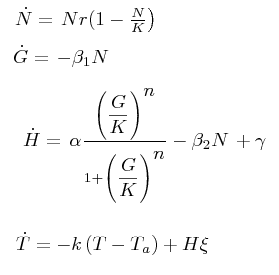Team:Valencia/Project/Modeling
From 2008.igem.org
(→Theoretical evaluation of the idea) |
(→Modeling the oxidative phosphorylation pathway) |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
==Modeling the oxidative phosphorylation pathway== | ==Modeling the oxidative phosphorylation pathway== | ||
| - | The energy, in form of ATP, necessary for all the cellular processes, is acquired mainly by the oxidative phosphorylation pathway. This pathway is wide-spread through the tree of life because it is a highly efficient way of releasing energy, compared to alternative fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis. In eukaryotic organisms, the reaction takes place in the mitochondria where the electron transport | + | The energy, in form of ATP, necessary for all the cellular processes, is acquired mainly by the oxidative phosphorylation pathway. This pathway is wide-spread through the tree of life because it is a highly efficient way of releasing energy, compared to alternative fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis. In eukaryotic organisms, the reaction takes place in the mitochondria where the electron transport chain catalyzes the electron flow from NADH and FADH <sub>2</sub> to oxygen (becoming reduced to water). This exergonic reaction is coupled with the proton pumping from the matrix through the inner mitochondrial membrane, which generates an electroosmotic gradient used for ATP synthesis. This mechanism is called chemiosmosis, proposed in 1961 by Peter Mitchell. |
Revision as of 11:28, 16 September 2008
Contents |
Oxidative phosphorylation model coupled with thermogenine expression
Our project consist of implementing a controlled heating system inside Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In order to obtain this we are going to use a mitocondrial membrane protein known as thermogenin used by mamalians cells to increase its temperature.
The working principle of thermogenin is based on the respiratory electron transport chain. The way in which the thermogenin increases the temperature of the system can be described approximately as follows: It produces a hole on the mitocondrial membrane which makes difficult the production of a proton gradient in the membrane. The release of the mitocondrial proton gradient increases the temperature. (ficar referencia)
In order to describe the system three complementary models have been developed :
- Black box model of the temperature increase by the thermogenin.
- Detailed model of the respiratory electron transport chain.
- Regulatory model of the thermogenin expresion.
Theoretical evaluation of the idea
To evaluate the reliability of the idea we are going to estimate the maximal attainable temperature (obviously, the minimal temperature value is the corresponding to the culture conditions). This means to estimate the maximum heat production. The maximal temperature can be determined by supposing that the proton motrive force is used solely in heat production mediated by thermogenine. The following calculations were made taking into account this assumption.
To calculate the energy produced per proton dissipated through the thermogenine we used the published turnover number (the maximum number of molecules of substrate that an enzyme can convert to product per catalytic site per unit time ) of ATP synthase( Abrams et al 1974) for Geobacillus stearothermophilus an estimation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae real value.
To calculate the energy produced per proton dissipated through the thermogenine we used the published rate of ATP flow as an estimation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae real value.
If ATP synthase needs four protons to produce one molecule of ATP, then we can easily calculate the proton flow through complex V.
The free energy associated to a single proton being dissipated through the ATP synthase is 20 Kj/mol. Balancing the units we get the energy dissipated per proton:
The energy flow is calculated by multiplying both figures and adjusting the result to the proper units:
Black box model of the temperature increase by the thermogenin
The black box model simulates the temperature evolution of the system as a function of the grow rate, galactose concentration and thermogenin expresion. We assume that the system can be reproduced by the following system of equations:
where:
- first equation: growth of the culture
- second equation: Galactose evolution in time. Galactose is the metabolite which induces the thermogenin expresion.
- third equation: Thermogenin concentration level.
- Fourth equation: Temperature evolution. the first term of the equation represents the losses to the ambient of the calorimeter and the second one the temperature increase as a consequence of the thermogenin expresion. This second term depens on the number of cells and also on other parameters like the number of mitocondria per cell and the like.
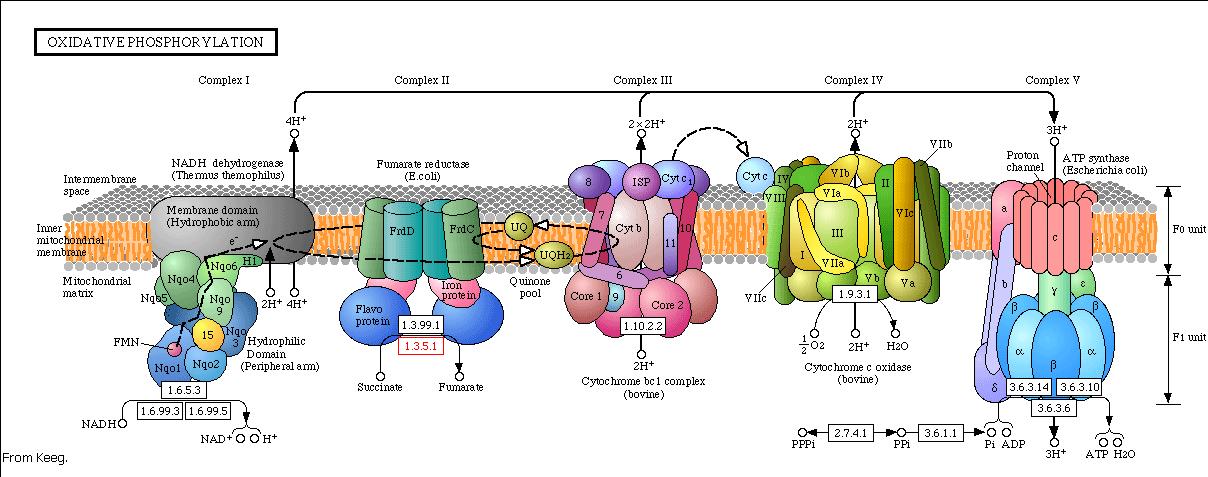
Modeling the oxidative phosphorylation pathway
The energy, in form of ATP, necessary for all the cellular processes, is acquired mainly by the oxidative phosphorylation pathway. This pathway is wide-spread through the tree of life because it is a highly efficient way of releasing energy, compared to alternative fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis. In eukaryotic organisms, the reaction takes place in the mitochondria where the electron transport chain catalyzes the electron flow from NADH and FADH 2 to oxygen (becoming reduced to water). This exergonic reaction is coupled with the proton pumping from the matrix through the inner mitochondrial membrane, which generates an electroosmotic gradient used for ATP synthesis. This mechanism is called chemiosmosis, proposed in 1961 by Peter Mitchell.
|
With this model we want to evaluate the effects of the UCP1 in the ATP synthesis. We will take into account general issues about the electron transport chain as well as the particularities of our yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We will have to consider the fermentative pathways presents for further applicability of the model.
References
Abrams, A.; Smith, J.B. (1974); The Enzymes, 3rd Ed. (Boyer, P.D., ed.) Bacterial membrane ATPase 10, 395-429.
 "
"