Team:Lethbridge CCS/Project
From 2008.igem.org
Our project centers on the development and optimization of a ligase-independent cloning (LIC) protocol.
Contents |
Abstract
Ligase-Independent Cloning as a Standard for BioBrick Preparation
While there is an established BioBrick format, there is not yet a standard method for turning a gene of interest into a BioBrick. Ideally, such a standard method would be easily adopted, even by amateurs, and would lend itself to automation. A significant drawback of several existing techniques is their dependence on ligase treatment, which is often problematic. We propose a ligase-independent cloning (LIC) method, based on the technique of [http://nar.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/18/20/6069 Aslanidis & de Jong (1990)], as a possible standard for novel BioBrick preparation. Instead of short overhangs and ligase treatment, LIC uses long overhangs to circularize plasmid vectors for transformation without the use of ligase. The LIC method reduces the number of enzyme steps required for cloning, thus lending itself to easy adoption, automation, and real biological 'engineering.'
Rationale
The underlying idea of iGEM is that an engineering approach can be applied to biology. Using a computer analogy, the goal is to have software (DNA sequences) that can be run on compatible hardware (microorganisms) anywhere in the world.
| | 
| |
| + | = | + |
 | 
|
The portability of such a biological hardware-software interface requires extensive standardization. The requisite standards exist for the definition of BioBricks, and for the use of BioBrick parts in composite devices. There is not yet a standard method, though, for constructing new BioBricks.
Ideally, whatever standard method is chosen would not only be highly portable, but also simple. The BioBricks used by iGEM are advertised with Lego® blocks, implying a very easy-to-use set of tools. Our team of high school students discovered that synthetic biology is not (yet, at least) at the stage of quick and easy implementation in just anyone's kitchen or garage.
Therefore, we chose to investigate ligase-independent cloning (LIC), a technique we believe can serve as a standard for BioBrick construction, in a way that is relatively easy to implement and that also lends itself to automation in the future. Our approach was based on a method described by [http://nar.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/18/20/6069 Aslanidis & de Jong (1990)].
Method
1.) Identify a Gene of Interest
2.) Amplify, using PCR primers that contain the BioBrick prefix (brown) & suffix (purple) as well as a LIC overhang sequence (pink).

|
3.) Obtain LIC plasmid (pSB_LIC; part [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K155000 K155000]).
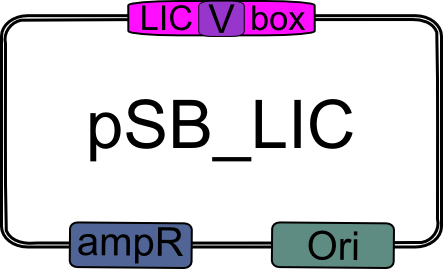
|
4.) Digest pSB_LIC with EcoRV.
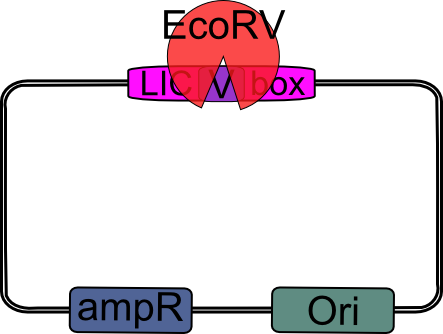
|
4.) Digest pSB_LIC with EcoRV.

|
Reference
Aslanidis, C. & de Jong P.J. (1990) “Ligation-independent cloning of PCR products (LIC-PCR).” Nucl. Acids Res. 18:20, 6069-6074.
Plasmid: [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K155000 K155000]
Main Page | Team | Project | Lab Notebook
 "
"