Team:Newcastle University/Notebook
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
|boxtype=bluewhitebox | |boxtype=bluewhitebox | ||
|title=Other progress | |title=Other progress | ||
| - | |detail-text=[[Team:Newcastle University/Meetings|Meetings]]<br>[[Team:Newcastle University/Protocols|Protocols]]<br>[[Team:Newcastle University/Results|Results]] | + | |detail-text=[[Team:Newcastle University/Meetings|Meetings]]<br>[[Team:Newcastle University/Protocols|Protocols]]<br>[[Team:Newcastle University/Results|Results]]<br>[[Team:Newcastle University/Notebook#journal|Wet Lab Journal]] |
|link=}} | |link=}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
* BBa_I647107 contains a partial ''agr'' operon, which includes ''agrC'' and ''A'' but has ''agrB'' and ''D'' deleted. This allows coding for the receptor (''C''/''A'') but not for production of the quorum peptides themselves (''B''/''D''). Eventually this will be linked to the ''spaRK'' system in a ''B. subtilis'' vector. | * BBa_I647107 contains a partial ''agr'' operon, which includes ''agrC'' and ''A'' but has ''agrB'' and ''D'' deleted. This allows coding for the receptor (''C''/''A'') but not for production of the quorum peptides themselves (''B''/''D''). Eventually this will be linked to the ''spaRK'' system in a ''B. subtilis'' vector. | ||
| + | <a name="journal"> | ||
== Wet Lab Journal == | == Wet Lab Journal == | ||
{|cellpadding="10" | {|cellpadding="10" | ||
Revision as of 19:22, 21 September 2008
Newcastle University
GOLD MEDAL WINNER 2008
| Home | Team | Original Aims | Software | Modelling | Proof of Concept Brick | Wet Lab | Conclusions |
|---|
Home >> Wet Lab
Introduction
Our construct:
Fig 1 shows the construct which contains:
- spaRK promotor
- rrnB - rRNA binding site
- spaR (subtilin peptide antibiotic Regulation) - the 220 amino acid product of this gene usually regulates the downstream production of subtilin antibiotic. It has an N-terminal domain that can be phosphorylated and a C-terminal domian that has DNA binding properties [http://http://aem.asm.org/cgi/reprint/59/1/296.pdf]
- spaK (subtilin peptide antibiotic Kinase) - this gene codes for a 325 amino acid histadine kinase peptide that phosphorylates the N-terminus of spaR [http://http://aem.asm.org/cgi/reprint/59/1/296.pdf]. This activates the DNA binding ability of the C-terminus of spaR, which in turn initiates transcription of the downstream gene. In the case of our construct, this gene is gfp.
- gfp (green fluorescence protein) - the marker being used to show activation of the spaRK system and therefore diagnosis of gram-positive bacteria by B. Subtilis
- spaS promotor - a strong promotor inducible by upstream activation of spaRK. It can be placed in front any gene to regulate its activity.
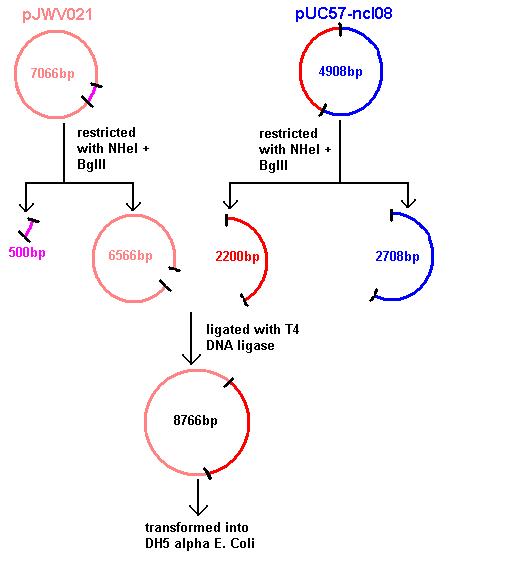
Aim 1: clone the spaRK system from pUC57 into pJWV021 and transform into DH5 alpha competent E. coli
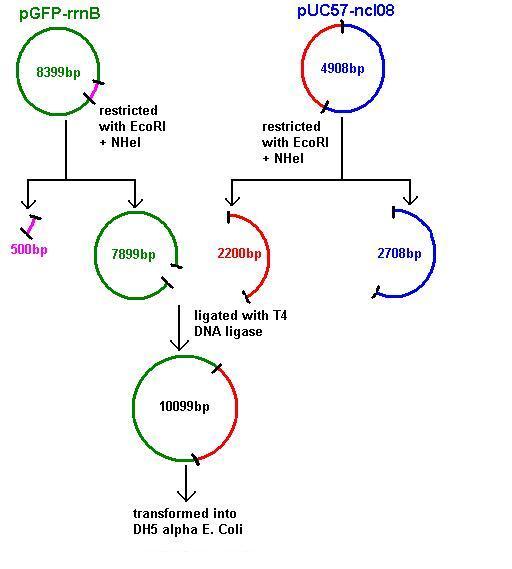
Aim 2: clone the spaRK system from pUC57 into pGFP-rrnB and transform into TOP10 competent E. coli
- The 2.2kb fragment (ncl08) contains the spaRK system and promotor-less gfp linked to this. This means that when spaR is activated, its positive regulatory effect on spaK will in turn activate gfp.
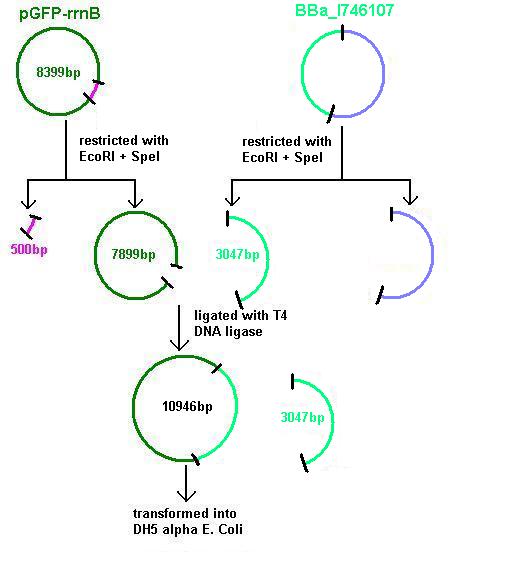
Aim 3: clone the agr system from the plasmid vector into pGFP-rrnB and transform into DH5 alpha competent E. coli
- BBa_I647107 contains a partial agr operon, which includes agrC and A but has agrB and D deleted. This allows coding for the receptor (C/A) but not for production of the quorum peptides themselves (B/D). Eventually this will be linked to the spaRK system in a B. subtilis vector.
<a name="journal">
Wet Lab Journal
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 "
"