|
A literature search revealed two models of IPTG-induced expression through the Plac promoter. Both models assume constitutive expression of LacI. Before IPTG is added, a steady-state is reached comprising basal (leaky) expression of GFP.
In the simpler model (2) IPTG competes with free promoter for LacI binding, but does not itself bind to the LacI-promoter complex.
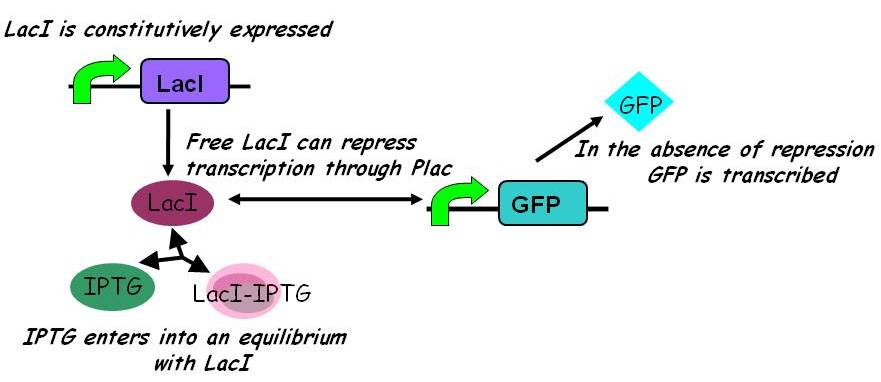
Assuming this model, all else equal, the steady-state concentration of free promoter and hence the steady-state concentration of GFP are independent of the initial concentration of IPTG. (See time evolution of GFP expression assuming different concentrations of IPTG are used for induction, right.)
ODEs
Simulation File
The pre-steady-state dynamic behaviour of the GFP concentration will differ with different initial concentrations of IPTG (but the steady-state behaviour will not). Hence, accurate data collection during the pre-steady-state phase is crucial for parameter estimation.
A more sophisticated model allows for interaction between IPTG and the promoter-LacI complex (3). IPTG can bind to the promoter-LacI complex to form IPTG-LacI and free promoter. This eases the repression by LacI and allows transcription of GFP.
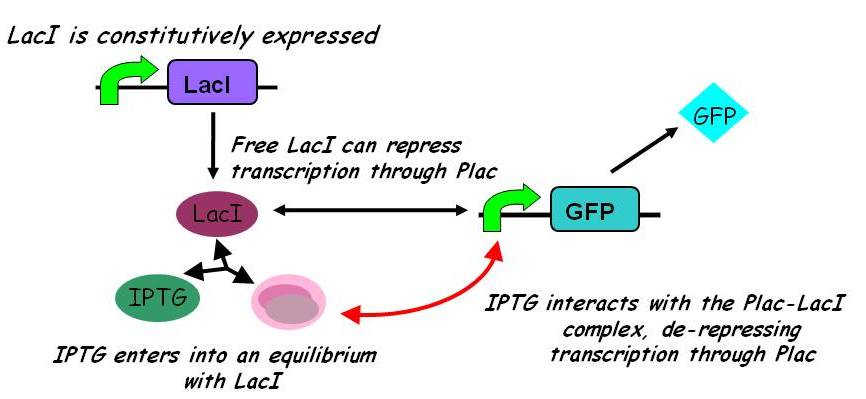
Under this model, the dynamic behaviour (whether or not [GFP] attains a maximum higher than its steady-state value) depends on the relative strengths of the kinetic constants describing the interactions underlying the model. Either way, all else equal the steady-state [GFP] will vary as a Hill-function dependent on the initial concentration of IPTG; this characteristic can be used to discriminate between the two models.
ODEs
Simulation File
>>> Details of equilibria and equations and qualitative discussion of parameter effects >>>
|