A. Genetic Engineering and Part Construction
A detailed summary of parts, design considerations, and genetic engineering progress can be accessed at the CONSTRUCTS page.
Please visit our Notebook for a summary of labwork and protocols.
B. Yeast Transformation
We are currently accumulating data for plasmid transformations into our brewing strain, SAB-Hefe. Data will be updated soon.
C. HPLC Data
To analyze our beer samples for resveratrol content, be will be using High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), which will allow us to separate the metabolites produced by the yeast and analyze these compounds by spectrophotometry. By comparing HPLC chromatogram peaks of metabolites produced by our yeast with a resveratrol-only standard, we can identify if resveratrol is being produced, and at what quantities. We will be monitoring the production of resveratrol and the consumption of p-coumaric acid, which will only be added to the media for the 4CL::STS-integrated yeast; the 4CL::STS+TAL . Below, we show our initial data for HPLC calibration curves using known quantities of resveratrol and p-coumaric acid standards and test chromatograms using extracts from different wine samples.
- HPLC Parameters
- Instrument: Shimadzu LC-10AT liquid chromatography unit, SPD-10A UV-vis detector, and SCL-10A system controller.
- Column: Agilent Eclipse XDB-C18, 5uM (9.4x250mm)
- Mobile Phases:
- (A) 5% acetonitrile / 0.95% acetic acid
- (B) 70% acetonitrile / 0.3% acetic acid
- Linear gradient: A to B over 29 minutes
- Flow rate: 0.9mL/min
- Absorbance monitoring: 290nm
- Sample injection volume: 25 microliters
|
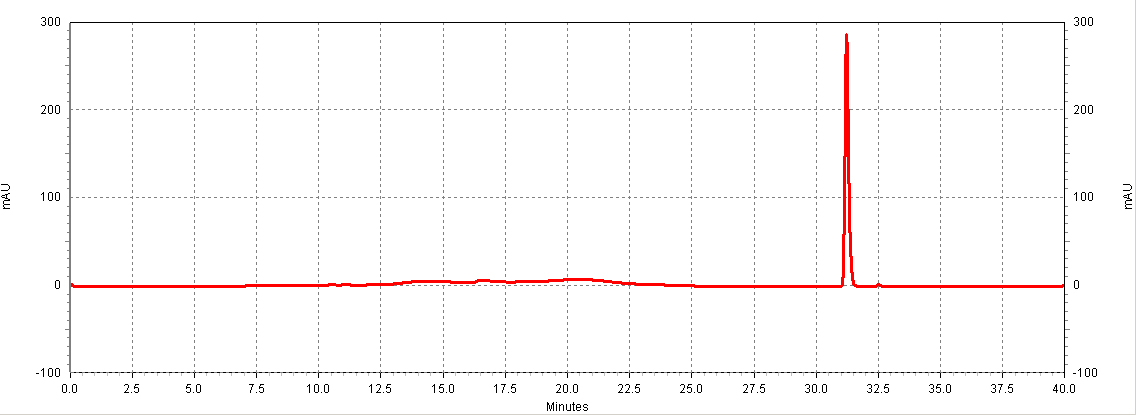 Figure C1. Example HPLC chromatogram of a trans-resveratrol standard.
HPLC: Calibration
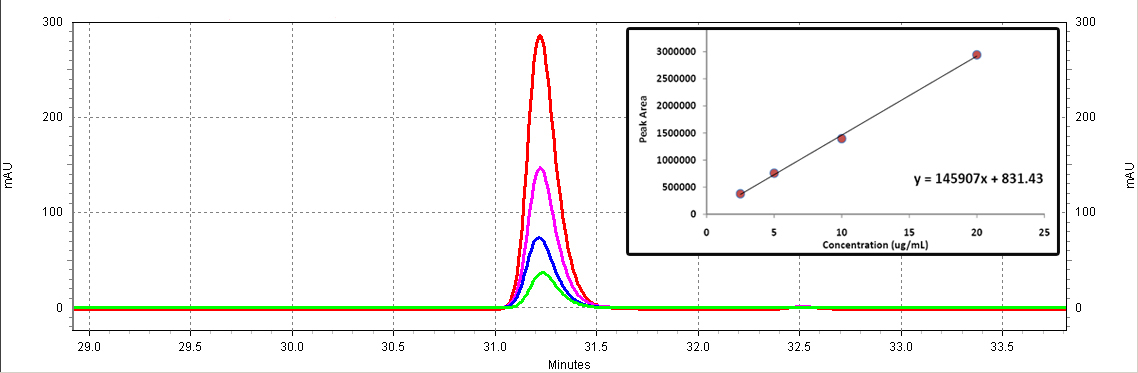 Figure C2: trans-resveratrol standards (Sigma). Different serial dilutions are shown: 20 ug/mL (red), 10ug/mL (purple), 5ug/mL (blue), 2.5ug/mL (green).
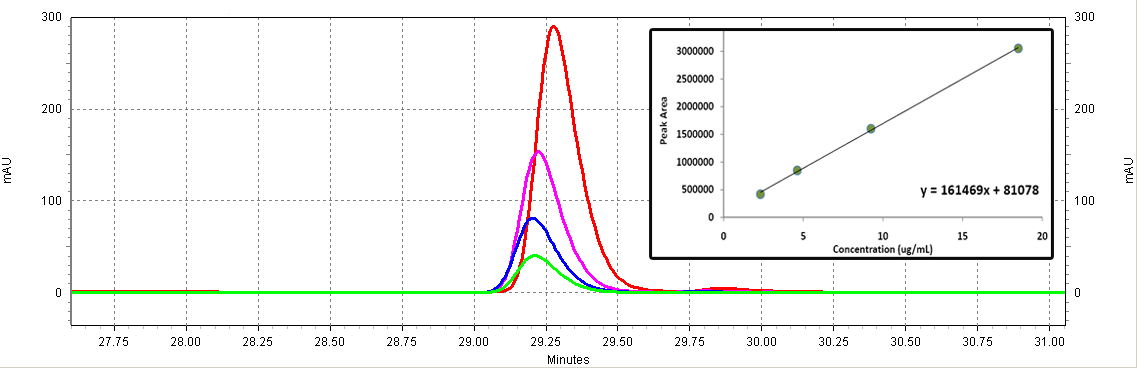 Figure C3: p-Coumaric acid standards (Sigma). Different serial dilutions are shown: 18.5ug/mL (red), 9.25ug/mL (purple), 4.63ug/mL (blue), 2.3ug/mL (green).
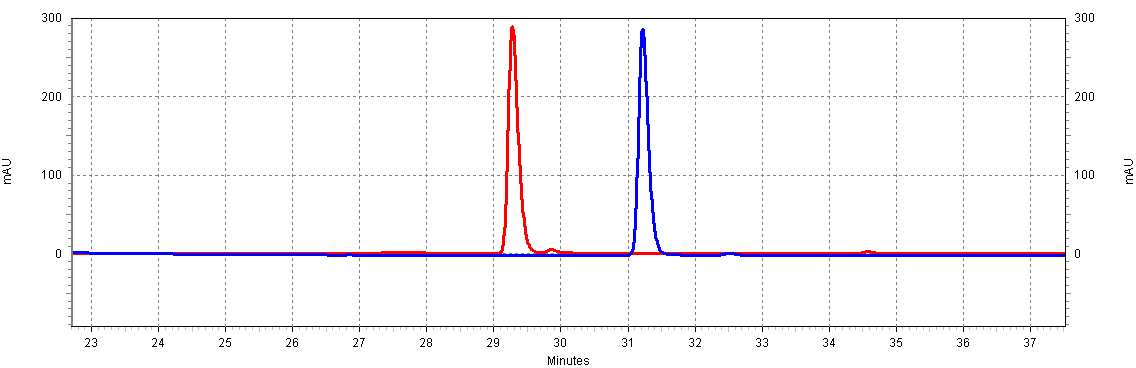 Figure C4: trans-resveratrol and p-coumaric acid separate at different times; this will allow us to resolve both molecules in a complex mixture, such as a yeast extract.
]]
HPLC: Fermenation batches
Fermentation
Coming Soon. For a sneak preview, check out the Gallery
|
 "
"






