Team:BrownTwo/Limiter/network
From 2008.igem.org
The Genetic LimiterTo build a genetic limiter, we employ the tools of a synthetic biologist and cybernetician. Defined by Dr. Norbert Wiener in 1948, cybernetics is the study of systems of regulation and control. Regulatory elements can be studied and modeled in the abstract, whether their manifestation is mechanical, electrical biological, natural or synthetic. Our limiter circuit is an example of a complex device built from smaller parts whose internal complexity can be abstracted away in the mode of the synthetic biologist. We began by devising the logical control network that results in threshold regulation of an element outside of its boundaries.
Leading to the limiter
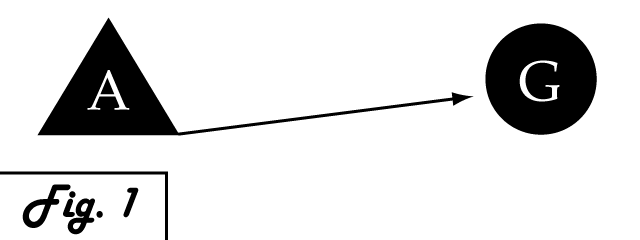
Consider a gene of interest (G) for which one inducing transcription factor (A) is known (Fig. 1). In the presence of unnaturally-heightened levels of inducer A, our gene will experience excessive activation. A logical method for addressing this problem would be to introduce an inhibitor for the gene of interest to attenuate its presence or activity. Traditional pharmaceutical interventions either block the activity of the protein encoded by gene G, causing interference on the level of protein interactions, or make changes upstream then can arrest expression of gene G. One concern that arises with the use of a chemical input is that, especially in the case of multi-cellular organisms, this often has diffuse, unspecified, and often undesirable effects. Drugs that are administered to biological systems in a therapeutic context particularly require an understanding of the intricate balance between efficacy and toxicity. An alternative may be to directly reduce the expression of gene G with an introduced transcriptional repressor. Although a genetically-based inhibitor is more difficult to implement, such a genetic tool would afford a great deal of specificity to the system, directly repressing only the gene of interest.
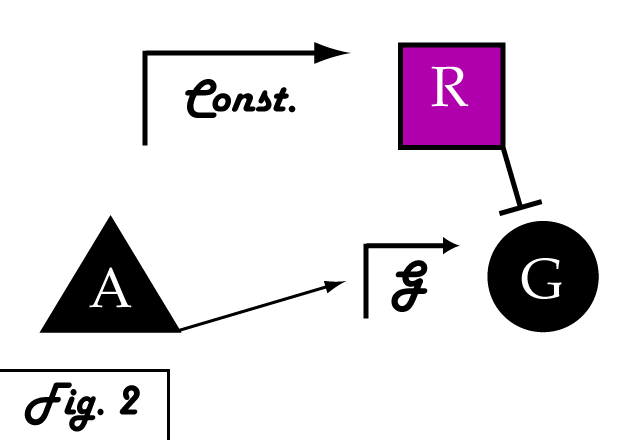
If we were to introduce a repressing transcription factor (R) driven by a constitutive promoter (Fig. 2), we would see a constant amount of repression of G, independent of its level of activation. We might face the issue that increased expression of inducer A would surpass the repressor's ability to oppose gene G's activation. Thus, instead of a constitutive promoter, we could ensure that the repressor for the gene of interest is under the control of a promoter that also takes the same inducer A as an input (Fig. 3). This would mean that the amount of repressor expressed in the system scales with the amount of inducer, eliminating the possibility of our repressor being swamped by incresing induction of G's transcription. However, both of these constructs have a critical flaw- they would always repress gene G, even when and where its expression is at a normal, healthy level. Repressing gene G completely could cause problems by eliminating the possibility of gene G functioning normally.
To keep our repressor from interfering with normal levels of transcription, we need a way to turn off its activity when activation of G falls below a certain level, the threshold of healthy expression.
Bistability & FeedbackA bistable switch is a simple circuit in which, depending upon the nature or quantity of the input, two stable outcomes are possible. Such a switch can afford a circuit the ability to alternate between two modes of activity in response to varying levels of input. In one of the seminal publications in the field of synthetic biology, Gardner, Canton, and Collins of Boston University developed a genetic bistable switch [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10659857] capable of switching between two distinct output states at a threshold level of input to the system.
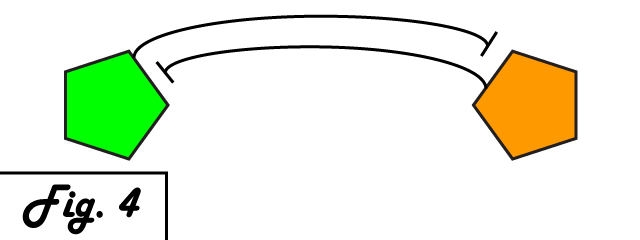
The mechanism of bistability in this genetic switch is mutual inhibition (Fig. 4). Two repressing transcription factors are put under the control of the promoter to which the other binds. Thus, whichever repressor has a slight edge net negative effect on the other's transcription will "win," repressing the other further and removing repression from its own transcription to create a feedback loop in which the system is stable. Either factor can exist in an induced state, and when it is, the other is repressed. The system can exist in two distinct, stable states.
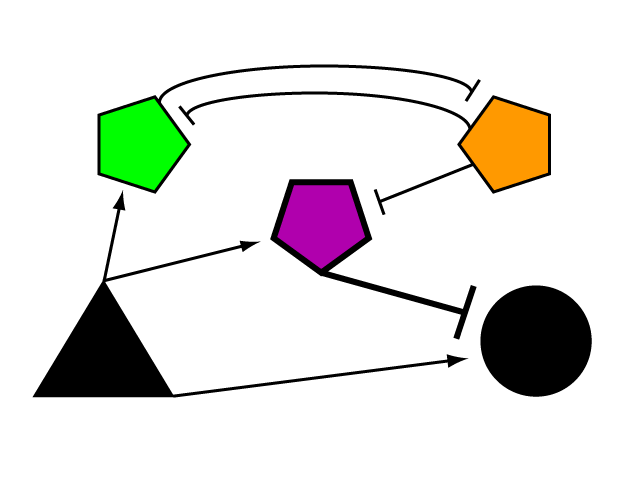
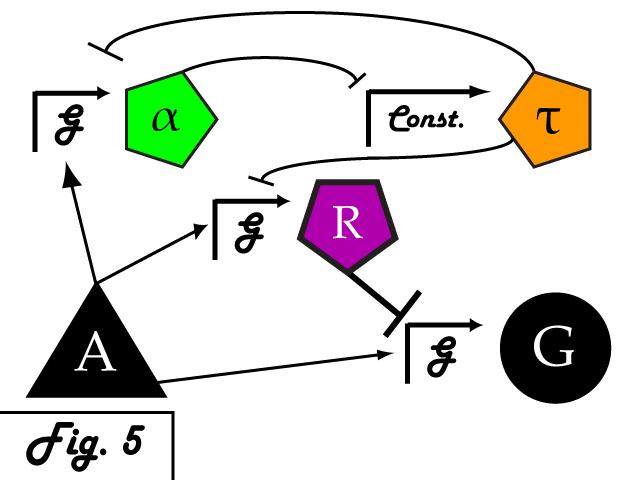
Bistable mutual inhibition between two repressors provides precisely the sort of threshold switching behavior that we would like to apply to our factor R. To set a threshold at which the system toggles between two stable states, we compare the expression induced by A on promoter G to a constitutive promoter by putting a repressor under the control of each (alpha and tau, respectively) and setting them in mutual inhibition.
Where A induces a level of expression below that of the constitutive promoter, tau represses alpha, is expressed at a stable level, and represses R as well. In this manner, the activity of R is switched off when G's expression is below the defined threshold. Where high levels of A cause G to be overexpressed, it induces alpha as well, repressing tau and allowing R to bring the expression of G back down to a normal level. In a possible end-use of this limiter network, the gene we wish to limit "G" and its activating transcription factor "A" are endogenous to the organism we wish to regulate. We introduce the transcription factor "R" to repress G, as well as the bistable pair alpha and tau that serve to regulate R's repression. As natural transcriptional control systems lack the modular specificity that our network requires, to implement our network we turn to a rationally-designed synthetic system of transcription factors.
Bistability in nature. |
 "
"