Team:ETH Zurich/Modeling/Overview
From 2008.igem.org
m |
m (→Overview on the modelling framework) |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
==Overview on the modelling framework== | ==Overview on the modelling framework== | ||
| - | This page is meant to give an introduction to the the overall modelling framework we have constructed in order to asses feasibility analysis, temporal scale details and other parameter estimations that regard our project setup. As introduced in the [[Team:ETH_Zurich/Project/Overview|project overview section]], four main components can be identified in the | + | This page is meant to give an introduction to the the overall modelling framework we have constructed in order to asses feasibility analysis, temporal scale details and other parameter estimations that regard our project setup. As introduced in the [[Team:ETH_Zurich/Project/Overview|project overview section]], four main components can be identified in the devised mechanism. Accordingly, we divided the modelling framework in four modules that tack the relative problematics. |
<br> | <br> | ||
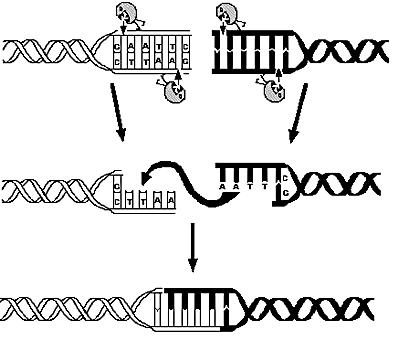
The first module is concerned with the analysis of restriction enzymes and their cutting pattern on E.Coli genome, the second module predict the cell's response to the selection pressure and the forced genome reduction from a system point of view (that is, using a genome scale model), the third module addresses issues related to the sensitivity and setting of the chemostat mechanism, the fourth and final module presents the mathematic model of the genetic switch circuit used to control the restriction enzymes expression. | The first module is concerned with the analysis of restriction enzymes and their cutting pattern on E.Coli genome, the second module predict the cell's response to the selection pressure and the forced genome reduction from a system point of view (that is, using a genome scale model), the third module addresses issues related to the sensitivity and setting of the chemostat mechanism, the fourth and final module presents the mathematic model of the genetic switch circuit used to control the restriction enzymes expression. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
In the table below, you can find a bird-eye view on the four modules, with the most important aspects highlighted. Since we believe that a model is useful only when it answers specific and well-posed questions, this is the first aspect we report in the summary view. Second we briefly report about the modelling method applied. As last, we summarize the results we obtained. | In the table below, you can find a bird-eye view on the four modules, with the most important aspects highlighted. Since we believe that a model is useful only when it answers specific and well-posed questions, this is the first aspect we report in the summary view. Second we briefly report about the modelling method applied. As last, we summarize the results we obtained. | ||
| - | By clicking on each module's title, you can browse the specific module pages containing all the detailed information, such as plots, modelling | + | By clicking on each module's title, you can browse the specific module pages containing all the detailed information, such as plots, modelling assumptions and data sources. It is as well possible to download all the data and code (MATLAB source) that we wrote and used in order to generate the results. |
{| border="1" | {| border="1" | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
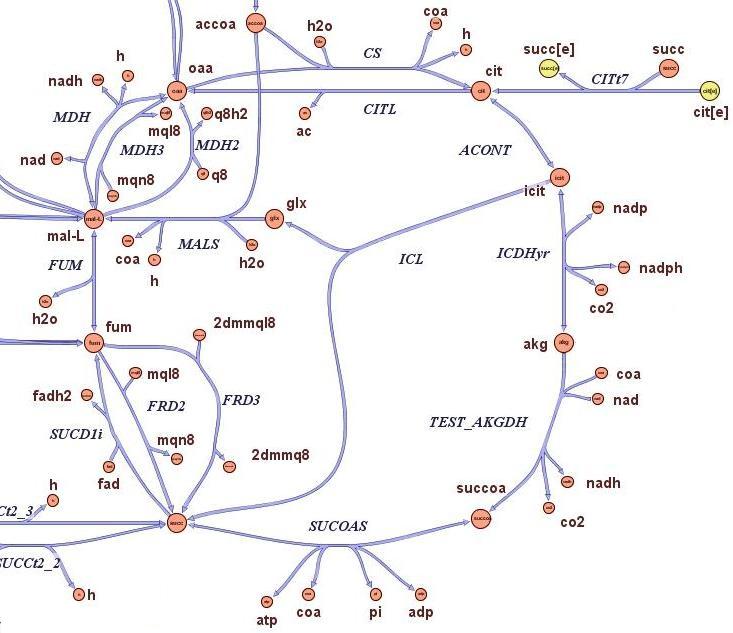
The state-of-the-art genome scale model for E.Coli iAF1260 (1260 genes included) was modified in order to account for thymidine auxotrophycity, thymidine uptaking limitation, genome reduction and growth on different medium. Stochastic algorithm and flux balance analysis were applied to predict growth rates.<br><br> | The state-of-the-art genome scale model for E.Coli iAF1260 (1260 genes included) was modified in order to account for thymidine auxotrophycity, thymidine uptaking limitation, genome reduction and growth on different medium. Stochastic algorithm and flux balance analysis were applied to predict growth rates.<br><br> | ||
'''Results:''' <br> | '''Results:''' <br> | ||
| - | It is indeed possible to select reduced genome strains using thymidine limitation. The quantification shows that the method is at the border line with the sensitivity of chemostat machinery setup. Predictions shows the possibility of reducing 4% of genes for a minimal medium growing strains and 8% of | + | It is indeed possible to select reduced genome strains using thymidine limitation. The quantification shows that the method is at the border line with the sensitivity of chemostat machinery setup. Predictions shows the possibility of reducing 4% of genes for a minimal medium growing strains and 8% of genes for rich medium growing strains.<br><br> |
</div> | </div> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
'''Method:''' <br> | '''Method:''' <br> | ||
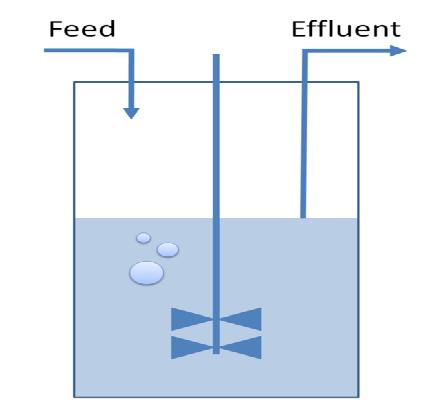
| - | A classical chemostat model using Ordinary Differential Equations was constructed and | + | A classical chemostat model using Ordinary Differential Equations was constructed and analyzed in terms of sensitivity analysis and simulation of realistic data.<br><br> |
'''Results:''' <br> | '''Results:''' <br> | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
* What are the temporal constrains for the device to be used in the selection scenario?<br><br> | * What are the temporal constrains for the device to be used in the selection scenario?<br><br> | ||
'''Method:''' <br> | '''Method:''' <br> | ||
| - | A novel transcriptional circuit able to sense a start and stop signal and control a pulse of restriction enzyme was designed and | + | A novel transcriptional circuit able to sense a start and stop signal and control a pulse of restriction enzyme was designed and analyzed using Ordinary Differential Equations.<br> <br> |
'''Results:''' <br> | '''Results:''' <br> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 16:32, 19 October 2008
Overview on the modelling frameworkThis page is meant to give an introduction to the the overall modelling framework we have constructed in order to asses feasibility analysis, temporal scale details and other parameter estimations that regard our project setup. As introduced in the project overview section, four main components can be identified in the devised mechanism. Accordingly, we divided the modelling framework in four modules that tack the relative problematics.
|
 "
"