Team:Tsinghua/Project
From 2008.igem.org
(→Overall project) |
(→Overall project) |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
The goal is to be achieved via three different subproject.CdLocalizer, DualReceptor and TheoRiboSwitch.TheoRiboSwitch Project focuses on the verification of signals transmission between GCS and motor while DualReceptor Project focuses on the integration of multiple signals at the sensor and GCS sections. CdLocalizer Project is designed to illustrate a more complicated correlation other than linear correlation between ligand concentration and GCS. | The goal is to be achieved via three different subproject.CdLocalizer, DualReceptor and TheoRiboSwitch.TheoRiboSwitch Project focuses on the verification of signals transmission between GCS and motor while DualReceptor Project focuses on the integration of multiple signals at the sensor and GCS sections. CdLocalizer Project is designed to illustrate a more complicated correlation other than linear correlation between ligand concentration and GCS. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | One canonical chemotactic behavior is the response of Escherichia coli toward certain nutrition, which plays a key role in seeking food. Researchers have investigated thoroughly into the molecular mechanism of it. | ||
| + | Motility in prokaryotes is accomplished by flagellum, a complex structure moving the cell by rotation, much like the propeller in a motor boat. In E.coli, counterclockwise rotation moves the cell in a direction called a run, while clockwise rotation results in tumbling of the cell. | ||
| + | The direction of rotation is controlled by phosphorylation of CheY, a signaling protein in the chemotaxis pathway of E.coli. Low level of phosphorylation results in counterclockwise rotation of flagella and makes the cell move forward. In contrast, phosphorylated CheY favors tumbling. | ||
| + | The level of protein phosphorylation is regulated by certain attractant or repellent, which can bind specific receptors on the cell surface. Signals are then passed through a series of intracellular biochemical reactions, in which phosphorylation of CheY is controlled. In this way bacteria accomplish chemotactic behavior. | ||
| + | Molecular mechanism involve in chemotaxis behavior can be simplified into following schematics. There are several kinds of receptors for different chemotactic ligands on the membrane of E.coli. These receptors sense correspondent ligands and convert the concentration of each ligand to their activity. The total activity of them represents whether the bacterium like or hate a certain position in the environment. We name the sum of chemotactic receptors’ activity “General Chemotaxis Signal (GCS)”. Then the decision of chemotaxis is converted into CheY phosphorylation level, which controls rotation bias of molecular motor. Thus, concentration of CheY-p is called “Motor Control Signal (MCS)” here. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:bacterium2.png]][[Image:block_small2.jpg]] | [[Image:bacterium2.png]][[Image:block_small2.jpg]] | ||
System Block Diagram of Chemotaxis | System Block Diagram of Chemotaxis | ||
Different types of receptors sense the concentrations of various ligands and conform them to General Chemotaxis Signal (GCS), which represents the chemotaxis decision. The rest of chemotaxis pathway is in charge of convert GCS to MCS (Motor Control Signal), which interferences motor rotation bias. The working state of motor are directly related to the positions of bacteria in medium, and coordinate of bacterium corresponds to the concentration of ligands there. Bacteria sense real-time environmental conditions and regulate its movement model through this mechanism in order to find a place with highest fitness. | Different types of receptors sense the concentrations of various ligands and conform them to General Chemotaxis Signal (GCS), which represents the chemotaxis decision. The rest of chemotaxis pathway is in charge of convert GCS to MCS (Motor Control Signal), which interferences motor rotation bias. The working state of motor are directly related to the positions of bacteria in medium, and coordinate of bacterium corresponds to the concentration of ligands there. Bacteria sense real-time environmental conditions and regulate its movement model through this mechanism in order to find a place with highest fitness. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
== Wetlab Work == | == Wetlab Work == | ||
Revision as of 02:33, 30 October 2008
| HOME | Team | Project 1 | Project 2 | Parts | Modelling | Notebook | Doodle Board |
|---|
Contents |
Background
| Motile bacteria can respond to chemical gradients in their environment. Such directed movement in response to special chemicals is defined as chemotaxis. If organisms detect substances beneficial for surviving, positive chemotaxis occurs and cells will move in the direction of increasing concentration. In contrast, negative chemotaxis occurs when motile bacteria move away from a repellant. Both kinds of responses adjust the behaviors of organisms to the environment, thus improve their ability of surviving.
One typical chemotactic behavior is the response of Escherichia coli toward certain nutritions, which plays a key role in seeking food. Researchers have investigated thoroughly into the molecular mechanism of it.Motility in prokaryotes is accomplished by flagellum, a complex structure moving the cell by rotation, much like the propeller in a motor boat. In E.coli, counterclockwise rotation moves the cell in a direction called a run, while clockwise rotation results in tumbling of the cell.The direction of rotation is controlled by phosphorylation of CheY, a signaling protein in the chemotaxis pathway of E.coli. Low level of phosphorylation results in counterclockwise rotation of flagella and makes the cell move forward. In contrast, phosphorylated CheY favors tumbling. The level of protein phosphorylation is regulated by certain attractant or repellent, which can bind specific receptors on the cell surface. Signals are then passed through a series of intracellular biochemical reactions, in which phosphorylation of CheY is controlled. In this way bacteria accomplish chemotactic behavior. Escherichia coli is a common kind of engineer bacteria, which is convenient for genetic manipulation. It is likely that we make use of the chemotactic pathway in E.coli, making them detect and move toward a special chemical substance, maybe a certain kind of pollutant. If the genetic engineering strain also has the ability of degrading aimed chemicals, efficiency of pollution treatment can be hopefully improved a lot. However, the natural ligands concerning chemotaxis in E.coli are limited in several kinds of nutrition, such as carbohydrate and amino acids. Strains that can detecting more kinds of organic substances and even heavy metal ions is planed to be got through the reconstruction of chemotaxis system. |
Overall project
This year we are trying to work at the motility of bacteria. E.coli senses some chemicals and moves toward or stays still, this behavior is called chemotaxis. Any modification of the pathway from the sensor to the motile apparatus will cause different chemotactic effcts.
Moreover,most of the biosensors today are designed for a specific target signal, and they can not substitute each other in most cases. By structural analysis we find that most receptors for the same type of ligands exhibit great similarity, both in sequence information and characteristics. Our project is designed for an "Interchangeable Biosensor". The strategy is almost trial and error, to find an appropriate pathway between chemical molecules and corresponding reactions. Signals other than chemicals are much harder to manipulate, and integrating all the signals seems even more challenging,we are trying to isolate the elements and standardize them.
Major inspiration of our idea comes from the Three Laws of Robotics(Isaac Asimov):
1. A robot may not injure a human being, or, through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm.
2. A robot must obey the orders given it by human beings except where such orders would conflict with the First Law.
3. A robot must protect its own existence as long as such protection does not conflict with the First or Second Law.
The goal is to be achieved via three different subproject.CdLocalizer, DualReceptor and TheoRiboSwitch.TheoRiboSwitch Project focuses on the verification of signals transmission between GCS and motor while DualReceptor Project focuses on the integration of multiple signals at the sensor and GCS sections. CdLocalizer Project is designed to illustrate a more complicated correlation other than linear correlation between ligand concentration and GCS.
One canonical chemotactic behavior is the response of Escherichia coli toward certain nutrition, which plays a key role in seeking food. Researchers have investigated thoroughly into the molecular mechanism of it. Motility in prokaryotes is accomplished by flagellum, a complex structure moving the cell by rotation, much like the propeller in a motor boat. In E.coli, counterclockwise rotation moves the cell in a direction called a run, while clockwise rotation results in tumbling of the cell. The direction of rotation is controlled by phosphorylation of CheY, a signaling protein in the chemotaxis pathway of E.coli. Low level of phosphorylation results in counterclockwise rotation of flagella and makes the cell move forward. In contrast, phosphorylated CheY favors tumbling. The level of protein phosphorylation is regulated by certain attractant or repellent, which can bind specific receptors on the cell surface. Signals are then passed through a series of intracellular biochemical reactions, in which phosphorylation of CheY is controlled. In this way bacteria accomplish chemotactic behavior. Molecular mechanism involve in chemotaxis behavior can be simplified into following schematics. There are several kinds of receptors for different chemotactic ligands on the membrane of E.coli. These receptors sense correspondent ligands and convert the concentration of each ligand to their activity. The total activity of them represents whether the bacterium like or hate a certain position in the environment. We name the sum of chemotactic receptors’ activity “General Chemotaxis Signal (GCS)”. Then the decision of chemotaxis is converted into CheY phosphorylation level, which controls rotation bias of molecular motor. Thus, concentration of CheY-p is called “Motor Control Signal (MCS)” here.
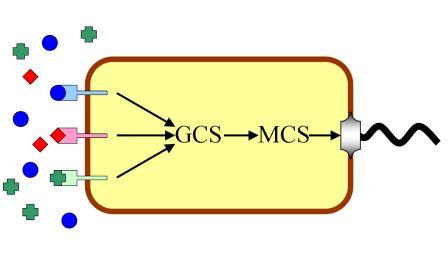
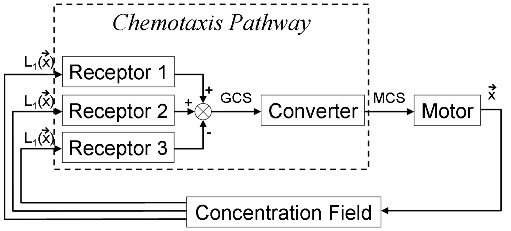 System Block Diagram of Chemotaxis
Different types of receptors sense the concentrations of various ligands and conform them to General Chemotaxis Signal (GCS), which represents the chemotaxis decision. The rest of chemotaxis pathway is in charge of convert GCS to MCS (Motor Control Signal), which interferences motor rotation bias. The working state of motor are directly related to the positions of bacteria in medium, and coordinate of bacterium corresponds to the concentration of ligands there. Bacteria sense real-time environmental conditions and regulate its movement model through this mechanism in order to find a place with highest fitness.
System Block Diagram of Chemotaxis
Different types of receptors sense the concentrations of various ligands and conform them to General Chemotaxis Signal (GCS), which represents the chemotaxis decision. The rest of chemotaxis pathway is in charge of convert GCS to MCS (Motor Control Signal), which interferences motor rotation bias. The working state of motor are directly related to the positions of bacteria in medium, and coordinate of bacterium corresponds to the concentration of ligands there. Bacteria sense real-time environmental conditions and regulate its movement model through this mechanism in order to find a place with highest fitness.
Wetlab Work
Simulation
Reference
1 Assessment of heavy metal bioavailability in contaminated sediments and soils using green fluorescent protein-based bacterial biosensors. Vivian Hsiu-Chuan Liao*, Ming-Te Chien, Yuen-Yi Tseng, Kun-Lin Ou. Environmental Pollution 142 (2006) 17e23
This literature helped us to introduce GFP into our project and gave us a description of heavy metal pollutants.
2 The C-terminal domain of the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase a subunit plays a role in the CI-dependent activation of the bacteriophage lambda pM promoter. Barbara Kedzierska , Anna Szambowska , Anna Herman-Antosiewicz , David J. Lee , Stephen J.W. Busby2, Grzegorz Wegrzyn1 and Mark S. Thomas3,* Nucleic Acids Research, 2007, Vol. 35, No. 7
This literature gives out a mechanism of CI-Pm promotor interaction.
3 Guiding Bacteria with Small Molecules and RNA.Shana Topp and Justin P. Gallivan. J. AM. CHEM. SOC. 2007, 129, 6807-6811 9
This literature lent us an overall vision of how bacteria movement happens and indicated out the central role of CheZ. It also introduced riboswitch into our project.
4 Luminescent bacterial sensor for cadmium and lead.Sisko Tauriainen, Matti Karp, Wei Chang, Marko Virta.Biosensors & Bioelectronics 13 (1998) 931–938
This literature descripted sensors for cadmium and lead.
5 Online and in situ monitoring of environmental pollutants: electrochemical biosensing of cadmium.I Biran, R Babai, K Levcov, J Rishpon, EZ Ron.Environmental Microbiology, 2000
This literature gives out a sensing and detecting method for cadmium.
6 Sensitivity of OR in Phage lambda.Audun Bakk, Ralf Metzler, and Kim Sneppen.Biophysical Journal Volume 86 January 2004 58–66
This literature explains the operation of operons in phage lambda.
| HOME | Team | Project | Parts | Modelling | Notebook | Doodle Board |
|---|
 "
"