Team:NYMU-Taipei/Project/Guanidine
From 2008.igem.org
| Home | Project Overview: | pH Sensor | Attachment | Time Regulation | Waste Removal | Experiments and Parts | About Us |
Contents |
Motivation
Renal failure can make one unable to regulate water, electrolyte balances, and metabolic waste. If not treated, lethargy, weakness, shortness of breath, and generalized swelling may occur.
Literature
[http://www.clinchem.org/cgi/reprint/25/7/1343.pdf Proposed Mechanism for Urea Nitrogen Re-Utilization: Relationship between Urea and proposed Guanidine cycles]
1. Ramesh Kekuda, Puttur D. Prasad, Xiang Wu, Haiping Wang, You-Jun Fei, Frederick H. Leibach, and Vadivel Ganapathy; Cloning and Functional Characterization of a Potential- sensitive, Polyspecific Organic Cation Transporter (OCT3) Most Abundantly Expressed in Placenta; THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY (1998).
2. Kazumasa Aoyagi; Significance of reactive oxygen in kidney disease elucidated by uremic toxins; J Artif Organs (2001).
3. Samuel Natelson, Hsiu-Yu Tseng, and John E. Sherwin; On the Biosynthesis of Guanidinosuccinate; CLIN. CHEM (1978).
4. Jinshu Qiu, Hans Lee, Chengfeng Zhou; Analysis of guanidine in high salt and protein matrices by cation-exchange chromatography and UV detection; Journal of Chromatography A (2005).
5. Toshihiko Hanai; Separation of polar compounds using carbon columns; Journal of Chromatography A (2003).
Background
Methylguanidine, guanidinosuccinic acid (GSA) and guanidinoacetic acid are the three compounds that provide alternative pathways for the excretion of nitrogen in patients with renal failure (J. Sawynok et al., 2007).
GSA was first detected in the urine of uremic patients. Its excretion in the urine is accompanied by a marked decrease in the production guanidinoacetate. This is because the formation of GSA and guanidinoacetate are alternative metabolites of aspartate, which condenses with ureidohomoserine to form canavaninosuccinate in a transamidination cycle (Samuel Natelson et al., 1978).
J. Sawynok et al., 2007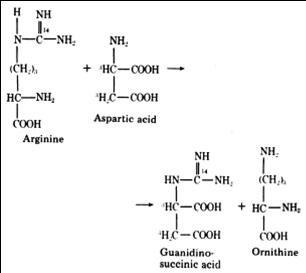
Toxicity: GSA (N-amidino-Laspartate) has been identified as one of the major causes of bleeding tendency, a Na-K ATPase inhibitor, and the cause of convulsions in end-stage renal disease. GSA was found to be an activator of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor that generates NO and plays an important role in nerve development and the death of neurons. In peripheral nerves, it functions in pain and itching sensations.
Strategy
In the renal proximal tubular epithelial cells, the cationic xenobiotics enter the cell across the basolateral membrane and exit the cell across the brush border membrane. A concerted action of the potential-sensitive transport system in the basolateral membrane and the H1-dependent transport system in the brush border membrane effectively mediates the elimination of several xenobiotics by the kidney. These transporters belong to the organic cation transporter (OCT) family, which contains OCT1, OCT2, OCT3, NKT, NLT, RST, and OCTN1. Compared with other transpoters, OCT3 is not only a transmembrane protein but also functions as an channel for anti-transporting cations, such as GSA and sodium ions.
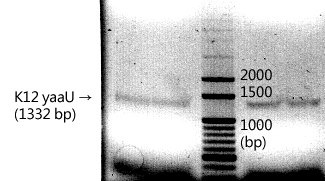
Initiated by pNhaA and promoted by urea sensors, the OCT3 homolog transporter from E. coli K-12 is aimed to remove guanidino compounds when the environmental pH is allowed and the urea concentration reaches the optimal state. http://www.vitrax.com/products/catalog.php
Experiment
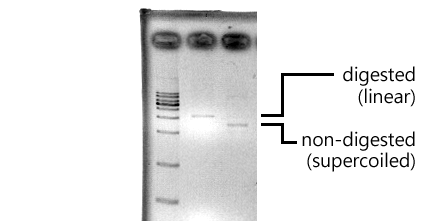
CLONING

|
| |

|
| |
|
| |
| ||
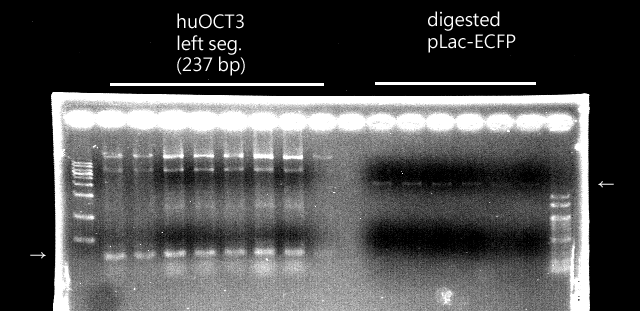 |
| |
 |
| |
| File:NYMU urea poor growth.png |
| |
 |
| |
| 400px |
| |
| 400px |
| |
| 400px |
|
HPLC
- Materials and methods
- UV (215 nm) and fluorescence (ex: 305nm, em: 395 nm)
- Sodium citrate, LB, TSKgel column G3000PW and TSKgel column ODS-120T
- GSA (stock concentration= 10 mg/ml) serial dilution factor: 2
- Background standard curve
- Total volumes are 1000 ml, concentrations are set to 5, 2.5, 1.25, 0.625, 0.3125 mg/ml (the supposed minimum detectable conc.= 10 mg/L)
- Prepare different GSA contained LB, and quantify each of them after incubation with "natural" E. coli by HPLC equipment.
- OCT-3 contained standard curve
- Choose a suitable GSA concentration to test with engineered E. coli.
- Be sure to add GSA in different time points (O.D.600=0.5). The presumed incubation times are 0, 5, 10, 30, 60 and 120 min.
 "
"