Team:BrownTwo/Implementation/syntf
From 2008.igem.org
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
=The Biofusion Standard= | =The Biofusion Standard= | ||
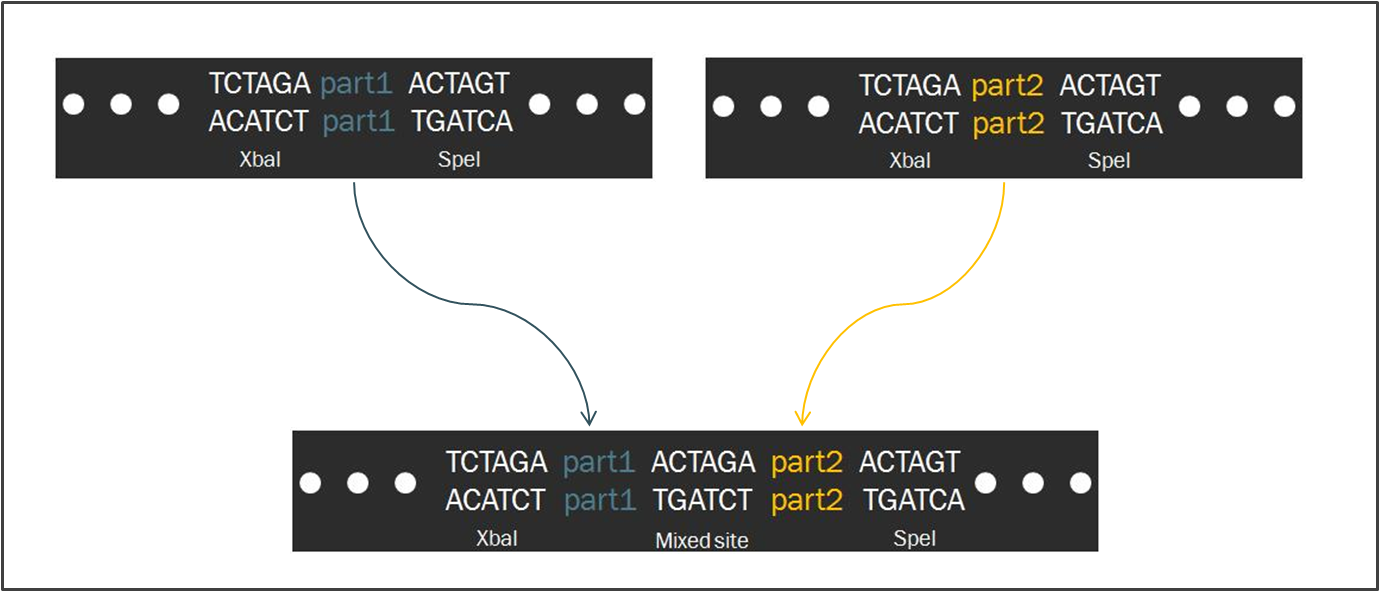
| - | Compared to other fields in biology, synthetic biology devotes a considerable amount of attention towards the standardization of parts and of practice. The inspiration for such a focus stems from similar concepts in engineering, which depends upon well-characterized systems for design. Indeed, this | + | Compared to other fields in biology, synthetic biology devotes a considerable amount of attention towards the standardization of parts and of practice. The inspiration for such a focus stems from similar concepts in engineering, which depends upon well-characterized systems for the design of complex systems that behave reliably according to predictions. Indeed, as readers of this wiki may be well aware, the iGEM competition focuses on the use of the Biobrick standard, which is an idempotent approach to cloning recombinant DNA. The Biobrick standard constitutes a conserved sequence of sites that envelop a genetic part, whether it be a coding gene, a promoter, or some other functional piece of DNA. |
| - | + | Our synthetic transcription factors were designed according to a | |
| - | [[image:Biofusion.jpg|center| | + | The differences between the two standards are minimal. In fact, the method of ligating two parts proves to be exactly the same, regardless of whether the part is destined to become a prefix or a suffix to another. Such a result is a consequence of the fact that the two standards share a similar However, |
| + | |||
| + | [[image:Biobrickin'.jpg|center|900px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[image:Biofusion.jpg|center|900px]] | ||
Revision as of 17:42, 29 October 2008
Transcription factorsThe syn. trans. factor system designed by caroline & david. cite memory.
The laboratory of Dr. Pamela Silver at Harvard developed synthetic transcription factors for the construction of a novel “memory device” in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. While the details of this device are not essential to understanding our own gene network, it is important to discuss the significance of these transcription factors to our design. A transcription factor is composed of a binding domain, which targets the protein either an activation domain or a repression domain, which Transcription factors are composed of a standard activation or repression domain linked to a variable binding domain. The binding domain is chosen such that it matches. Other features of these . A handful of these parts were available in the Registry, but we found it necessary to
The Biofusion StandardCompared to other fields in biology, synthetic biology devotes a considerable amount of attention towards the standardization of parts and of practice. The inspiration for such a focus stems from similar concepts in engineering, which depends upon well-characterized systems for the design of complex systems that behave reliably according to predictions. Indeed, as readers of this wiki may be well aware, the iGEM competition focuses on the use of the Biobrick standard, which is an idempotent approach to cloning recombinant DNA. The Biobrick standard constitutes a conserved sequence of sites that envelop a genetic part, whether it be a coding gene, a promoter, or some other functional piece of DNA. Our synthetic transcription factors were designed according to a The differences between the two standards are minimal. In fact, the method of ligating two parts proves to be exactly the same, regardless of whether the part is destined to become a prefix or a suffix to another. Such a result is a consequence of the fact that the two standards share a similar However,
Stipulation: If G is a transcription factor that is known to auto-regulate, one will have to alter the modeling to account for this situation. modifications to current scheme:
Possible further modifications to these transcription factors include the use of different regulation domains, Involves the consideration of multiple binding sites |
 "
"