Team:Heidelberg/Notebook/Visualization/Methods
From 2008.igem.org
(→computer-assisted analysis) |
(→computer-assisted analysis) |
||
| Line 539: | Line 539: | ||
Each file was a stack of 2 pictures with to different channels. The plugin opens the files merges them to one RGB picture, converts them to Jpeg and saves the new pictures in the same folder.<br> | Each file was a stack of 2 pictures with to different channels. The plugin opens the files merges them to one RGB picture, converts them to Jpeg and saves the new pictures in the same folder.<br> | ||
| - | [[Image:20081024_col_kill_6h_24_R3D11.jpg|left| | + | [[Image:20081024_col_kill_6h_24_R3D11.jpg|left|150px|]] [[Image:20081024_col_kill_6h_24_R3D12.jpg|middle|150px|]] [[Image:20081024_col_kill_6h_24.jpg|right|150px|]] |
Revision as of 00:16, 29 October 2008


Visualization - Methods revealed
Contents |
Microscope
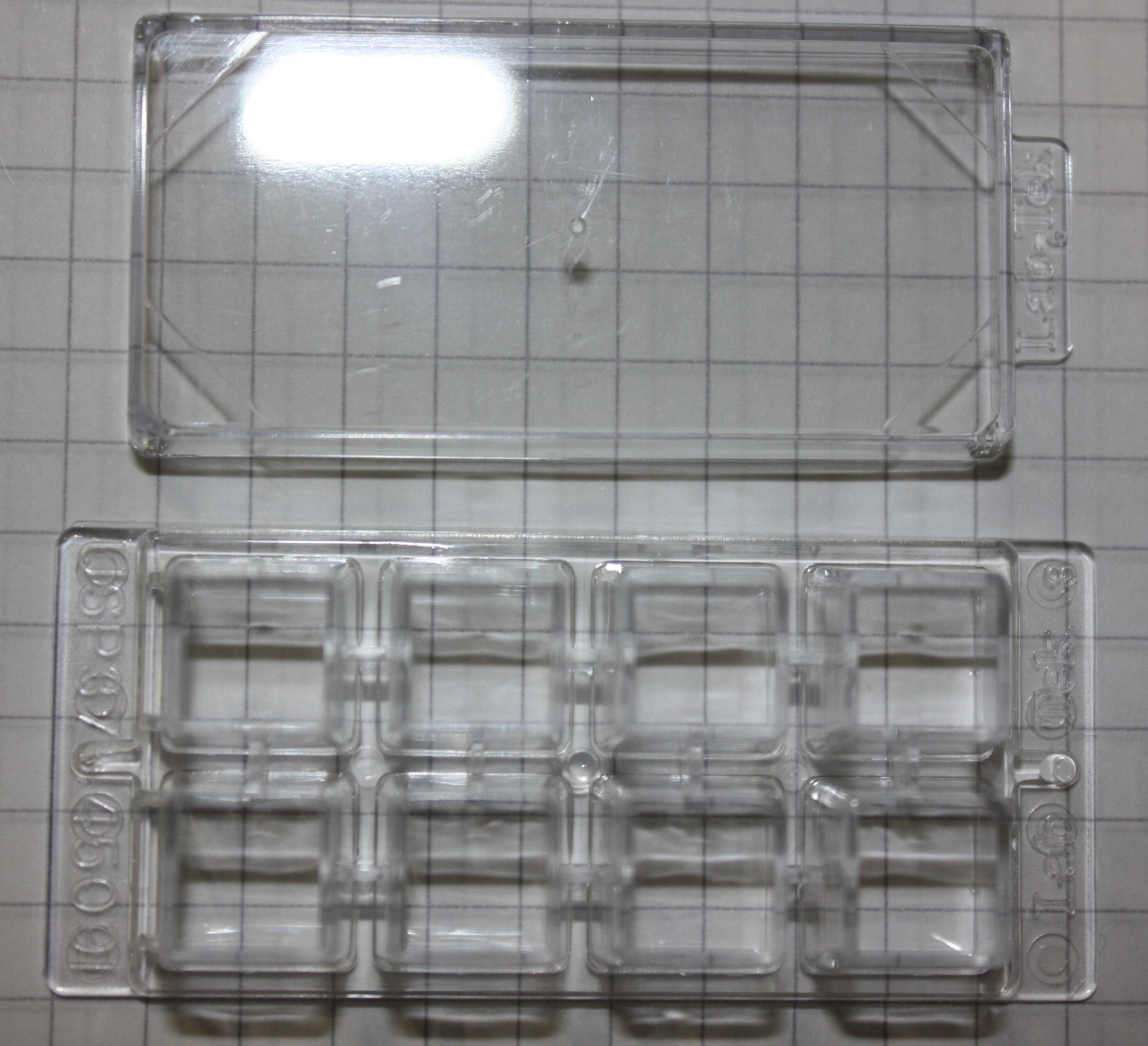
Was performed using LabtekTM chambered coverglass systems (Nunc). In most analysises mainly two versions were used.
All those samples were monitored using an Applied Precision - DeltaVision confocal microscope. After the first experiments have been finished, further experiments were only performed with fluorescent strains. They are much more accurate and may be used for quantified analysis methods.
[back up]
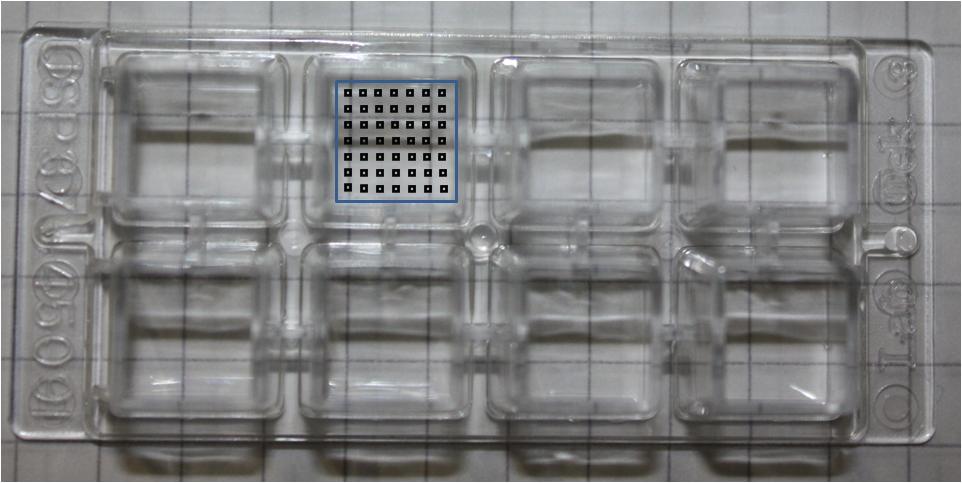
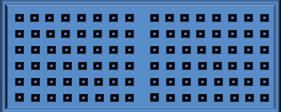
Frames
To analyse chamber samples in several time steps (e.g. after 3,6,9 hours ...)
under the microscope a system was needed, limiting the amount of data and making an analysis possible.
Therefore several frames have been developed, which cover the chamber as good as possible and allows the best estimation about the events of the experiment.
On the right side is one example for each type of chamber:
Every black spot stands for a taken picture at this position.
These draws are just examples of potential frames.
For small chambers square frames were used like 10x10 or 8x8 meaning 100 or 64 pictures at the end. To cover enough space of large chambers two separate frames had to be used. Each of those frames was usually about 6x8 (6 in heigh and 8 in length) fields.
[back up]
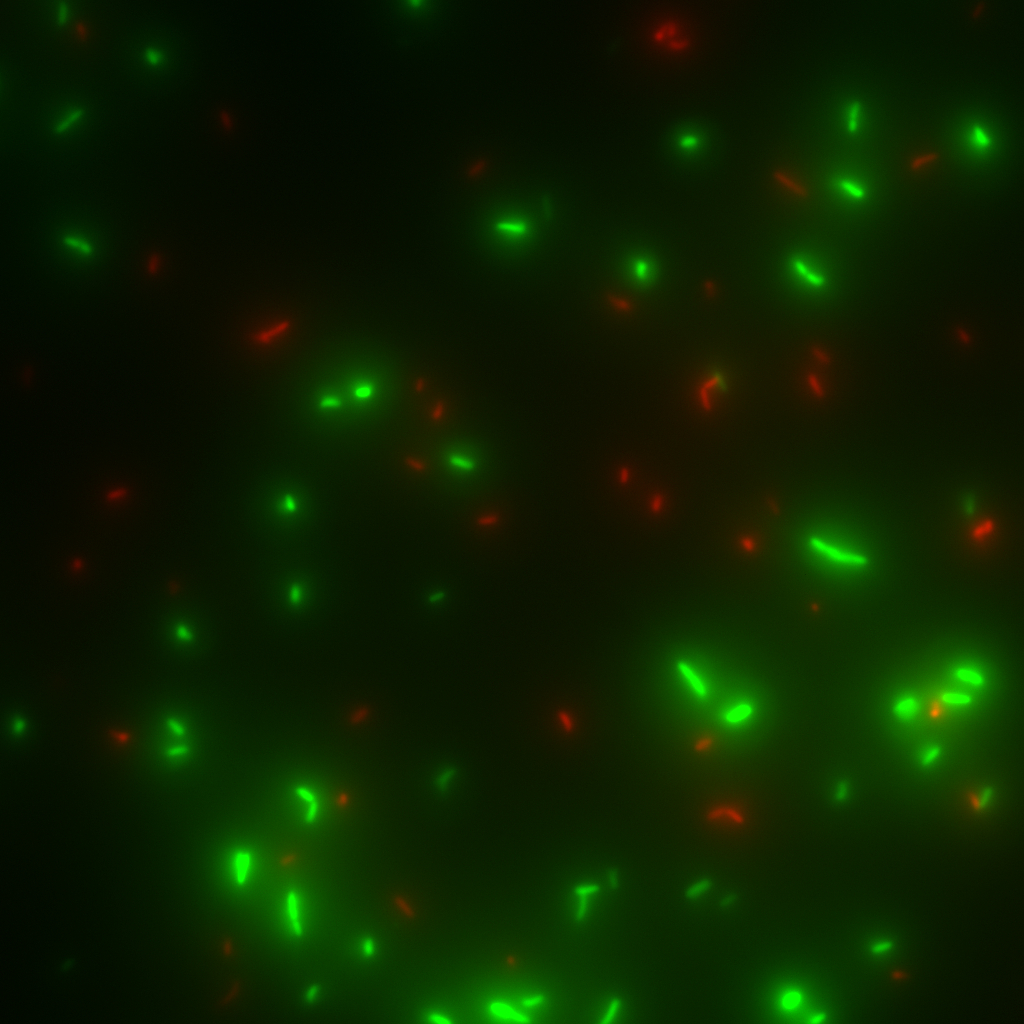
chemotactical activity
This test serie was used test the chemotactical activity of strains depending on special strain abilities and the media they were incubated in or transferred to.
3 µl of an overnight culture were put into a small chamber filled with 200 µl of the appropriate media.
The status of the bacteria has been observed over several hours. Depending on the experiment sometimes after a specific time an attractant like casamino acids have been added to the media to test the effect of the attractant on the activity of the specific strain.
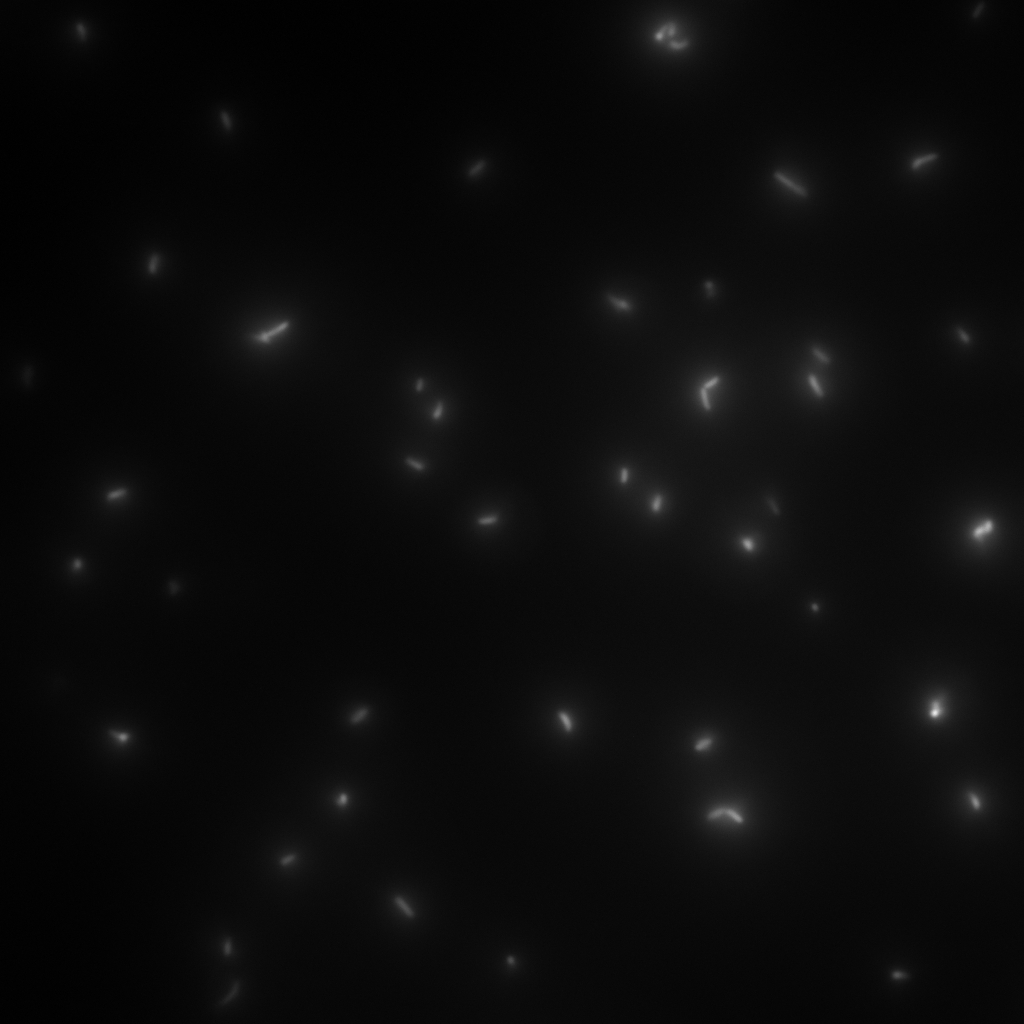
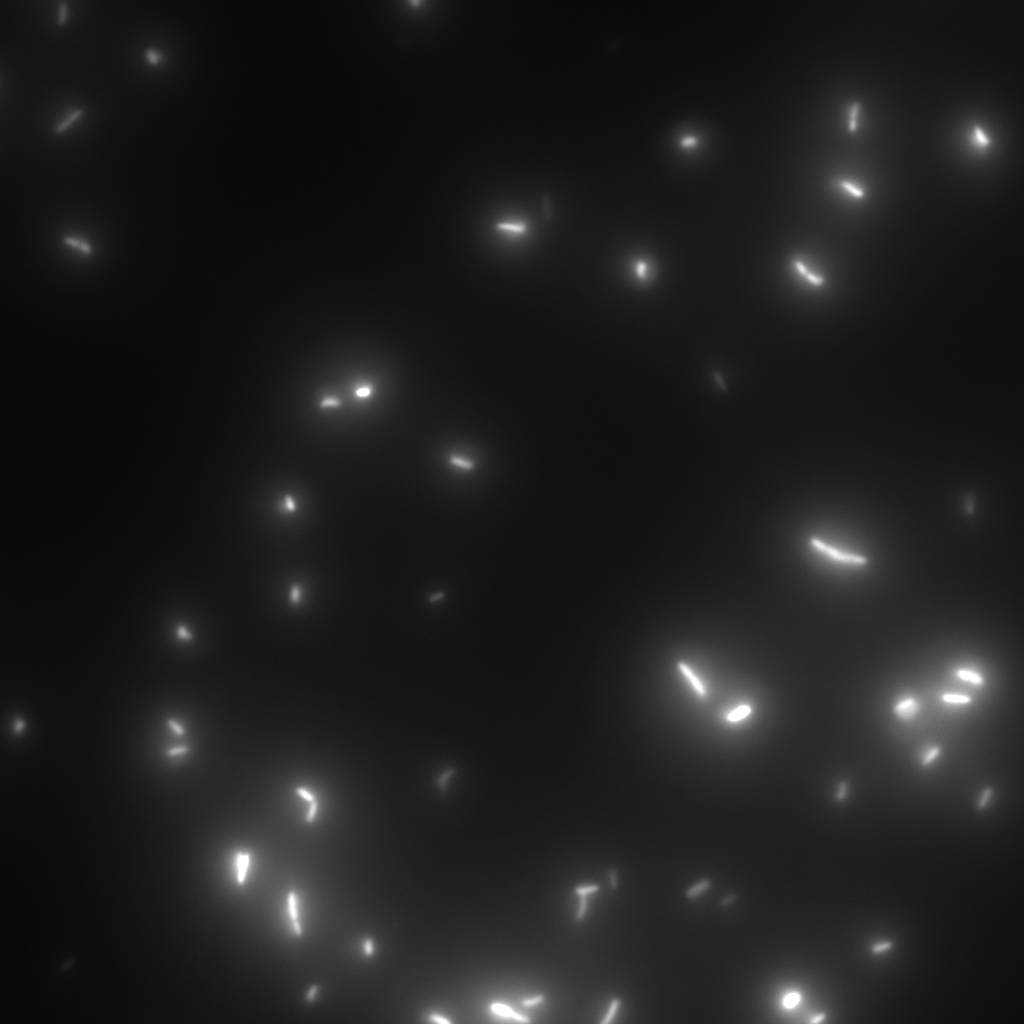
This was performed with short time lapse series like taking 90 pictures at one position with a time lapse of less than 0.33 seconds.
This experiment may give an idea of the behavior of certain strains under specific conditions.
With this information it is more easy to choose the right strain and the best conditions for further experiments.
It is also possible to predict the bacterial behavior, so that some parameters can be excluded if the bacteria do not act as expected.
Here is one example of such a time lapse serie:
[back up]
computer-assisted analysis
The Deltavision confocal microscope gives usually Deltavision-files (.dv) as output, which are not easy to handle and may also be in stacks or somehow or not colored as wanted. It is much more easy to work with Jpeg-files and proccess the images during the coonversion. But the amount of images is to high to convert image per image.
Therefore homemade plugins for ImageJ were used to convert those files to Jpeg-files and if needed processes them. (For example by color and/or merging.)
Furthermore for the automatic processing a http://www.loci.wisc.edu/ome/formats-imagej.html LOCI Bio-Formats importer plugin was used. The link can be found by clicking on the name.
This plugin enables the automatic processing of Deltavision-files.
An example for such a plugin would be:
Just click on the picture to see the plugin.
This plugin takes a serie of 64 pictures taken with the Deltavision microscope in the specific folder.
Each file was a stack of 2 pictures with to different channels. The plugin opens the files merges them to one RGB picture, converts them to Jpeg and saves the new pictures in the same folder.

[back up]
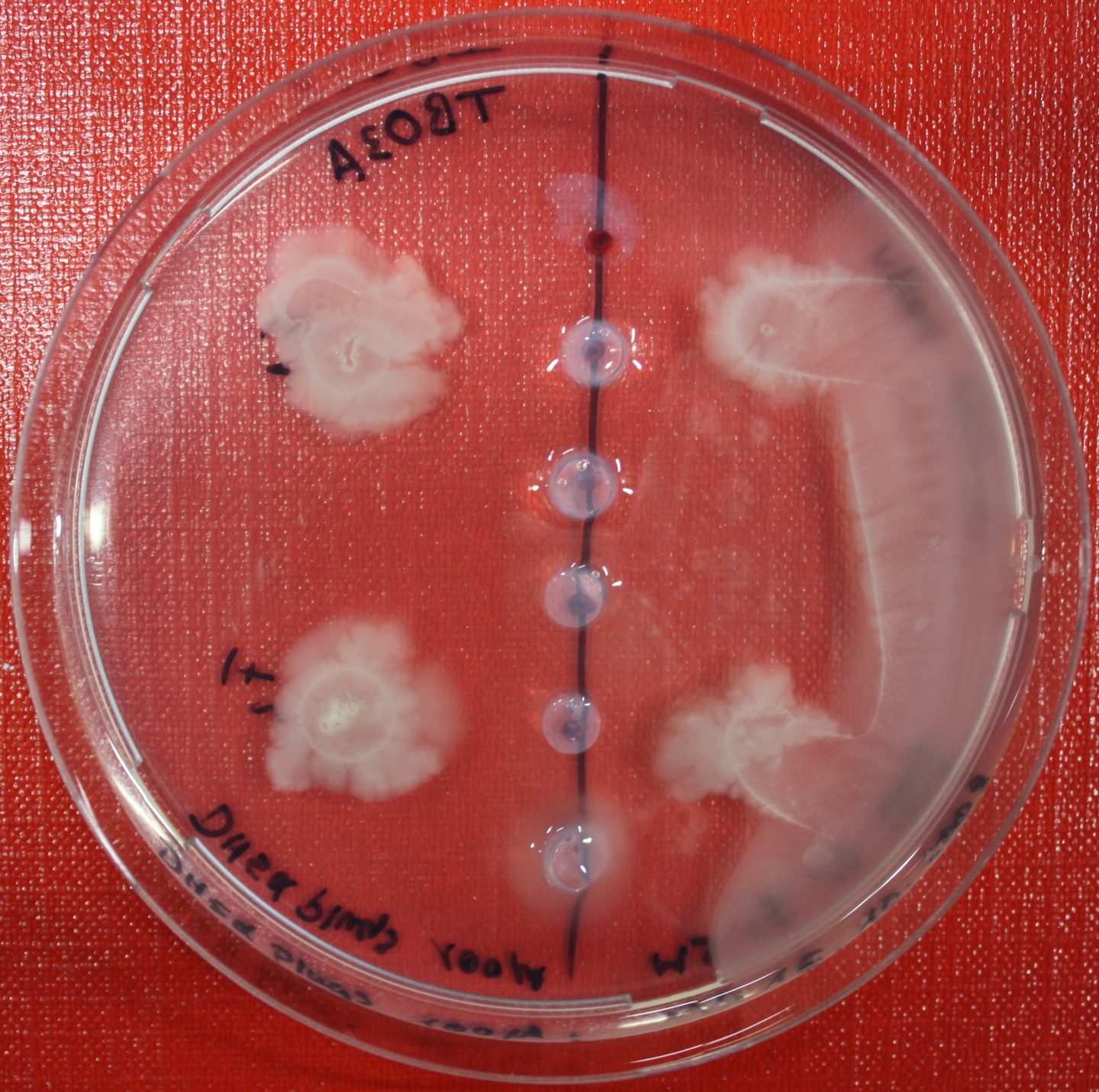
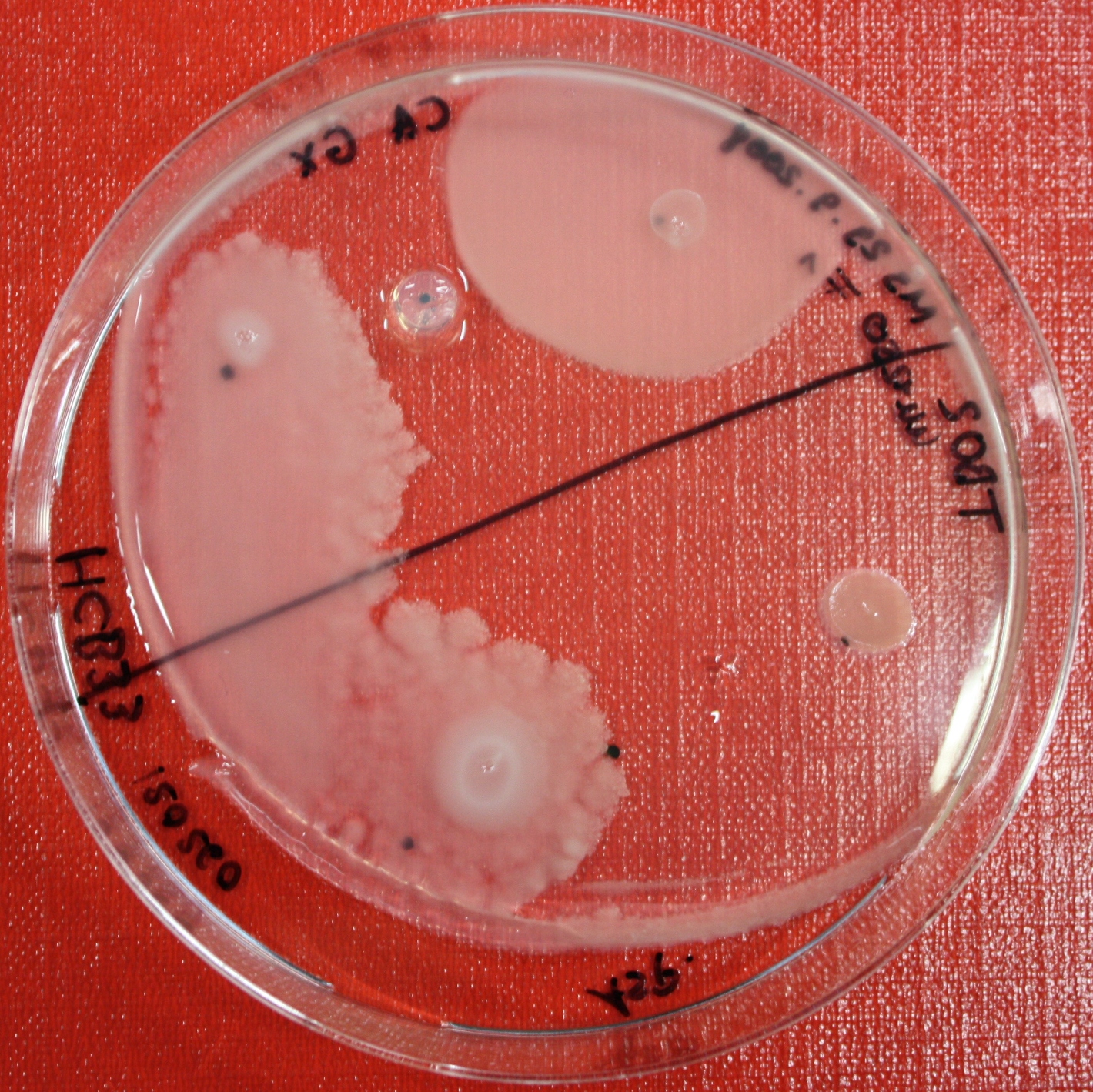
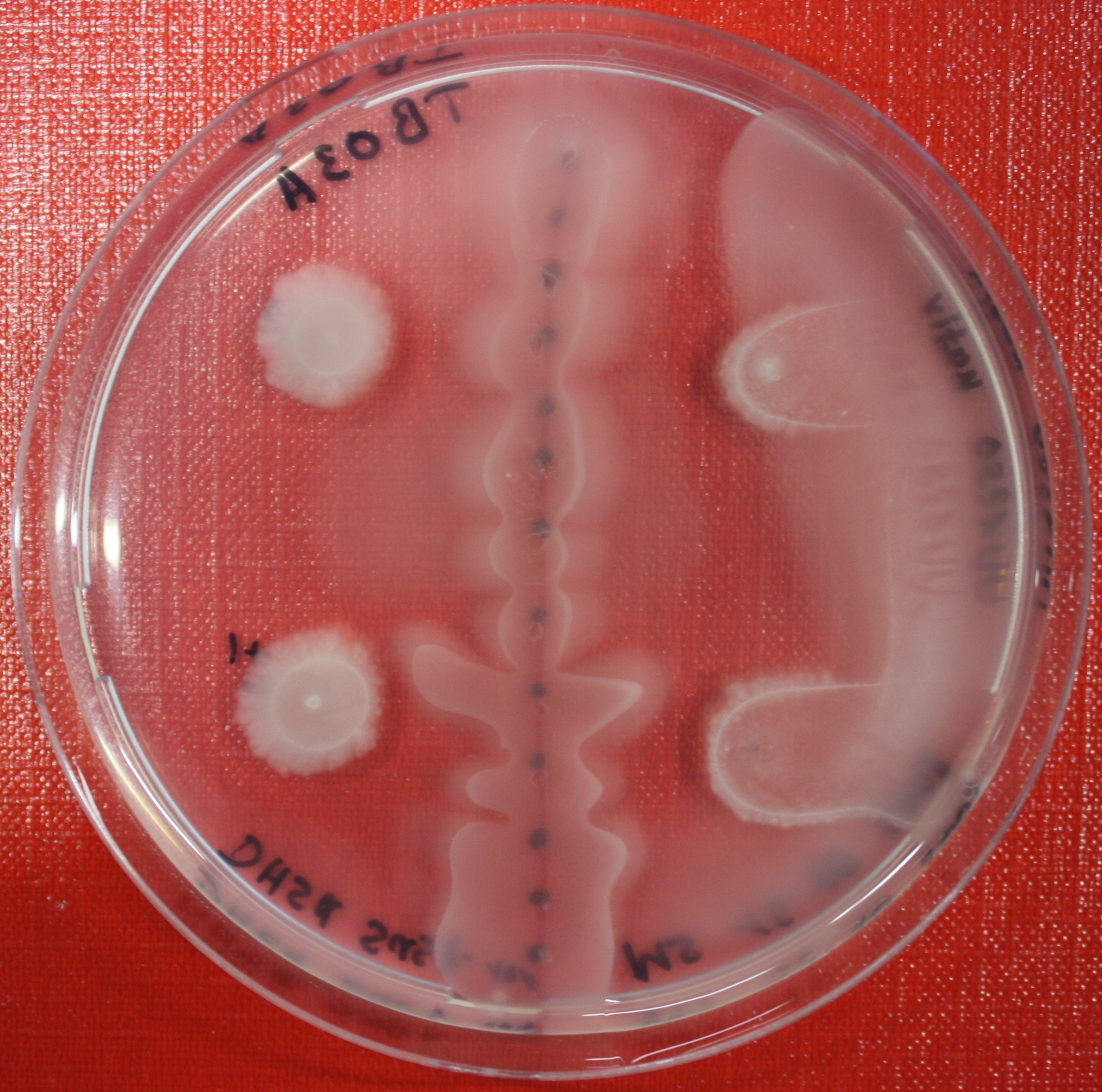
Swarm Assays
PROTOCOL FOR SWARM-PLATE CHEMOTAXIS AGAINST A POSSIBLE ATTRACTANT:
This protocol was created using petri-dishes. But every other chamber could be used as well.
- Step 1: Make sure you have everything ready to get started. You need:
- Petri-dishes. !!! sign your petri-dishes before You pour in the media. Also mark the spots where you want to set the attractant or attractant line and the bacteria. !!!
- 50 ml falcons
- 25 ml media containig 0.2%-0.3% Agar for every petri-dish.
- samples of the appropriate attractants. The concentration depends on several substance depending attributes.
- Other substances like antibiotics (Amp, Kan, Cm) or inducer (IPTG, Arabinose)
- Step 2: Your agar-media solution should be clear and the agar completely solved. If you want to use attractant plugs1 or other non fluid attractants, go first through step 5 then back through 2,3,4 skip 5, further with 6 and so on...
- Step 3: Take Take a 50 ml falcon pour 25 ml of your agar containing media in it and add antibiotics or inducing substances. If no extra substances are needed just skip this step.
- Step 4: Let your media polimerize. At least let it rest for 15/20 min.
- Step 5: Then add the attractant. e.g.: a casamino acid solution
- Step 6:
- Put the whole plate into a 4°C fridge for 12-16 hours to allow the attractant to build up a gradient.
- Make an overnight culture of the strains you want to test, use TB media and add inducing substances if something has to be induced.
Next day:
- Step 7: Take your overnight culture. It should be at an OD of 0.4-0.6. Then take 1 ml of the bacteria suspension and centrifuge it for 10 minutes at 4,000 rpm. Resolve the pellet at 100 µl of the media you are using in the petri-dish.
- Step 8: Place 3-6 µl of your purrified bacteria at the premarked spots on the petri-dish sample.
- Step 9: Put the whole plate into the incubator at ~30°C and take a look at your plates after 24, 48 and 72 hours. Put the plates into a plastic bag like the small ones for the bench trash to protect the plates from running dry to fast. Only move the plates if necessary.
1: Attractant plugs can be created by adding agar to the attractant solution.
[back up]
[back to the overview over the visualization notebook]
 "
"