para-Aminobenzoic Acid (pABA) HPLC Assay Protocol
Purpose
To test for para-aminobenzoic acid levels in E. coli overexpressing the pABA synthesis genes pabA and pabB.
Materials
- Buffer A: 0.1% formic acid in H2O
- Buffer B: 0.1% formic acid in MeOH
- A high performance liquid chromatography machine.
- Column size ?
Procedure
Sample Prep
- Centrifuge the cell culture max speed, 10 minutes.
- Separate pellet from supernatant.
- Resuspend the pellet in 1mL 0.1M Tris-HCl buffer
- Sonicate the resuspended pellet for 1 minute, alternating between 0 and 12Hz.
- Filter sterilize the cell lysate and the supernatant.
- Load 500uL of each into the HPLC.
HPLC Method
- Injection volume was 20uL, column temperature was kept at 40°C.
- Flush the lines individually with Buffer A and B for two minutes each, flush the column with 92% A, 8% B for 10 minutes.
- From the source: "The starting eluent was 92% A mixed with 8% B; the proportion of B was increased linearly to 50% in 7 min, then to 100% in 3 min. The mobile phase was then immediately adjusted to its initial composition and held for 4 min in order to re-equilibrate the column."
- We found the retention time of pABA to be 4.9-5.0 minutes, however the literature states the retention time as 6.0 minutes.
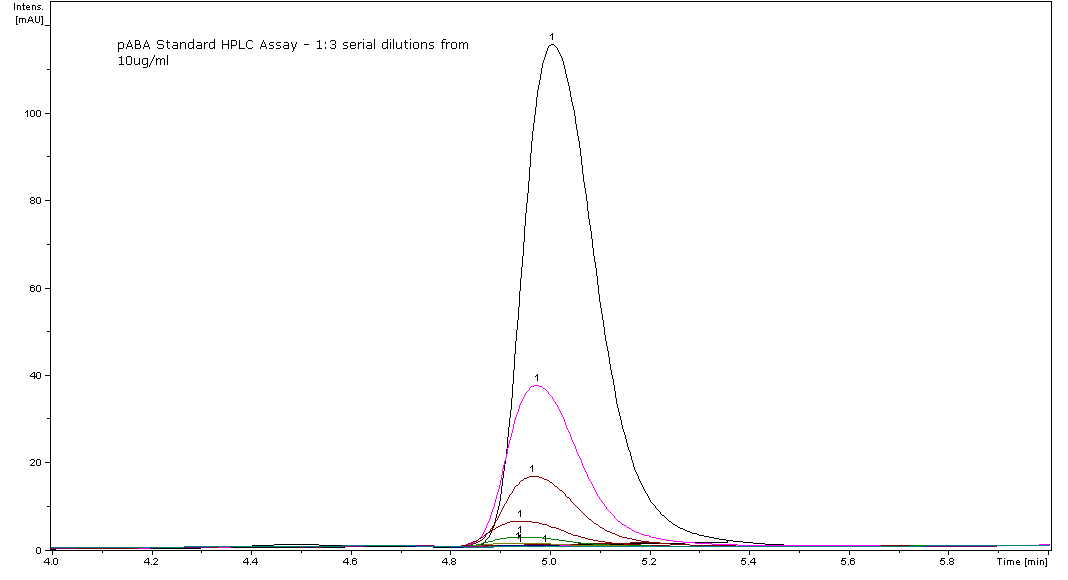 pABA eluting at 4.9-5.0 minutes for the standard curve. Standard Curve
1. Run 1:3 dilutions starting from 10ug/ml pABA in wild type bacterial lysate using the same protocol to generate a linear standard (see below).
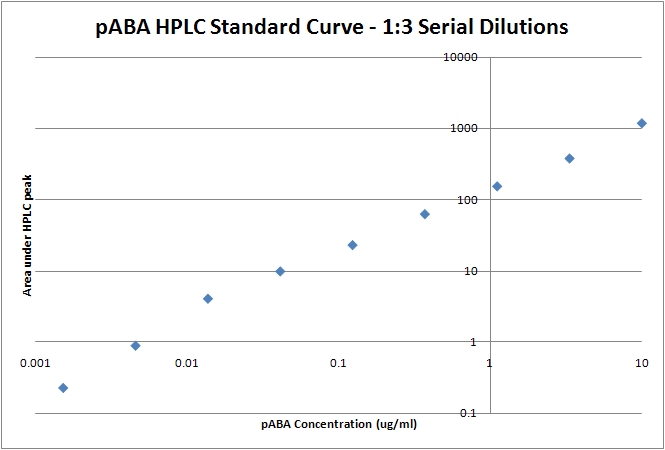 pABA HPLC standard curve with 1:3 dilutions starting from 10ug/ml pABA. The integral of the peak is plotted against the known pABA amount. Sources
Guo-Fang Zhang, Kjell A. Mortier, Sergei Storozhenko, Jet Van De Steene, Dominique Van Der Straeten, Willy E. Lambert. Free and total para-aminobenzoic acid analysis in plants with high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry: Volume 19, Issue 8 , Pages 963 - 969, 2005.
|
 "
"


