Team:Paris/Modeling/Esai
From 2008.igem.org
Mathematical Interpretation and Simulation of the Molecular Reactions
First, we consider the complexation phenomenon. We show, under the quasi steady-state hypothesis, how it leads to Non-Linear interactions like "Hill functions".
Then, we apply these results to the Molecular Reactions of our system. That gives all the theoretical calculation of the complexations, and finally, with the previous assumptions, we get the equations of the full system of ODEs.
Complexation Steady-State
The double triangle (><) is a symbol for complexations :
![]() means n1 molecules of FlhDC complexed with a pFliA promoter
means n1 molecules of FlhDC complexed with a pFliA promoter
|On the Example :
| How given amounts of FlhDC and FliA would produce FP1 ?
|
|* FlhDC and FliA bind to pFliL
|following "Hill functions" :
|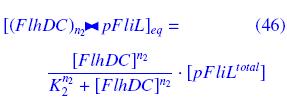 |
|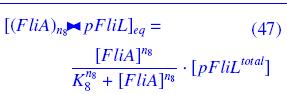
Equations of the Full System
The double triangle (><) is a symbol for complexations :
![]() means n1 molecules of FlhDC complexed with a pFliA promoter
means n1 molecules of FlhDC complexed with a pFliA promoter
|[On the Example :
]
|[[ How given amounts of FlhDC and FliA would produce FP1 ? ]]
|
|* FlhDC><pFliL and FliA><pFliL causes "production" of FP1, diluted along times :
|
| |the outlined parameters are necessary and enough to fully characterize ƒ5
|the outlined parameters are necessary and enough to fully characterize ƒ5
 "
"