Team:Paris/Flagella
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Description of the genetic pathway that lead to flagella assembly) |
(→Description of the genetic pathway that lead to flagella assembly) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
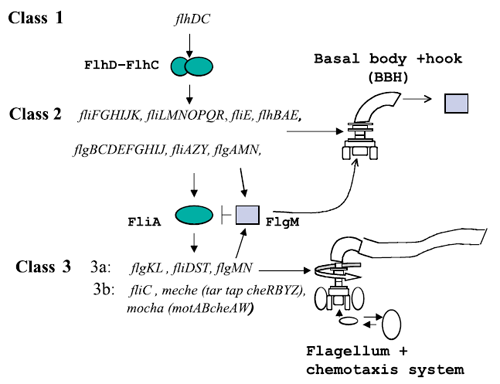
[[Image:Flagella.png|thumb|350px|Figure 1 : The genetically defined hierarchy of the flagellar operons in ''Escherichia coli''.]] <br> | [[Image:Flagella.png|thumb|350px|Figure 1 : The genetically defined hierarchy of the flagellar operons in ''Escherichia coli''.]] <br> | ||
===Description of the genetic pathway that lead to flagella assembly=== | ===Description of the genetic pathway that lead to flagella assembly=== | ||
| - | <br> | + | <br><br> |
The construction of ''E. coli'' flagellar system is organized into a complex hierarchy. The different parts of the flagella are successively assembled parts by parts. This architecture is also present in the network of genes that contributes to its set-up. | The construction of ''E. coli'' flagellar system is organized into a complex hierarchy. The different parts of the flagella are successively assembled parts by parts. This architecture is also present in the network of genes that contributes to its set-up. | ||
Revision as of 09:14, 29 October 2008
Description of the genetic pathway that lead to flagella assembly
A global transcription factor FlhDC activates the synthesis of the flagella. This class 1 gene encodes a protein that activates the expression of class 2 genes. Those genes lead to the construction of the basal body of the flagella and its hook. Then FliA, a protein coded by a class 2 gene activates, with FlhDC to the expression of class 3 genes (Figure 1).
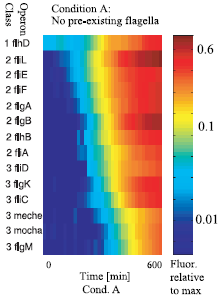
The expression of the flagellar genes is precisely orderedBibliography
|
 "
"