Team:Freiburg Transfection
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | <h3>''' | + | <h3>'''Testing the transfection protocol'''</h3> |
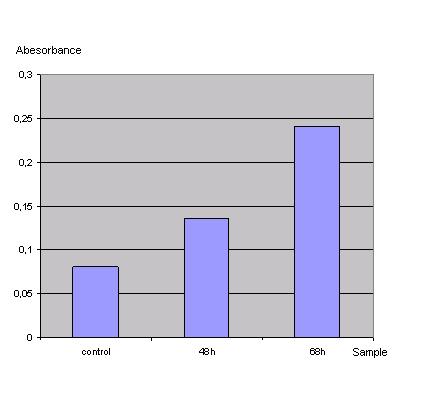
In order to check if the transfection protocol is suitable to transfect 293T cells a 'test'transfection with a lac z gene was done and the β-galactosidase was detected with an ONPG test.<br> | In order to check if the transfection protocol is suitable to transfect 293T cells a 'test'transfection with a lac z gene was done and the β-galactosidase was detected with an ONPG test.<br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
ONPG-assay: <br> | ONPG-assay: <br> | ||
<br>[[Image:FreiGEMTable3onpg.JPG]]<br> | <br>[[Image:FreiGEMTable3onpg.JPG]]<br> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
Control was done with untransfected cells using the same procedure.<br> | Control was done with untransfected cells using the same procedure.<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | <h3>''' | + | <h3>'''Testing the transfectionvector-CMV promoter construct'''</h3> |
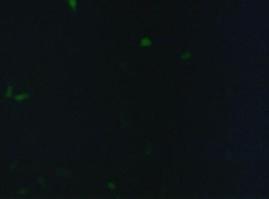
To test the functionality of the transfectionvector and the CMV-promoter, CFP and YFP was cloned behind the promoter and the plasmid was brought into 293T cells.<br> | To test the functionality of the transfectionvector and the CMV-promoter, CFP and YFP was cloned behind the promoter and the plasmid was brought into 293T cells.<br> | ||
The transfected cells show fluorescence by excitation of 510-520nm while the untransfected remain dark at this wavelength <br> | The transfected cells show fluorescence by excitation of 510-520nm while the untransfected remain dark at this wavelength <br> | ||
| Line 23: | Line 24: | ||
| - | <h3>''' | + | <h3>'''Localization at the cell membrane'''</h3> |
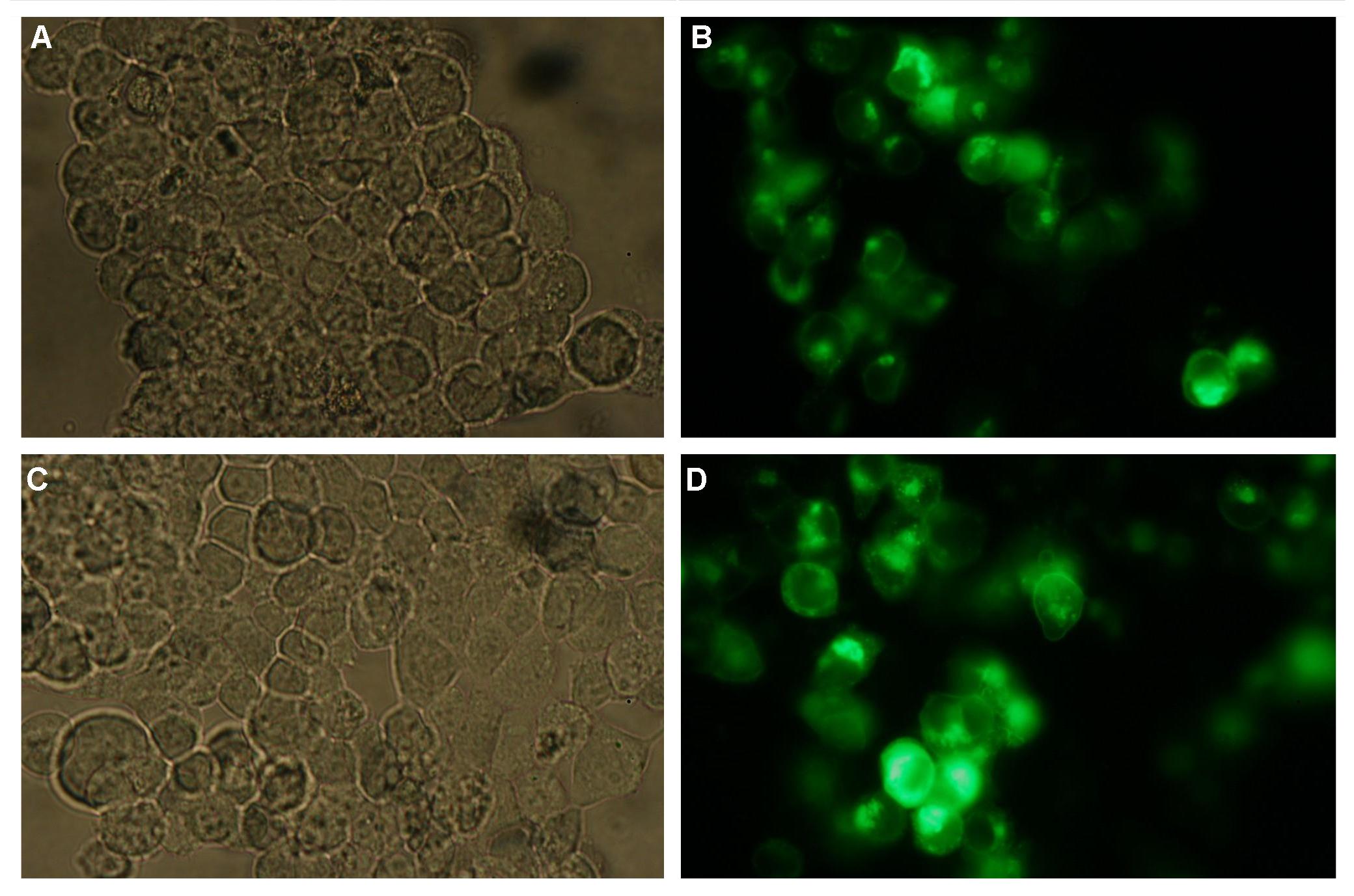
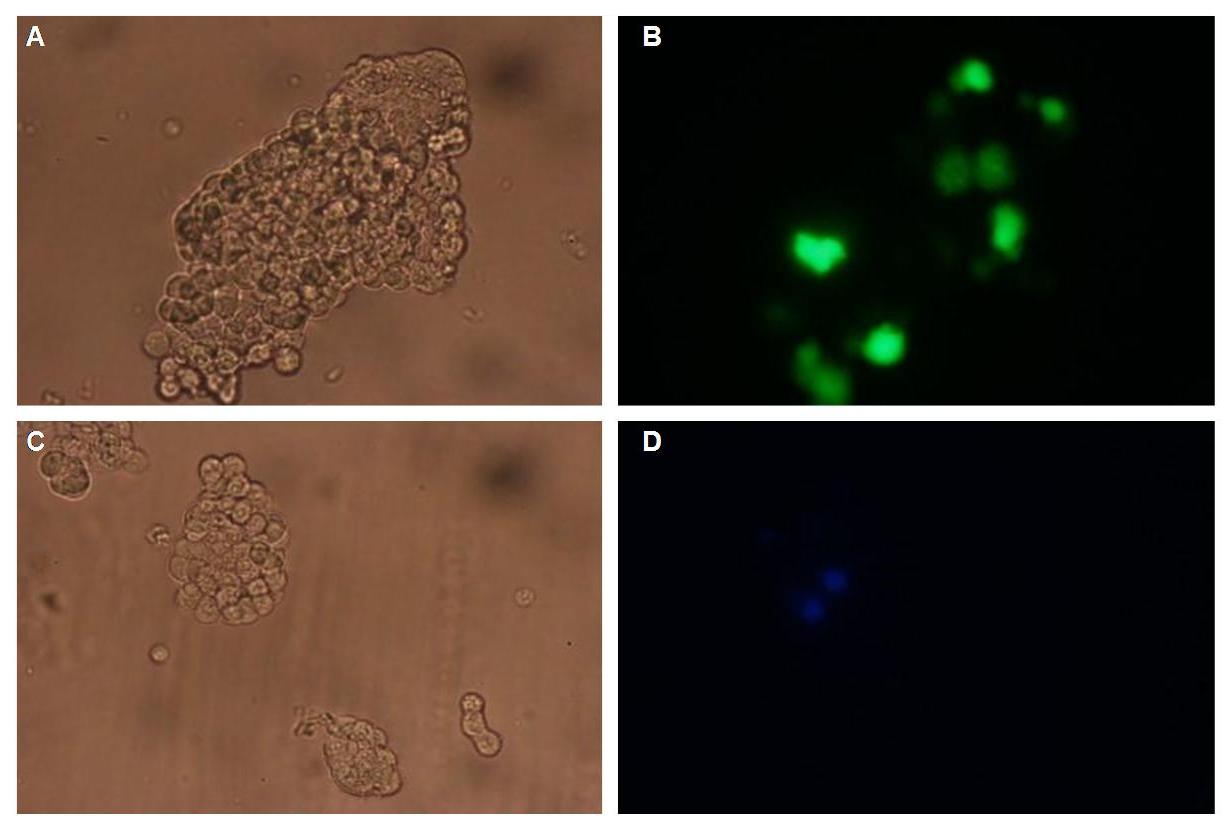
To show the localization of the constructs at the cell membrane transfection of the construct signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-betaLactamase1-YFP was performed.<br> | To show the localization of the constructs at the cell membrane transfection of the construct signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-betaLactamase1-YFP was performed.<br> | ||
Figure 1_Transfection shows the configuration of the construct. Lipocalin, the fluorescein binding Anticalin, exhibits the extracellular part of the construct. The transmembrane region is appropriate to that of the EGF-receptor erbb1. Split-beta-Lactamase, the intracellular part is labeled to the yellow fluorescent protein to detect membrane localization.<br> | Figure 1_Transfection shows the configuration of the construct. Lipocalin, the fluorescein binding Anticalin, exhibits the extracellular part of the construct. The transmembrane region is appropriate to that of the EGF-receptor erbb1. Split-beta-Lactamase, the intracellular part is labeled to the yellow fluorescent protein to detect membrane localization.<br> | ||
| Line 42: | Line 43: | ||
'''Figure 3_Transfection'''<br> | '''Figure 3_Transfection'''<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | <h3>''' | + | <h3>'''Double transfections with Splitfluorophor-/Splitenzyme-constructs'''</h3> |
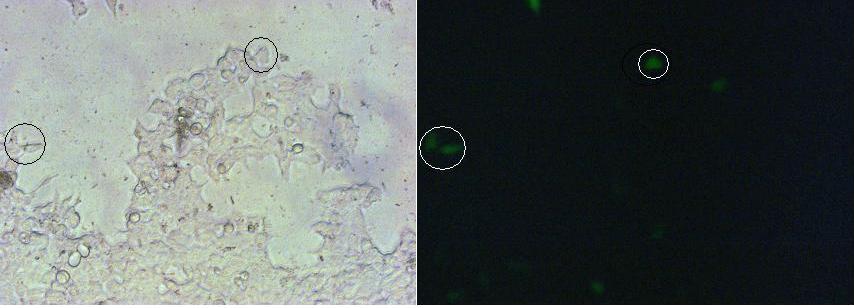
On Figure 4_Transfection the structures of the signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-nCFP and signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-fluolinker-cCFP are visible (exemplary for the Splitfluorophore-/Splitenzyme-constructs). The extracellular fragment is build of Lipocalin (fluorescein binding Anticalin) and a GGGSLinker. Intracellular either the N-terminal part or the C-terminal part of the splitfluorophore is fused to the transmembrane region of the EGF-receptor. To achieve more flexibility and to support the assembly of the two splitfluorophore parts a fluolinker is fused in between the transmembrane region and the C-terminal part of the splitfluorophores.<br> | On Figure 4_Transfection the structures of the signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-nCFP and signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-fluolinker-cCFP are visible (exemplary for the Splitfluorophore-/Splitenzyme-constructs). The extracellular fragment is build of Lipocalin (fluorescein binding Anticalin) and a GGGSLinker. Intracellular either the N-terminal part or the C-terminal part of the splitfluorophore is fused to the transmembrane region of the EGF-receptor. To achieve more flexibility and to support the assembly of the two splitfluorophore parts a fluolinker is fused in between the transmembrane region and the C-terminal part of the splitfluorophores.<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 17:16, 28 October 2008
 "
"