Team:Rice University/STRATEGY
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
StevensonT (Talk | contribs) (→Metabolic Parts) |
StevensonT (Talk | contribs) (→Metabolic Parts) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
=== Metabolic Parts === | === Metabolic Parts === | ||
[[Image:TAL.png|right|190px|thumb|[http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1T6P TAL] monomer.]] | [[Image:TAL.png|right|190px|thumb|[http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1T6P TAL] monomer.]] | ||
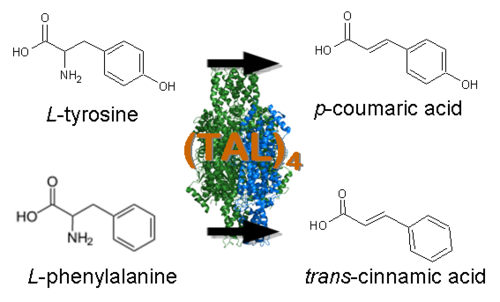
| - | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/viewer.fcgi?db=nucleotide&val=169745 Tyrosine Ammonia Lyase] (TAL) - Begins the resveratrol biosynthetic pathway by catalyzing the the conversion of L-tyrosine to ammonia and ''p''-coumaric acid. TAL also has activity as Phenylalanine Ammonia Lyase (PAL) via conversion of L-phenylalanine to ammonia and ''trans''-cinnamic acid. The [http://www.atcc.org/ATCCAdvancedCatalogSearch/ProductDetails/tabid/452/Default.aspx?ATCCNum=36575&Template=fungiYeast ''Rhodotorula glutinis''] TAL was selected specifically because of its relatively high TAL/PAL activity ratio, and its successful expression in ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' and ''Escherichia coli''. The ''p''-coumaric acid produced by TAL will later be converted to resveratrol, while the ''trans''-cinnamic acid will add a "floral" and "honey-like" bouquet to the beer. | + | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/viewer.fcgi?db=nucleotide&val=169745 Tyrosine Ammonia Lyase] (TAL) [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K122010 BBa_K122010] - Begins the resveratrol biosynthetic pathway by catalyzing the the conversion of L-tyrosine to ammonia and ''p''-coumaric acid. TAL also has activity as Phenylalanine Ammonia Lyase (PAL) via conversion of L-phenylalanine to ammonia and ''trans''-cinnamic acid. The [http://www.atcc.org/ATCCAdvancedCatalogSearch/ProductDetails/tabid/452/Default.aspx?ATCCNum=36575&Template=fungiYeast ''Rhodotorula glutinis''] TAL was selected specifically because of its relatively high TAL/PAL activity ratio, and its successful expression in ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' and ''Escherichia coli''. The ''p''-coumaric acid produced by TAL will later be converted to resveratrol, while the ''trans''-cinnamic acid will add a "floral" and "honey-like" bouquet to the beer. |
[[Image:TAL catalysis.png|left|500px]] | [[Image:TAL catalysis.png|left|500px]] | ||
Revision as of 21:14, 29 October 2008
| SUMMARY ::: BACKGROUND ::: STRATEGY ::: CONSTRUCTS ::: RESULTS ::: ONGOING WORK ::: OUR TEAM ::: NOTEBOOK ::: GALLERY
SUMMARY ::: BACKGROUND ::: STRATEGY ::: CONSTRUCTS ::: RESULTS ::: ONGOING WORK ::: OUR TEAM ::: NOTEBOOK ::: GALLERY |
 "
"