Team:Calgary Software/Project
From 2008.igem.org
(→Evolutionary Algorithm) |
(→Evolutionary Algorithm) |
||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
* complex systems | * complex systems | ||
* emergence | * emergence | ||
| - | + | ||
Multiple agents are simulated in an environment to simulate and hypothesize the actions of complex phenomena. </div> | Multiple agents are simulated in an environment to simulate and hypothesize the actions of complex phenomena. </div> | ||
<br style:"clear:both"/> | <br style:"clear:both"/> | ||
Revision as of 01:39, 29 October 2008

|
| Home | The Team | The Project | Modeling | Notebook |
|---|
| Evolutionary Algorithm | Data Retrieval | Modeling | Graphical User Interface |
|---|
Contents |
Introduction
We created EvoGEM, a software program that uses the registry of genetic parts provided by the iGEM competition. In this design, we used evolutionary and genetic strategies, which are useful modeling methods, especially when coupled with agent-based designs.
Paradigm of Evolution
EvoGEM uses the paradigm of evolution to select efficient designs and produce a product or output that is generated independently by the system. EvoGEM uses the strategies of genetics and evolution to simulate an environment inside of a prokaryotic cell. This entails various events and structures that are present inside the organism, such as:
- RNA polymerase
- messenger RNA
- ribosomes
- transcription and translation.
Goals and Achievements
The last team from University of Calgary presented EvoGEM during the 2007 iGEM Jamboree, where it sparked a lot of interest. This summer, our team has expanded EvoGEM by:
- improving EvoGEM's fitness function.
- introducing more complex pattern recognition.
- testing the system under a much larger search space.
Our goal was to create a system sophisticated enough to rebuild working designs from previous years' teams' projects, as well as intelligent enough to simulate successes and failures of functional and dysfunctional systems, respectively. We achieved our goals by:
- building Perl scripts that support EvoGEM's need for a flat file registry.
- creating a graphical user interface (GUI) to make the software-user interaction easier.
- creating a simulation of the processes in the cell such as transcription and translation.
Essentially, this software will allow users to determine whether a specific circuit is feasible before they experimentally test it. This will reduce financial and time constraints associated with traditional lab work. The user will only need to invest time and money into those circuits that our program selects as functional.
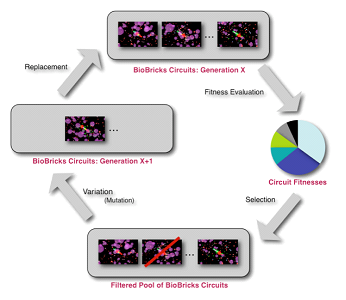
Evolutionary Algorithm
Evolution involves the changes of inherited traits in a population for successive generations. Each generation carries genetic information, expressing certain characteristics. Mutation enables manipulation of these traits as well as genetic recombination. Evolution is a result of heritable traits becoming more prevalent or rare. Agent-based modeling is a computational method that replicates the behavior and interaction of individual components of a network such that their overall effect on the system can be observed. This involves many different aspects, including:
- game theory
- evolutionary programming
- complex systems
- emergence
Data Retrieval and Storage
- its type.
- its function.
- whether it codes for a protein.
- how well the parts work.
If the part coded for a protein, we retrieved its DNA sequence. We, then, found the amino acid sequence (using the BLAST algorithm) from UniProt, which is a large database of proteins. If the protein catalyzed an associated prosthetic or a biochemical reaction, we retrieved additional information from ChemSpider - a chemical database - to find the data characterizing any compounds that the particular enzymatic protein catalyzes. Finally, we stored the data in a database during run-time of EvoGEM.
Modeling
Graphical User Interface
| Evolutionary Algorithm | Data Retrieval | Modeling | Graphical User Interface |
|---|
| Home | The Team | The Project | Modeling | Notebook |
|---|
 "
"