Team:Edinburgh/Modelling
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Modelling) |
|||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
CH1.8O0.5N0.2 + 0.41915O2 = 0.62CH1.77O0.49N0.24 + 0.0512NH3 + 0.2745H2O + 0.38CO2 | CH1.8O0.5N0.2 + 0.41915O2 = 0.62CH1.77O0.49N0.24 + 0.0512NH3 + 0.2745H2O + 0.38CO2 | ||
| - | === | + | ===Production Process Model=== |
| - | H.-J. Rehm and G. Reed. Biotechnology, Vol.4: Measuring, Modelling and Control. | + | Below we show an outline of a possible process for large scale production of 'Micromaize' from cellulosic waste material. Some useful sources for information on large scale microbial processes in general, and processes for polysaccharide/food production specifically, include: |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | * H.-J. Rehm and G. Reed. Biotechnology, Vol.4: Measuring, Modelling and Control. | ||
| + | * Glazer, A.N. and Nikaido, H. 1995. Microbial Biotechnology: Fundamntals of applied microbiology. W.H. Freeman Co., NY. | ||
| + | * Angold, R., Beech, G., and Taggart, G. 1989. Food Biotechnology. Cambridge University Press, UK. | ||
| + | * Crueger, W., and Crueger, A. 1990. Biotechnology: a textbook of industrial microbiology. Sinauer Associates Inc, Sunderland, MA. | ||
| + | * Ratledge, C., and Kristiansen, B. (eds). 2006. Basic Biotechnology, 3rd edition. Cambridge University Press, UK. | ||
[[Image:Produce model.jpg]] | [[Image:Produce model.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 09:37, 29 October 2008
Contents |
Process Considerations
In developing a commercial version of the 'Edinburgh Process' for conversion of cellulose to starch, the following points must be considered:
- Some of the glucose released by cellulose hydrolysis will be used by the 'Micromaize' organisms for growth and enzyme synthesis. We therefore envisage use of an aerobic process (rather than an anaerobic process, as envisaged by most developers of cellulose bioconversion processes) to minimise the amount of glucose which is used in this way, leaving the maximum amount of glucose available for conversion to starch.
- Aerobic processes are more expensive to operate than anaerobic processes due to the greater cost of aeration, mixing, and cooling. However, cellulose degradation is intrinsically slower than use of soluble substrates, so the power requirements for aeration and mixing are expected to be much lower than for a typical aerobic process, and it may be possible to use a non-traditional bioreactor such as a rotating drum device, rather than a more usual (and more expensive) aerated stirred tank reactor. Alternatively it may be possible to use a continuous tower reactor (airlift or pressure cycle reactor).
- Since starch is an insoluble product (unlike glucose, the more usual taarget product of cellulose bioconversion processes), it can be recovered simply by harvesting and drying the cells. Further processing requirements will be dictated by the size of starch grain that can be achieved in bacterial cells. Starch granules are generally much larger than glycogen granules, but we cannot accurately estimate this until some experimental evidence is available.
- Since starch is insoluble, it does not exert osmotic pressure and should not cause product inhibition, unlike glucose. We therefore hope that it will accumulate to much higher levels than glucose, decreasing downstream processing costs.
Modelling
Equation of fermentation reaction
CH1.8O0.5N0.2 + 0.41915O2 = 0.62CH1.77O0.49N0.24 + 0.0512NH3 + 0.2745H2O + 0.38CO2
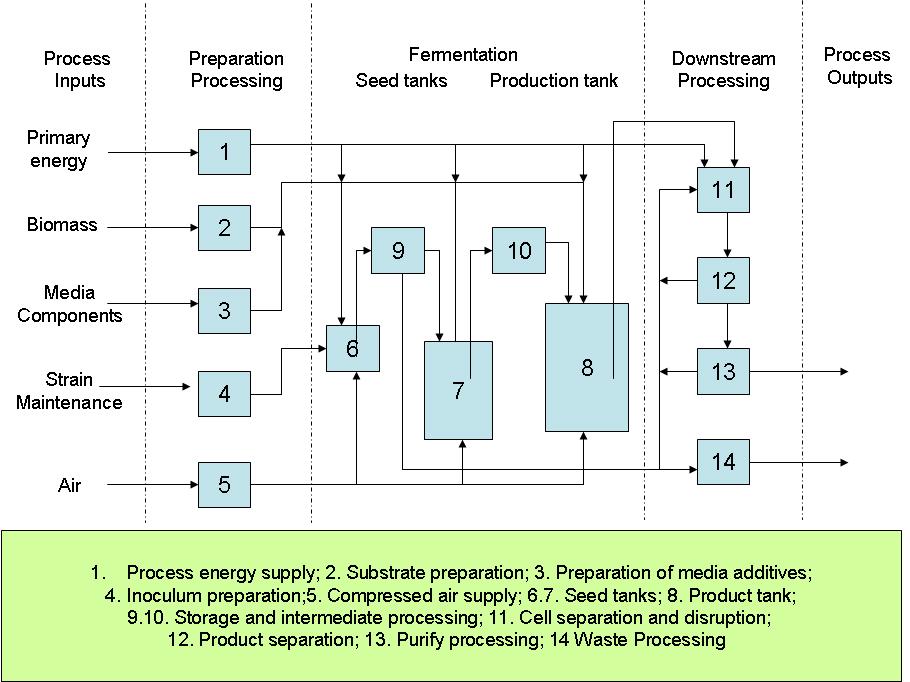
Production Process Model
Below we show an outline of a possible process for large scale production of 'Micromaize' from cellulosic waste material. Some useful sources for information on large scale microbial processes in general, and processes for polysaccharide/food production specifically, include:
- H.-J. Rehm and G. Reed. Biotechnology, Vol.4: Measuring, Modelling and Control.
- Glazer, A.N. and Nikaido, H. 1995. Microbial Biotechnology: Fundamntals of applied microbiology. W.H. Freeman Co., NY.
- Angold, R., Beech, G., and Taggart, G. 1989. Food Biotechnology. Cambridge University Press, UK.
- Crueger, W., and Crueger, A. 1990. Biotechnology: a textbook of industrial microbiology. Sinauer Associates Inc, Sunderland, MA.
- Ratledge, C., and Kristiansen, B. (eds). 2006. Basic Biotechnology, 3rd edition. Cambridge University Press, UK.
 "
"