Team:Paris/Flagella
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Description of the genetic pathway that lead to flagella assembly) |
(→The expression of the flagellar genes is precisely ordered) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
===The expression of the flagellar genes is precisely ordered=== | ===The expression of the flagellar genes is precisely ordered=== | ||
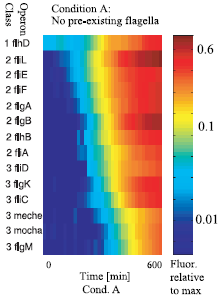
| - | [[Image:order flag.png|thumb|left|221px|Figure 2 : The sequential expression of flagellar genes]] | + | [[Image:order flag.png|thumb|left|221px|Figure 2 : The sequential expression of flagellar genes]]When the flagella system is turned on, the genes are expressed sequentially. flhD is expressed first, then the class 2 genes, and lastly the class 3 genes. At the heart of each class, the promoters are turned on sequentially, with significant delays, in the order ''fliL, fliE, fliF, flgA, flgB, flhB,'' and ''fliA'' (''Figure 2''). The observed order correponds to the spatial position of the gene products during flafellar motor assemblu, going from the cytoplasmic to the extracellular sides. |
===Bibliography=== | ===Bibliography=== | ||
Revision as of 09:20, 29 October 2008
Description of the genetic pathway that lead to flagella assembly
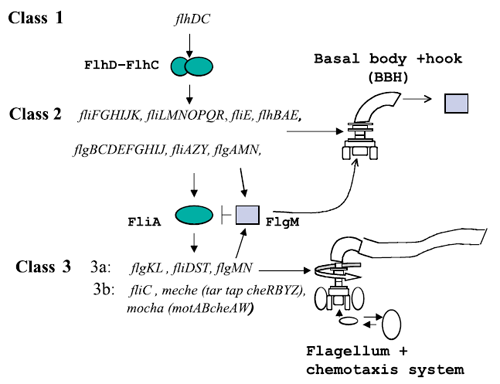
A global transcription factor FlhDC activates the synthesis of the flagella. This class 1 gene encodes a protein that activates the expression of class 2 genes. Those genes lead to the construction of the basal body of the flagella and its hook. Then FliA, a protein coded by a class 2 gene activates, with FlhDC to the expression of class 3 genes (Figure 1).
The expression of the flagellar genes is precisely orderedWhen the flagella system is turned on, the genes are expressed sequentially. flhD is expressed first, then the class 2 genes, and lastly the class 3 genes. At the heart of each class, the promoters are turned on sequentially, with significant delays, in the order fliL, fliE, fliF, flgA, flgB, flhB, and fliA (Figure 2). The observed order correponds to the spatial position of the gene products during flafellar motor assemblu, going from the cytoplasmic to the extracellular sides.Bibliography
|
 "
"