Team:Hawaii/Antibiotic test for BB-pRL1383a
From 2008.igem.org
(→Discussion) |
(→Discussion) |
||
| Line 247: | Line 247: | ||
Antibiotic selection is necessary to distinguish between the colonies that contain BB-pRL1383a and those that do not. | Antibiotic selection is necessary to distinguish between the colonies that contain BB-pRL1383a and those that do not. | ||
| - | sp<sub>100</sub> appears to be the ideal concentration of antibiotic necessary for single colony isolation. Lower concentrations resulted in growth of untransformed ''E. coli''. The smear created by these bacteria gradually faded as antibiotic concentration was increased. Higher antibiotic concentration also appears to increase the likelihood of obtaining transformants with the desired plasmid+insert. | + | sp<sub>100</sub> appears to be the ideal concentration of antibiotic necessary for single colony isolation, though single colonies can be observed at sp<sub>40</sub>. Lower concentrations resulted in growth of untransformed ''E. coli''. The smear created by these bacteria gradually faded as antibiotic concentration was increased. Higher antibiotic concentration also appears to increase the likelihood of obtaining transformants with the desired plasmid+insert. |
However, it was observed that none of the colonies at higher sp concentrations were blue. The tiny colonies from the first trial at lower sp concentration were blue. It was likely that our DH5α strain was been contaminated with some ''E. coli'' that are not sp resistant but are ''lacZ'' <sup>+</sup>. | However, it was observed that none of the colonies at higher sp concentrations were blue. The tiny colonies from the first trial at lower sp concentration were blue. It was likely that our DH5α strain was been contaminated with some ''E. coli'' that are not sp resistant but are ''lacZ'' <sup>+</sup>. | ||
Revision as of 20:10, 29 October 2008
Contents |
Antibiotic test and Blue/White screen for BB-pRL1383a
Objective
- To verify the successful construction of BB-pRL1383a, a pRL1383a derivative in BioBrick format with blue/white screening capabilities
- To determine the ideal concentration of spectinomycin for isolation of E. coli colonies transformed with BB-pRL1383a
- To verify the ability to use blue/white screening for selection of transformed cells and to determine length of incubation necessary for this screen
Materials and Methods
Media
To test for antibiotic selection, 30 ml LB + 1.5% agar plates were made. Spectinomycin were added at the following concentrations:
- sp2.5
- sp5
- sp10
- sp15
- sp20
- sp25
- sp40
- sp50
- sp75
- sp100
Thirty microliters of 20X X-gal (20 mg/ml) was added to each plate to a final concentration of 1 μg/ml.
Control plates, also 30 ml LB + 1.5% agar, were as follows:
- LB only
- + X-gal (1 μg/ml)
- + sp100
Transformation
- 100 μl of competent DH5α cells were thawed on ice for 10 minutes.
- 5 μl of a [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J33207 J33207] and pRL1383a ligation reaction were added to the cells. Ten microliters of cells were left untransformed.
- Cells were incubated on ice for 5 minutes.
- Cells were heat shocked at 42C for 1 minute, then returned to ice for 2 minutes.
- 400 μl SOC were added to the transformed cell mixture and 50 μl were added to the untransformed aliquot.
- Cells were incubated at 37C with shaking at 250 rpm for 70 minutes.
- 50 μl of transformed cells + SOC were plated LB+spvariable. 20 μl of untransformed cells + SOC were plated on control plates.
- Oops. 100 μl was plated on LB+sp<sub.100</sub> plate.
- Plates were incubated at 37C for 19 hours.
Verification of plasmid construct
- Plates were stored at 4C for 19 hours after incubating at 37C.
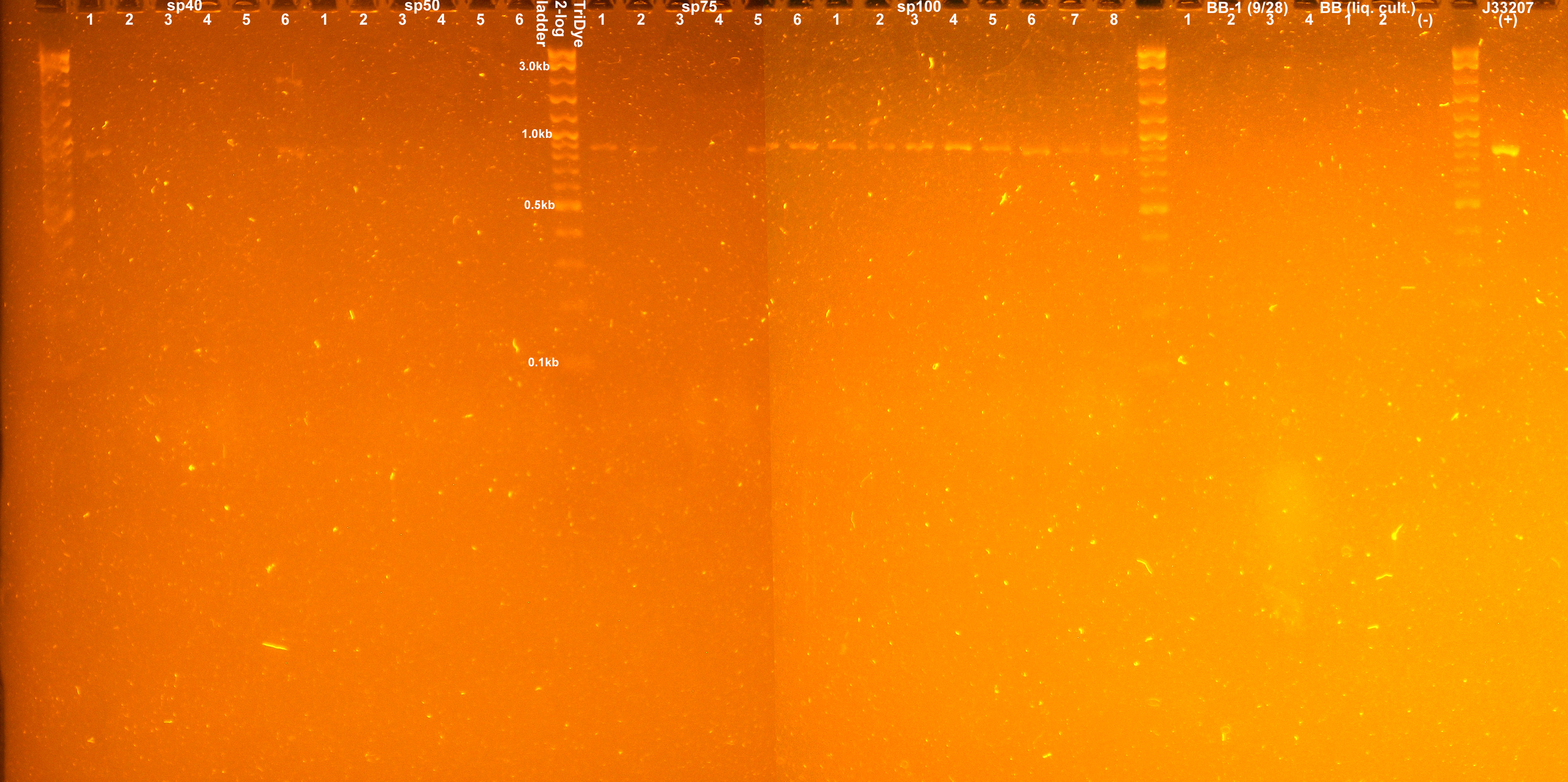
- 6 colonies from LB+sp40, 50, 75, 100 plates were colony PCR'd to verify presence of insert (and by inference, plasmid)
- Initial denaturing: 94C for 10 minutes
- Denature: 94C for 30 seconds
- Anneal: 62C for 30 seconds
- Elongate: 72C for 75 seconds
- Final elongation: 72C for 10 minutes
- Cycles: 30
- PCR reaction:
- 1 μl [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_G00100 VF2 primer]
- 1 μl [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_G00101 VR primer]
- 3 μl PCR water
- 5 μl REDTaq DNA Polymerase mixture (Sigma-Aldrich)
- colony (a sterile toothpick was used to scrape part of the colony to inoculate the PCR reaction)
- 2 μl PCR product were loaded onto a 1% EtBr stained 2% agarose gel for visualization
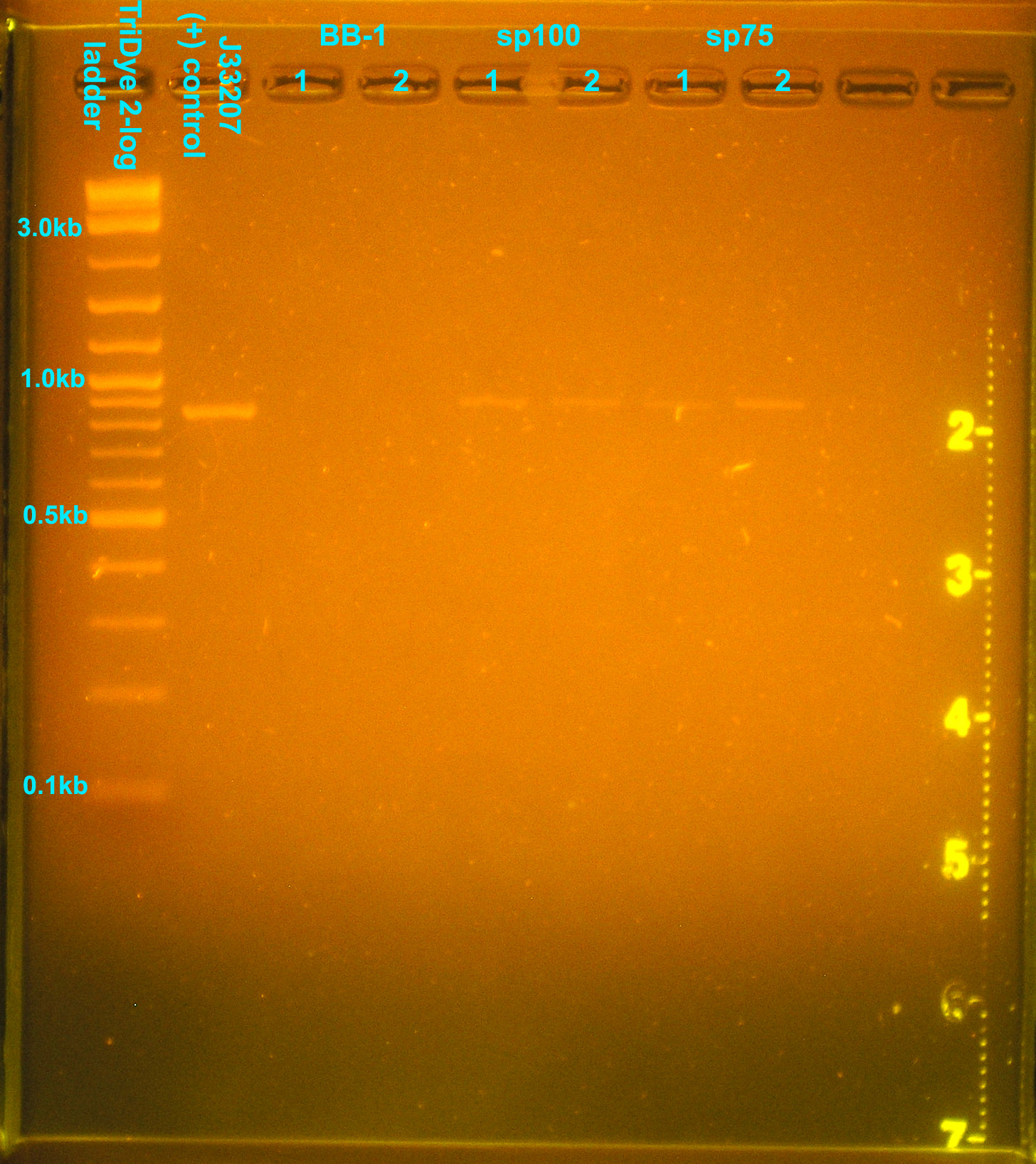
- Colonies #1, 2 from sp100 plate and a (tiny) blue colony from sp2.5 plate were restreaked on LB (+), LB+amp100 (to verify J33207 plasmid transformation from before wasn't a fluke due to contamination), and LB+sp100 (purification). X-gal was added at the aforementioned concentration to all plates. Plates were incubated at 37C for 13 hours.
Verification of results
- The entire experiment was repeated using DH5α MCR cells obtained from Douglas Risser from SC lab.
Results
| Plate | Cells | Colonies | Blue? |
|---|---|---|---|
| LB (+) control | untransformed DH5α | lawn | no |
| LB+X-gal (+) control | untransformed DH5α | lawn | yes |
| LB+sp100 (-) control | untransformed DH5α | 0 | no |
| LB+sp2.5 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | lawn | yes |
| LB+sp5 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | lawn | yes |
| LB+sp10 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | lawn | yes |
| LB+sp15 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | lawn | yes |
| LB+sp20 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | lawn | yes |
| LB+sp25 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | lawn | yes |
| LB+sp40 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | 56 large, too many to count pinpoint, smear present | no |
| LB+sp50 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | 29 large, too many to count pinpoint, smear present | no |
| LB+sp75 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | 41 large, ~30 pinpoint | no |
| LB+sp100 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | 75 large, 12 small | no |
After 19 hours, distinct colonies could be seen on plates with sp concentration >/= 40. However, none of these colonies were blue, suggesting that sp may somehow interfere with expression of lacZ. The controls show that the transformation process did not kill the E. coli and that DH5α are lacZ + but not sp resistant.
After 19 additional hours, colonies did not turn blue.
A colony PCR of transformants yielded the following gel picture:
Two colonies from the sp40 plate appeared to have the correct insert. None of the colonies PCR'd contained the correct insert from the sp50 plate. All PCR'd colonies from the sp75 and sp100 plates appeared to have the desired insert.
| Plate | Colony | Growth? | Blue? |
|---|---|---|---|
| LB+amp100 | sp2.5 blue | No | No |
| sp100 #1 | No | No | |
| sp100 #2 | No | No | |
| LB | sp2.5 blue | Yes | Yes, ~20 |
| sp100 #1 | Yes | No | |
| sp100 #2 | Yes | No | |
| LB+sp100 | sp2.5 blue | No | No |
| sp100 #1 | Yes | No | |
| sp100 #2 | Yes | No |
Observations were collected 19 hours after initial plating. The "contamination" bacteria (blue) are not ampicillin resistant. Colonies that expressed the original J33207 (lac promoter + lacZ) as supplied in pSB1A2 by iGEM were true transformants and not products of contaminated DH5α competent cells.
The experiment was repeated using DH5α MCR cells obtained from Douglas Risser of the SC lab to verify ideal antibiotic concentration.
| Plate | Cells | Colonies | Blue? |
|---|---|---|---|
| LB+Amp100X-gal (+) control | J33207 in pSB1A2 in DH5α | too many to count, medium | yes |
| LB+X-gal (+) control | untransformed DH5α | lawn/smear | no |
| LB+sp2.5+X-gal (-) control | untransformed DH5α | lawn/smear | no |
| LB+sp100 (-) control | untransformed DH5α | 0 | no |
| LB+sp2.5 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | lawn/smear | no |
| LB+sp5 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | lawn/smear | no |
| LB+sp10 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | lawn/smear | no |
| LB+sp20 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | lawn/smear | no |
| LB+sp25 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | lawn/smear | no |
| LB+sp40 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | too many to count, small | no |
| LB+sp50 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | too many to count, small to medium | no |
| LB+sp75 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | too many to count, small to medium | no |
| LB+sp100 | J33207+pRL1383a ligation in DH5α | too many to count, small to medium | no |
After 17 hours, distinct colonies could be seen on plates with sp concentration >/= 40. The controls show that the transformation process did not kill the E. coli, DH5α are not sp resistant, and J33207 (in pSB1A2) is a functional part. It is troubling that none of the colonies transformed with our plasmid are blue. A colony PCR of transformants yielded the following gel picture:
Discussion
Antibiotic selection is necessary to distinguish between the colonies that contain BB-pRL1383a and those that do not.
sp100 appears to be the ideal concentration of antibiotic necessary for single colony isolation, though single colonies can be observed at sp40. Lower concentrations resulted in growth of untransformed E. coli. The smear created by these bacteria gradually faded as antibiotic concentration was increased. Higher antibiotic concentration also appears to increase the likelihood of obtaining transformants with the desired plasmid+insert.
However, it was observed that none of the colonies at higher sp concentrations were blue. The tiny colonies from the first trial at lower sp concentration were blue. It was likely that our DH5α strain was been contaminated with some E. coli that are not sp resistant but are lacZ +.
 "
"