Team:HKUSTers/Project
From 2008.igem.org
Cygladyswong (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 199: | Line 199: | ||
! Name of test !! Purpose !! Circuit involved | ! Name of test !! Purpose !! Circuit involved | ||
|- | |- | ||
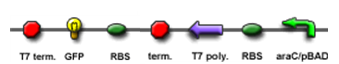
| - | | T7 polymease | + | | T7 polymease production test || Check the T7 polymease production circuit using IPTG as inducer and GFP as reporter || [[Image:T7_production_test.PNG]] || |
|- | |- | ||
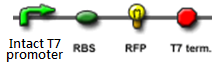
| GFP test || Check if the intact T7 promoter and GFP is functional|| [[Image:GFP_test.PNG]] || | | GFP test || Check if the intact T7 promoter and GFP is functional|| [[Image:GFP_test.PNG]] || | ||
| Line 205: | Line 205: | ||
| Adjacent bidirectional promoters test || Evaluate if two promoters in opposite directions can function properly if they are placed adjacently || [[Image:Adj_promoters_test.png]] || | | Adjacent bidirectional promoters test || Evaluate if two promoters in opposite directions can function properly if they are placed adjacently || [[Image:Adj_promoters_test.png]] || | ||
|- | |- | ||
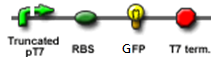
| - | | Truncated promoter test || Stimulate the condition in the overlapped version, where the first two non-essential base pairs of cl434 promoter are altered. We want to know if the cl434 can still function under such | + | | Truncated promoter test || Stimulate the condition in the overlapped version, where the first two non-essential base pairs of cl434 promoter are altered. We want to know if the cl434 can still function under such conditions.|| [[Image:Truncated_promoter_test.PNG]] || |
|- | |- | ||
| - | | Left/right induction test || To see | + | | Left/right induction test || To see whether the overlapping promoter can drive transcription of both directions || [[Image:Left_right_test.png]] || |
|} | |} | ||
===Strain and vector used=== | ===Strain and vector used=== | ||
| - | * '''Strain''': '' | + | * '''Strain''': ''E. coli'' BBa_V1001 DH5a, with genotype |
F-φ80dlacZΔM15 Δ(lacZYA-argF)U169 deoR recA1 endA1 hsdR17(rk- mk+ phoA supE44 λ- thi-1 gyrA96 relA1) | F-φ80dlacZΔM15 Δ(lacZYA-argF)U169 deoR recA1 endA1 hsdR17(rk- mk+ phoA supE44 λ- thi-1 gyrA96 relA1) | ||
* '''Vector''': pUC18+ λ-''InCh''2 | * '''Vector''': pUC18+ λ-''InCh''2 | ||
| Line 223: | Line 223: | ||
The advantages of this approach include: | The advantages of this approach include: | ||
* No risk of >1 copy of target gene in our machine, so as to give a sharp output instead of "blurred" output caused by multiple copies | * No risk of >1 copy of target gene in our machine, so as to give a sharp output instead of "blurred" output caused by multiple copies | ||
| - | * Stable integration of a single copy of the | + | * Stable integration of a single copy of the construct DNA fragment |
| - | * Most ordinary '' | + | * Most ordinary ''E. coli'' strains and a variety of pBR322-derived Amp-resistant plasmids can be used |
* λ-phage as the only specialized vector required | * λ-phage as the only specialized vector required | ||
| - | * Source: | + | * Source: |
| + | Boyd D., Weiss D.S., Chen J.C., Beckwith J., | ||
| + | Towards single-copy gene expression systems making gene cloning physiologically relevant: Lambda InCh, a simple Escherichia coli plasmid- chromosome shuttle system | ||
| + | (2000) Journal of Bacteriology, 182 (3), pp. 842-847. | ||
Revision as of 22:42, 29 October 2008
| Home | The Team | The Project | Parts to the Registry | Modelling | Notebook | Gallery |
Randomness is everywhere!
You may not have realized it, but randomness is very important even outside the casino. It plays an important role in mathematics, statistics, engineering, computer science and even medicine. Randomness is often needed in reducing bias. Here are some examples of natural occuring random events:
- Random motions of molecules that explains phenomena in thermodynamics and properties of gases
- Random genetic mutations that lead to diversity of life and makes natural selection possible
True Randomness?
There are various scientific or social areas in which randomness is required for fair analysis. When random numbers are needed, they are usually generated by computers. The computers may use information say, time, and long complicated mathematical processes to generate the number. So, is this true randomness?? The result may actually just be determined by the time at which the generation is kicked start. It is still not absolutely random.
Therefore, we have decided to design a . . .
This is going to be biologists' random generator. It is not just a biological slot machine, but a random number generator. The cell will have an either 0 or 1 state. By using more than 1 cell, a multi-digit binary number can be generated. The results cannot be controlled or altered by humans. It is true randomness!!! (yes, ideally)
The Design
"Making the dice"
We "tell" our cells to start making the "dice"--T7 polymease by applying a pulse of IPTG. IPTG can activate the araC/pBAD promoter which leads to transcription of T7 promoter.
"Throwing the dice"
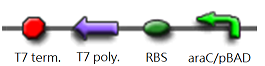
The core part of the randomizer consists of a pair of overlapping T7 promoters having similar binding affinities. The T7 polymerase binds absolutely randomly onto either the left or the right promoter to give an either 0 or 1 signal eventually, i.e. a mutually exclusive binding event. There are two operators on the sides of the promoters, they are c1434 and TetR operators.
Reciprocal inhibiton
Then there are TetR and C1434 repressor repressor genes on both sides respectively. A repressor protein can be produced to interrupt transcription on the other side of the circuit.
For example, say, the T7 polymerase binds onto the promoter on the left side. The TetR repressor on the left, which was coded by TetR repressor gene, will bind to TetR operator on the right and repress transcription of right side of the promoter. Thus, the intial random event (binding of polymease) can be captured and amplified in a postive feedback circuit.
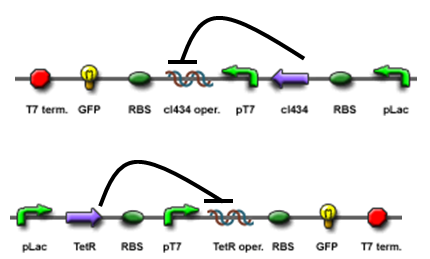
Final outcome
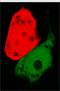
- Continous production of GFP if the polymease binds to the left of overlapped T7 promoter
- Continous production of RFP if the polymease binds to the right of overlapped T7 promoter
The signal output is shown by green or red fluorescent protein (GFP/RFP) respectively.
Construction details
Testing
Strain and vector used
- Strain: E. coli BBa_V1001 DH5a, with genotype
F-φ80dlacZΔM15 Δ(lacZYA-argF)U169 deoR recA1 endA1 hsdR17(rk- mk+ phoA supE44 λ- thi-1 gyrA96 relA1)
- Vector: pUC18+ λ-InCh2
Integration system
We have chosen the λInCh system as the vehicle for intergration.
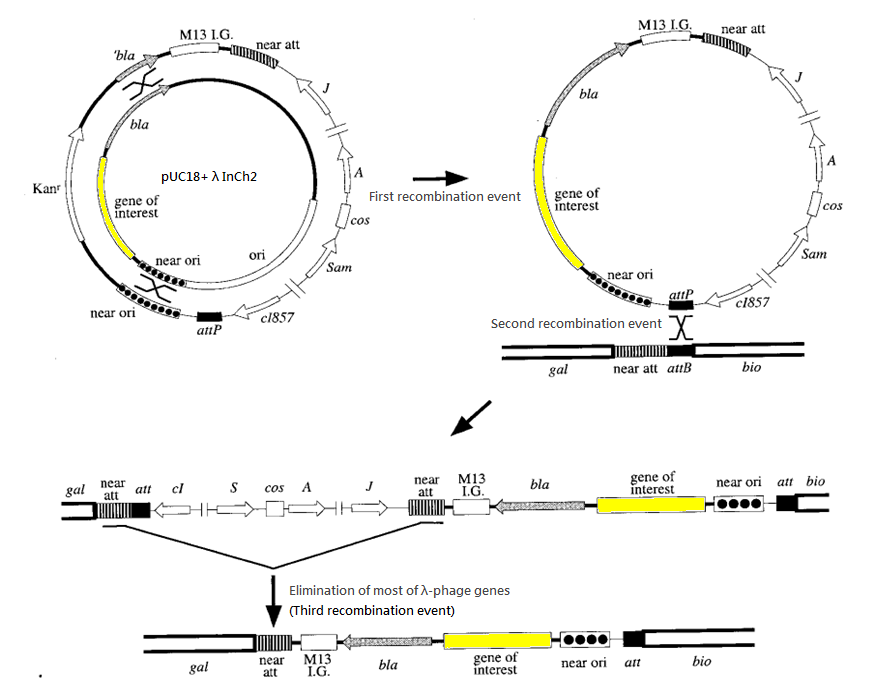
The success rate for recombination is about 1 in 1000 cells. Ampicillin is used to screen for the second recombination event and temperatute of 42 degree Celsius is used to screen for the third recombination event. (Such temperature deactivates the cl857 repressor and hence activates the harmful gene of λ-phage introduced in second recombination event, killing the host cells.)
The advantages of this approach include:
- No risk of >1 copy of target gene in our machine, so as to give a sharp output instead of "blurred" output caused by multiple copies
- Stable integration of a single copy of the construct DNA fragment
- Most ordinary E. coli strains and a variety of pBR322-derived Amp-resistant plasmids can be used
- λ-phage as the only specialized vector required
- Source:
Boyd D., Weiss D.S., Chen J.C., Beckwith J., Towards single-copy gene expression systems making gene cloning physiologically relevant: Lambda InCh, a simple Escherichia coli plasmid- chromosome shuttle system
(2000) Journal of Bacteriology, 182 (3), pp. 842-847. "
"