Team:Tsinghua/Project2
From 2008.igem.org
Ylzouyilong (Talk | contribs) (→Reference) |
Ylzouyilong (Talk | contribs) (→Reference) |
||
| Line 175: | Line 175: | ||
'''This literature introduced a method to release PHB granules from Escherichia coli.''' | '''This literature introduced a method to release PHB granules from Escherichia coli.''' | ||
| - | 4 Simultaneous Expression of Vitreoscilla Globin Gene and | + | 4 Simultaneous Expression of Vitreoscilla Globin Gene and Lytic Genes of Phage lambda Novel RecombinantEscherichia Coli Used for Production of PHB.YU Huimin,SHI Yue,YIN Jin,and SHEN Zhongyao.ChineseJ.ofChem.Eug,(4)407一411(2001) |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
'''This literature introduced phage lambda lytic gene into Escherichia coli strains.''' | '''This literature introduced phage lambda lytic gene into Escherichia coli strains.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | 5 Autoregulator Protein PhaR for Biosynthesis of Polyhydroxybutyrate [P(3HB)] Possibly Has Two Separate Domains That Bind to the Target DNA and P(3HB): Functional Mapping of Amino Acid Residues Responsible for DNA Binding.Miwa Yamada,Koichi Yamashita,Akiko Wakuda,Kazuyoshi Ichimura,Akira Maehara,Michihisa Maeda,and Seiichi Taguchi.JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Feb. 2007, p. 1118–1127 | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''This literature illustrates how PhaR works in the PHB synthesis regulation.''' | ||
Revision as of 04:52, 29 October 2008
PHA Project
DNA Template Resources: PhbCAB: PBHR68 Plasmid Lac I: PET28a CRE: PpPhaP: Ralstonia eutropha H16 genome PrPhaR: Ralstonia eutropha H16 genome SRRz: EGFP:
Primers:
(1) SRRz Primers
IGEM-ZouYLP-SRRZ-NcoI-for
5- ATCCATGGATGAAGATGCCAGAAAAACATGACCTGTTG-3
IGEM-ZouYLP-SRRZ-rev-in 5 - ACCCCGCCGAAGCGGGGTTTTTTTTTCTACTATCTGCACTGCTCATTAATA-3
IGEM-ZouYLP-SRRZ-BamHI-rev-out 5 -TATGGATCCAAAAAAAAACCCCGCCGAAGCGGGGTT-3
(2) IGEM-ZouYLP-PP-PhaP-NotI-for 5- TATGCGGCCGCTGTTTGTGCATTGCACAAAATCCA-3
IGEM-ZouYLP-PP-PhaP-HindIII-rev 5- CACCATGTCGACTTTCTCCTCTTTAAGCTTTCAGGCAGCCGTCGTCTTCTTTG-3
IGEM-ZouYLP-LacILVA-HindIII-for 5-TGCCTGAAAGCTTAAAGAGGAGAAAGTCGACATGGTGAATGTGAAACCAGTAAC-3
IGEM-ZouYLP-LacILVA-rev-in 5- AGCTACTAAAGCGTAGTTTTCGTCGTTTGCAGCCTGCCCGCTTTCCAGTCGGGAAACCT-3
IGEM-ZouYLP-LacILVA-rev-PstI-out 5- ATTGGACATGCGCGCTTTCTCCTCTTTCTGCAGTTATTAAGCTACTAAAGCGTAGTTTT-3
IGEM-ZouYLP-CreT7ter—PstI-for 5- TGCAGAAAGAGGAGAAAGCGCGCATGTCCAATTTACTGACCGTACACCAAAATT-3
IGEM-ZouYLP-CreT7ter-rev-in 5-AGCGGGGTTTTTTTTTCTACTAATCGCCATCTTCCAGCAG-3
IGEM-ZouYLP-CreT7ter-EcoRI-rev-out 5-ATGAATTCGAGCTCGAAAAAAAAACCCCGCCGAAGCGGGGTTTTTTTTTCTACTAAT-3
(3) IGEM-ZouYLP-PR-PhaR-NotI-for 5-ATGCGGCCGCAGTGCCTTGTTGGGCATAGAATCAGGGCAGCGGCGCAGC-3
IGEM-ZouYLP-PR-PhaR-NdeI-rev 5-ACGAAGTTATCATATGTTATTACTTCTTGTCCGGCTGGTTGAACGGGAACGTCCCGAAC-3
IGEM-ZouYLP-LRLacILP-for-in 5-TGCTATACGAAGTTATAAAGAGGAGAAACTCGAGATGGTGAATGTGAAACCAGTAACGT-3
IGEM-ZouYLP-LRLacILP-NdeI-for-out 5-ACAAGAAGTAATAACATATGATAACTTCGTATAATGTATGCTATACGAAGTTATAAAGA-3
IGEM-ZouYLP-LRLacILP-rev-in 5-TACGAAGTTATCTACTGCCCGCTTTCCAGTCGGGAAACCT-3
IGEM-ZouYLP-LRLacILP-KpnI-rev-out 5-ATGGTACCATAACTTCGTATAGCATACATTATACGAAGTTATCTACTGCCCGCTT-3
(4) EGFP IGEMZouYLP-EGFP-for-KoZg-for 5-ccatgggcagcaagggcgaggagctgttc-3
IGEMZouYLP-EGFP-rev-in 5-AAAAAAAAACCCCGCCGAAGCGGGGTTTTTTTTTCTATCACTTGTACAGCTCGTC-3
IGEMZouYLP-EGFP-rev-out 5-TTTTC GAGCTC GAATTC GGATCCAAAAAAAAACCCCGCCGAA-3
IGEMZouYLP-EGFP-KoZg-rev 5-TTTTCGAGCTCGAATTCGG-3
Designed Molecule
Plasmid constructs: 1 pUCPhbCAB
2 pACYC(lacI+) DuetSRRz
3 pACYC(lacI+) DuetEGFP
4 pACYC(lacI-) DuetSRRz
5 pACYC(lacI-) DuetEGFP
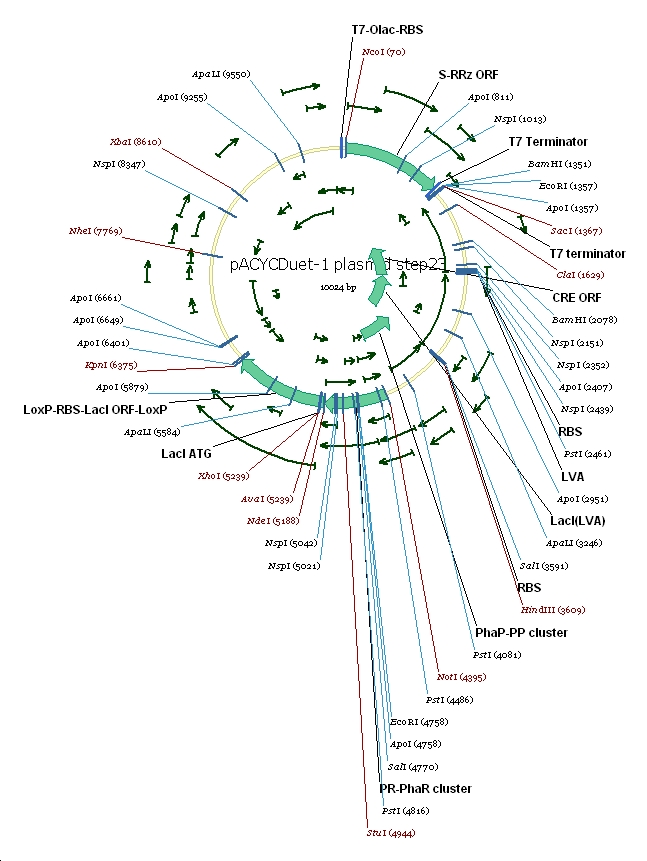
6 pACYC(LacI-)DuetSRRzPpPhaPLacILVACret7terPrPhaRLoxPLacILoxP
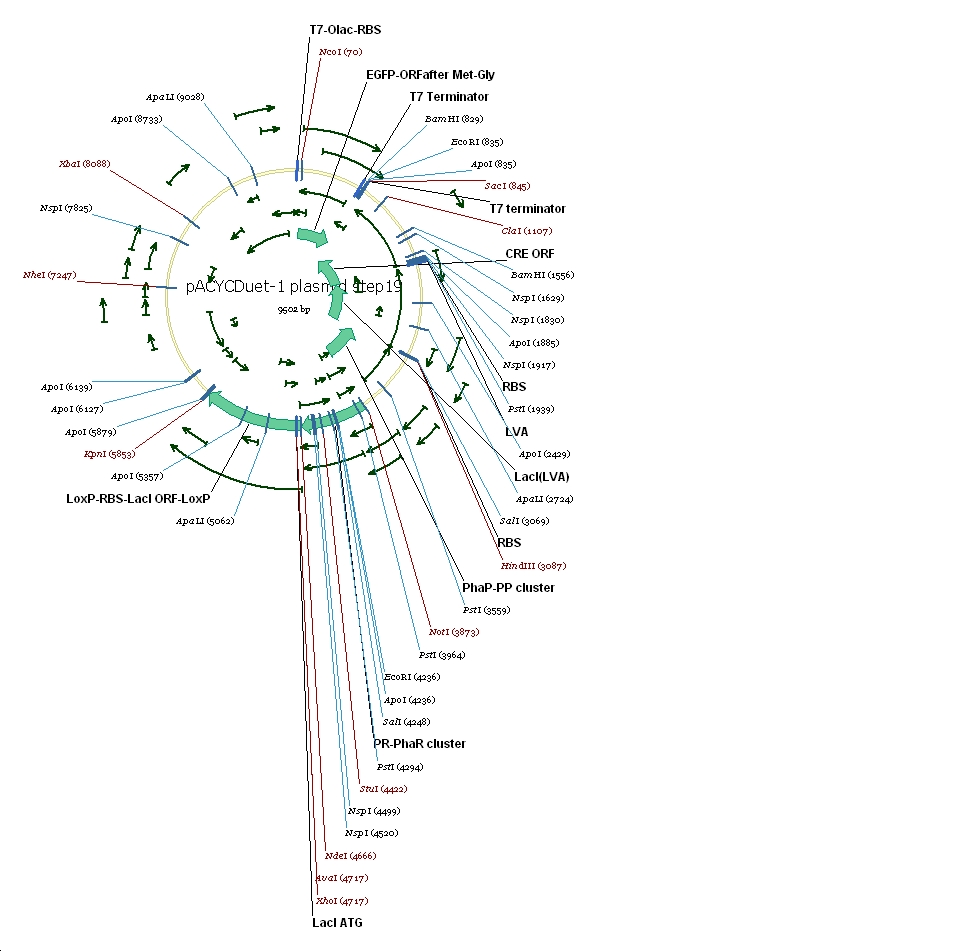
7 pACYC(LacI-)DuetEGFPPpPhaPLacILVACret7terPrPhaRLoxPLacILoxP
Cloning Strategy: (1) Fragment Preparation: SRRz: PCR with primer SRRZ-NcoI-for and SRRZ-rev-in;
Purify the product and run PCR with primer SRRZ-NcoI-for and primer SRRZ-BamHI-rev-out;
EGFP: PCR with primer EGFP-for-KoZg-for and EGFP-rev-in;
Purify the product and run PCR with primer EGFP-for-KoZg-for and primer EGFP-rev-out;
PpPhaP: PCR with primer PP-PhaP-NotI-for and PP-PhaP-HindIII-rev;
LacI(LVA): PCR with primer LacILVA-HindIII-for and LacILVA-rev-in;
Purify the product and run PCR with primer LacILVA-HindIII-for and primer LacILVA-rev-PstI-out;
CRE(T7ter): PCR with primer CreT7ter—PstI-for and CreT7ter-rev-in
Purify the product and run PCR with primer CreT7ter—PstI-for and CreT7ter-EcoRI-rev-out;
PrPhaR: PCR with primer PR-PhaR-NotI-for and PR-PhaR-NdeI-rev;
LoxPLacILoxP: PCR with primer LRLacILP-for-in and LRLacILP-rev-in
Purify the product and run PCR with primer LRLacILP-NdeI-for-out and primer LRLacILP-KpnI-rev-out.
(2) Fragment Fusion Fuse LacI(LVA) and CRE(T7ter) together and amplify with the primer LacILVA-HindIII-for and CreT7ter-EcoRI-rev-out; Fuse PrPhaR and LoxPLacILoxP together and amplify with the Primer PR-PhaR-NotI-for and LRLacILP-KpnI-rev-out.
We’ve tried to fuse more by PCR, but failed.
(3) Vector preparation We choose pACYCDuet-1 as our second vector while PhbCAB operon is cloned into PUC18. Since lacI is one of the elements we also used in our own system, we knocked out the lacI coding region in pACYCDuet-1 successfully. (4) Cut and Insert The restriction enzymes are chosen as following: Fragment Enzyme A Enzyme B SRRz/EGFP NcoI BamHI PpPhaP NotI HindIII LacI(LVA)Cre(T7ter) HindIII SacI PrPhaRLoxPLacILoxP NotI KpnI
Reference
1 A sensitive, viable-colony staining method using Nile red for direct screening of bacteria that accumulate polyhydroxyalkanoic acids and other lipid storage compounds. Patricia Spiekermann · Bernd H. A. Rehm · Rainer Kalscheuer · Dirk Baumeister · Alexander Steinbüchel. Arch Microbiol (1999) 171:73–80
This literature explains how pBHR68 works and how PHA granules are detected.
2 Construction and Selection of the Novel Recombinant Escherichia cob Strain for Poly(Hydroxybutyrate) Production.HUIMIN YU,JIN YIN,HONGQI LI,SHENGLI YANG,AND ZHONGYAO. JOURNALOF BIOSCIENCEAND BIOENGWEERING Vol. 89, No. 4, 307-311. 2000
This literature indicates how PHA sysnthesis is realized in Escherichia coli.
3 Spontaneous liberation of intracellular polyhydroxybutyrate granules in Escherichia coli.Il Lae Jung, Ki Heon Phyo, Kug Chan Kim, Hyo Kook Park, In Gyu Kim.Research in Microbiology 156 (2005) 865–873
This literature introduced a method to release PHB granules from Escherichia coli.
4 Simultaneous Expression of Vitreoscilla Globin Gene and Lytic Genes of Phage lambda Novel RecombinantEscherichia Coli Used for Production of PHB.YU Huimin,SHI Yue,YIN Jin,and SHEN Zhongyao.ChineseJ.ofChem.Eug,(4)407一411(2001)
This literature introduced phage lambda lytic gene into Escherichia coli strains.
5 Autoregulator Protein PhaR for Biosynthesis of Polyhydroxybutyrate [P(3HB)] Possibly Has Two Separate Domains That Bind to the Target DNA and P(3HB): Functional Mapping of Amino Acid Residues Responsible for DNA Binding.Miwa Yamada,Koichi Yamashita,Akiko Wakuda,Kazuyoshi Ichimura,Akira Maehara,Michihisa Maeda,and Seiichi Taguchi.JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Feb. 2007, p. 1118–1127
This literature illustrates how PhaR works in the PHB synthesis regulation.
 "
"