From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
|
|
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown) |
| Line 16: |
Line 16: |
| | |width=50px| | | |width=50px| |
| | |width=700px| | | |width=700px| |
| - | *Different biomacromolecules have different bioactivities due to their different physical and chemical characters.The molecular weight of the biomacromolecule plays an essential role. If we can obtain a biomacromolecule with homogeneous molecular weight with some methods, this would dramatically increase our ability to manipulate the biomacromolecule structure and function. Our aim is to design a device which can synthesize a biomacromolecule with homogeneous molecular weight in a fixed time controlled by the concentration of the lactose. During that time, different enzymes are expressed alternatively with different operators critically modulation. Then with the catalysis of the enzyme, a biomacromolecule which has a homogeneous molecular weight is synthesized. As a result, we can further study the relationship between the structure and the function of the biomacromolecule. | + | *In glycobiology, wide ranges of molecular weight of polysaccharide often lead to obstacles to study their structure and function. More over, polysaccharide would present various function with different molecular weight. How to obtain polysaccharide with the certain molecular weight is an unsolved problem. |
| - | |width=300px align=right|示意图 | + | *In our project, we intend to design a device which composed of a bio-timer and alternatively expressed two glycosyltransferases. The timer could be controlled by the concentration of the inducer, and the glycosyltransferase are in charge of synthesizing the polysaccharide. As a result, the molecular weight of polysaccharide could be controlled by concentration of the inducer. By exchanging glycosyltransferase, this device would provide a useful tool to obtain different polysaccharide with certain molecular weight. |
| | + | |[[image:cpu-project2.jpg|300px]] |
| | |} | | |} |
| | | | |
| | == <font color=#3d5bb1 size=6>'''R'''</font>'''esults ''' == | | == <font color=#3d5bb1 size=6>'''R'''</font>'''esults ''' == |
Latest revision as of 02:31, 28 October 2008
Project 1: Adding new notes to the song of life
|
|
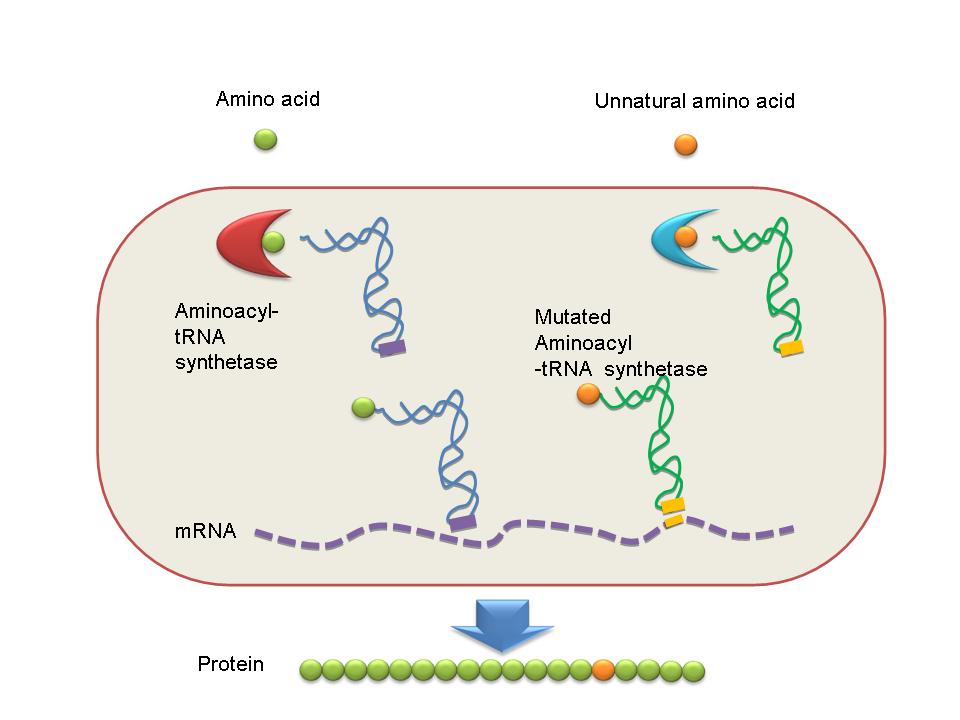
- The word protein comes from the Greek word πρώτα ("prota"), meaning "of primary importance." They are the chief actors within the cell, said to be carrying out the duties specified by the information encoded in genes. If we regard life as a beautiful song, proteins, of course, are the most important strains of this song.
- Proteins in nature are usually composed of 20 “standard” amino acids. They are basic notes in life songs. However, as for people who are interested in synthetic biology, 20 “standard” amino acids are not enough. Could we insert some unnatural notes to write a new song apart from natural “bio-parts”?
- In our project, we designed a novel device by which we could insert different unnatural amino acids into a certain site in target protein expressed in E coli. Of course these unnatural amino acids would bring some new characteristics of the target protein.
| 
|
Project 2: Customizing a biomacromolecule
|
|
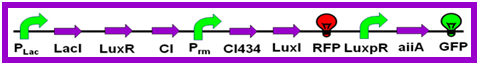
- In glycobiology, wide ranges of molecular weight of polysaccharide often lead to obstacles to study their structure and function. More over, polysaccharide would present various function with different molecular weight. How to obtain polysaccharide with the certain molecular weight is an unsolved problem.
- In our project, we intend to design a device which composed of a bio-timer and alternatively expressed two glycosyltransferases. The timer could be controlled by the concentration of the inducer, and the glycosyltransferase are in charge of synthesizing the polysaccharide. As a result, the molecular weight of polysaccharide could be controlled by concentration of the inducer. By exchanging glycosyltransferase, this device would provide a useful tool to obtain different polysaccharide with certain molecular weight.
| 
|
Results







 "
"
