{Imperial/Box2||For a more in-depth look at how we got to where we finished, you may want to start with our [[Team:Imperial_College/Dry_Lab | '''>>> Dry Lab Hub >>>''']]}} | |
| - | | | + | |
| - | | | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
{{Imperial/EndPage|Summary|Dry_Lab}} | {{Imperial/EndPage|Summary|Dry_Lab}} | ||
Revision as of 17:12, 24 October 2008
Example Application: Biocouture
|
|||||||||||||||||||
 "
"