Team:Bay Area RSI/Project
From 2008.igem.org
(→Effectors To Aid In Integration, Anti-apoptosis, And The Alteration Of The Tissue Microenvironment) |
(→Effectors To Aid In Integration, Anti-apoptosis, And The Alteration Of The Tissue Microenvironment) |
||
| Line 132: | Line 132: | ||
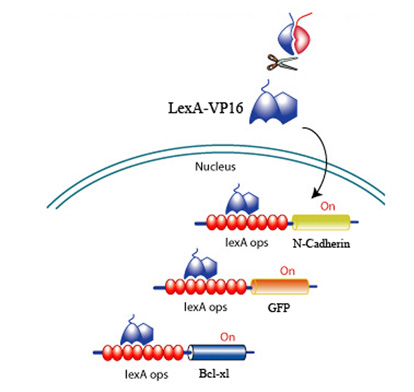
'''Fig 6. LexA-VP16 transcriptional activation of effectors under the control of a lexA operator''' | '''Fig 6. LexA-VP16 transcriptional activation of effectors under the control of a lexA operator''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Ncad flourescent.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
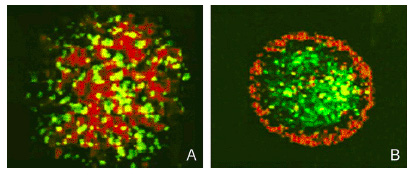
| + | '''Fig 6. Sorting of Transfected L cells expressing N-Cad at 2.4 (green):1 (red) ratio. Foty and Steinberg, 2005 | ||
| + | ''' | ||
| + | |||
One of the biggest problems with current MI therapies is the cell death of stem cells/cardiomyocytes. | One of the biggest problems with current MI therapies is the cell death of stem cells/cardiomyocytes. | ||
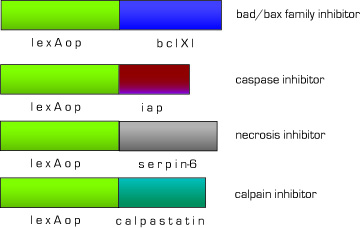
| - | Therefore, we designed a set of effectors to block endogenous apoptotic and necrotic pathways. We have targeted the major apoptosis family of effector proteins, bad/bax and caspases, as well as the calpain family of proteases. | + | Therefore, we designed a set of effectors to block endogenous apoptotic and necrotic pathways. We have targeted the major apoptosis family of effector proteins, bad/bax and caspases, as well as the calpain family of proteases. In the case of unprogrammed cell death, we added an anti-necrotic effector. |
Revision as of 03:18, 29 October 2008
| You can write a background of your team here. Give us a background of your team, the members, etc. Or tell us more about something of your choosing. | |
|
Tell us more about your project. Give us background. Use this is the abstract of your project. Be descriptive but concise (1-2 paragraphs) | |
| Team Example 2 |
| Home | The Team | The Project | Parts Submitted to the Registry | Modeling | Notebook |
|---|
(Or you can choose different headings. But you must have a team page, a project page, and a notebook page.)
Abstract
Every year over 1.2 million people suffer myocardial infarction (MI). The resulting heart damage requires new approaches for effective repair. Stem cell therapies provide hope. However none of the stem cell therapies currently in clinical trials addresses the need for efficient stem cell targeting to cardiac tissue or the need to replace efficiently dead tissue with new cardiomyocytes. To address these problems, we have built several genetic circuits that work sequentially to repair the heart. First, we have built an inducible differentiation circuit that closely resembles the endogenous differentiation pathway, to program cells to become cardiomyocytes. Second, we have built circuits that use the extracellular domains of chimeric proteins to target cells to damaged cardiac tissue. Upon binding, novel receptor-coupled intein-mediated signaling domains activate effector genes that then aid in integration, inhibition of cell death, and the alteration of the tissue microenvironment.
Introduction
There are many problems that existing therapies, and those currently in clinical trials, continue avoid addressing. Some of the main issues include: how to recognize damaged heart tissues, how to deliver stem cells to areas beneath the surface, the inability of adult stem cells to differentiate into cardiomyocytes in the absence of external cues, the prevention of stem cell death during therapy, and how to stimulate advantageous pathways for new cardiac cell integration. Because all our current therapies fail to address any one or a combination of these problems, cell-based therapies for MI patients do not work very well and provide only modest improvement in function, if any.
In 2007 the RSI Bay Area Consortium Team designed and engineered novel methods of targeting damaged cardiomyocytes. Since then, we have shown that our targeting circuit for damaged cardiomyocytes binds and relays effectors in rat cardiomyoblasts. To complement this circuit, the 2008 RSI Bay Area Consortium Team designed and created an efficient inducible method for the differentiation of cardiomyocytes. Together, the two circuits resolve many of the problems associated with the current therapies for MI patients.
Targeting Infarcted Cardiac Tissue
To target cells efficiently to damaged cardiac tissue, the 2007 RSI Bay Area Consortium Team choose three different targets: C-reactive protein (CRP), ICAM, and myosin heavy chain. From these three targeting systems, we focused on continuing the characterization of the CRP based intein system.
CRP As A Target of Infarcted Cardiac Tissue
During an MI, the inflammation causes a several fold increase in CRP serum levels as well as the generation of CRP by damaged cardiomyocytes. However, it is the deposition and immobilization of serum CRP onto exposed small nuclear ribonucleoproteins of infarcted cardiac tissue that makes it an ideal target for therapeutic applications. Because nuclear ribonucleoproteins are contained intracellularly, and only exposed upon serve cellular damage, there is minimal or no non-specific binding of the receptors.
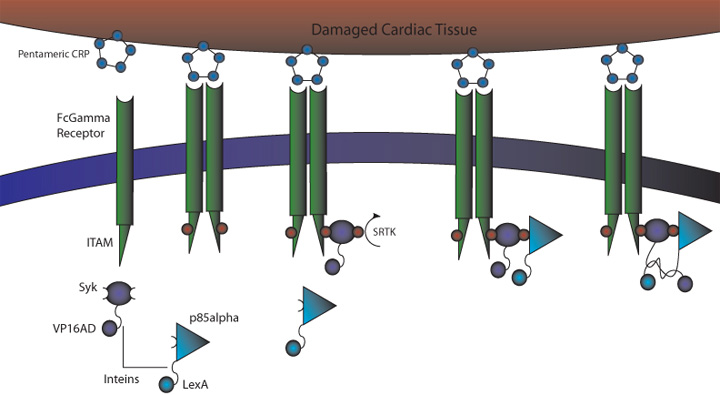
C-Reactive Protein Intein Mediated Receptor Signaling Circuit
Figure 1. CRP Signaling System
1) MI induces large increase in serum CRP levels
2) CRP deposits onto damaged cardiomyocytes
3) Pre-programmed cells expressing FcGammaRIIa-R131 bind CRP on the surface of damaged cardiomyocytes and in the serum surrounding the damaged area
4) Crosslinking of the receptors induces the phosphorylation of the ITAMs in the intracellular region of the receptor
5) Syk is recruited to the receptor and becomes phosphorylated at ITAMs
6) Crosslinking of the receptors also recruits p85 which binds to the phosphorylated Tyr-317 residue on Syk
7) This interchange allows for the inteins (dnaEc-VP16AD at C terminus of Syk and dnaEn-mLexA at N terminus of p85) to interact and self-splice
8) Self splicing of the inteins produces the VP16AD-mLexA transcription factor needed for downstream effector expression
FCGamma Receptor Binds Immobilised CRP on Damaged Cardiomyocytes In Vitro
As proof of principle to test targeting and how well the circuit works, we transfected human HEK293T kidney cells which transfect at very high efficiency (50-95%).
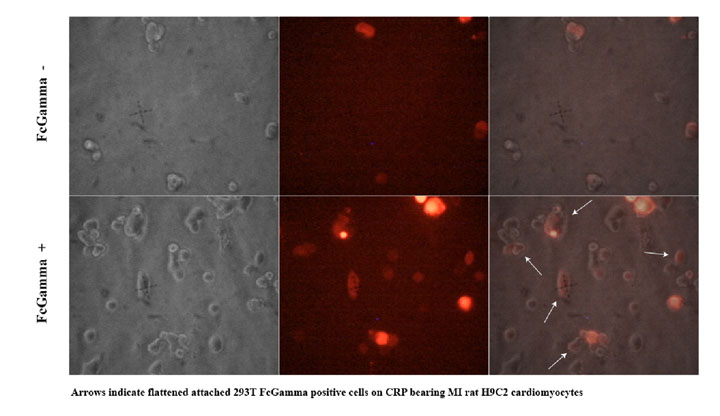
To test how well the targeting works we used the H9C2 rat cardiomyocyte cell line to model infarction. Confluent H9C2 cells were exposed to ischemic buffer for 45 minutes and incubated with 300ug/ml CRP for 2 hours. 293T cells transfected with CMV- FcGammaRIIa and a control plasmid expression DsRed2 at a molar ratio of 10:1 were removed from plates by treatment with PBS/EDTA, washed and plated on H9C2 cells. After 30 minutes cells were washed vigourously 3x and viewed with fluorescent microscopy to detect binding of FcGammaRIIa positive cells.
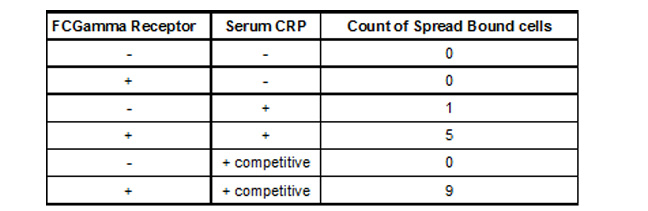
We observed (Fig 2 and Table 1) that FcGammaRIIa positive cells (red) bound the CRP coated H9C2 ischaemic cells at much greater affinity than FcGammaRIIa. It is important to note that cells were still capable of binding in the presence of 150ug/ml competitor CRP, which is promising for in vivo experiments given that CRP is sometimes found in the blood at nearly these levels after MI.
Figure 2. FcGammaRIIa containing cells bind CRP coated H9C2 ischemic cells in the presence of 150ug/ml CRP. FcGamma negative cells bind poorly.
Table 1. Binding of 293T FCGamma Receptor Positive Cells To MI H9C2 with C-Reactive Protein
To demonstrate whether this system would work with cardiomyocytes targeted to damaged cardiomyocytes, we used the ischemic system described to target normal H9C2 ectopically expressing FcGammaRII (Fig 3). FcGamma RII expressing cells bind to ischemic H9C2 monolayer (Fig 3d), but cells carrying the control vector do not (Fig 3b). Also, H9C2 cells infected with FcGammaRII construct were able to differentiate into muscle (data not shown).
Figure 3. H9C2 rat cardiomyocytes infected with lentiviral vector expressing dsRED2 and FcGammaRII bind monolayer of ischemic H9C2 cardiomyocytes treated with CRP. a,b) H9C2 infected with control vector. c-d) H9C2 infected with FcGammaRII. 3 red cells in d demonstrate binding to ischaemic CRP positive cardiomyocytes.
CRP activates GFP signaling upon FCGamma Binding
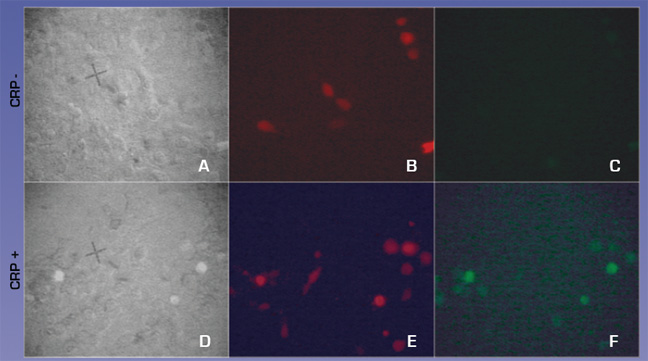
We also tested whether CRP could activate our CRP circuit when transfected into H9C2 cells. H9C2 cells were transfected with equimolar ratios of CMV-FcGammaRIa, cmv- Syk-dnaEc-VP16, cmv- Syk-dnaEc-VP16,and LexApro-GFP reporter. DsRed2 plasmid was included at a 1:10 molar ratio to mark transfected cells. 150ug/ml CRP was added at 48 hours post-transfection. Cells were visualized 24 hours later. 4c and 4f compare the full circuit in the absence or presence of CRP. Fig. 4f shows green GFP expressing cells indicating that the circuit worked, demonstrating proof of concept.
Figure 4. CRP activates the CRP circuit in HEK293T cells
Generation of Clonal lines of H9C2-FCGammaR2a Cardiomyocytes
To characterise the affinity of the FCGammaR2a receptor we infected H9C2 cells with the FCGammaR2a lentiviral construct. 14 days post-infection we diluted H9C2-FCGammaR2a positive cells, DsRed2 positive cells, so that colonies would form from single cells. We have created 5 clonal H9C2-FCGammaR2a lines.
Fig 5. Clonal line of H9C2-FCGammaR2a cells
Effectors To Aid In Integration, Anti-apoptosis, And The Alteration Of The Tissue Microenvironment
Upon CRP binding by the receptors and the subsequent reconstitution of the split inteins, the formation of a transcription factor, lexA-VP16 is released to activate effectors to promote survival, promote angiogenesis, and discourage scarring.
Fig 6. LexA-VP16 transcriptional activation of effectors under the control of a lexA operator
Fig 6. Sorting of Transfected L cells expressing N-Cad at 2.4 (green):1 (red) ratio. Foty and Steinberg, 2005
One of the biggest problems with current MI therapies is the cell death of stem cells/cardiomyocytes.
Therefore, we designed a set of effectors to block endogenous apoptotic and necrotic pathways. We have targeted the major apoptosis family of effector proteins, bad/bax and caspases, as well as the calpain family of proteases. In the case of unprogrammed cell death, we added an anti-necrotic effector.
Fig 7. Anti-apoptosis constructs
Advantages of the CRP Signaling System
Benefits: Binds to CRP on damaged cells to allow for targeting of therapeutic agents (versatile since CRP is expressed in a variety of inflammed tissues). Our system also removes CRP from the region surrounding the damaged area, lessening the damage caused by CRP and increasing the chance of full recovery.
Widespread usability/adaptability Signaling system is endogenous and proven to work Limited potential for cross-talk
CRP Targeting Circuit Concerns
Problems: FcGamma can bind IgG present in serum. Although the FcGammaRIIa-R131 exhibits weak affinity for IgG the possibility of binding and crosslinking the receptor is still there. This problem can be alleviated if the the FcGamma-CRP system is used as part of an AND gate with another receptor system.
CRP is present at a basal level in plasma/may interfere with signaling Activation on of pathway in SC/cardiomyocytes has an unknown effect
Future Directions
Sensor sensitivity-> , avidity, affinity More universal receptor --> 2nd gen SCFV to target other tissue
Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Circuit
endogenous pathways pathway overview construct image + explanation data
Differentiation Circuit Concerns
CA, efficiency, transdiff,
Future Directions
inducible, non-SC progenitor, native cardiofiobroblast
Use As a Novel Therapy For MI Patients
Current therapies and problems Diff types of MI and need for better solution Therpeautic approach with combined circuitry use in tandem, synergistic application
 "
"