Team:Edinburgh/Plan/Beta-Carotene
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→β-carotene synthesis) |
(→Directly involved genes from P. ananatis:) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
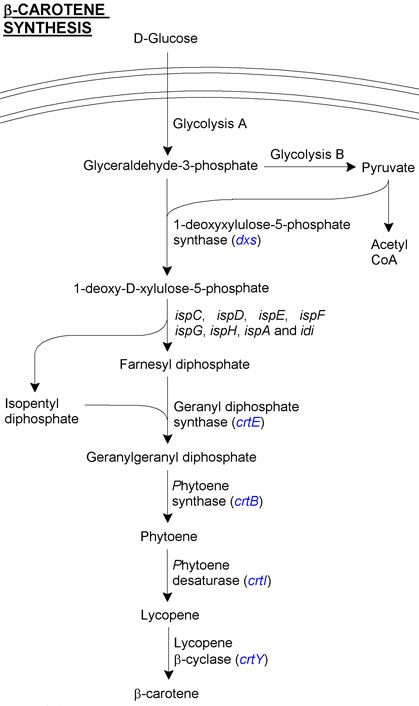
β-carotene is produced from the products of glycolysis, as can be seen in the overview figure. We have concentrated on two areas of β-carotene for our project. The first involves transfering genes from ''Pantoea ananatis'', a member of the proteobacteria naturally capable of synthesising β-carotene. The second involves upregulating the glycolysis pathways in ''E. coli'' in order to concentrate more energy into making β-carotene. | β-carotene is produced from the products of glycolysis, as can be seen in the overview figure. We have concentrated on two areas of β-carotene for our project. The first involves transfering genes from ''Pantoea ananatis'', a member of the proteobacteria naturally capable of synthesising β-carotene. The second involves upregulating the glycolysis pathways in ''E. coli'' in order to concentrate more energy into making β-carotene. | ||
| - | == Directly involved genes from ''P. ananatis'' | + | == Directly involved genes from ''P. ananatis'' == |
# Geranyl diphosphate synthase ([https://2008.igem.org/Team:Edinburgh/crtE '''''crtE''''']) converts the substrates farnesyl diphosphate and isopentyl diphosphate into geranyl geranyl diphosphate. | # Geranyl diphosphate synthase ([https://2008.igem.org/Team:Edinburgh/crtE '''''crtE''''']) converts the substrates farnesyl diphosphate and isopentyl diphosphate into geranyl geranyl diphosphate. | ||
Revision as of 15:22, 29 October 2008
Contents |
β-carotene synthesis
β-carotene is produced from the products of glycolysis, as can be seen in the overview figure. We have concentrated on two areas of β-carotene for our project. The first involves transfering genes from Pantoea ananatis, a member of the proteobacteria naturally capable of synthesising β-carotene. The second involves upregulating the glycolysis pathways in E. coli in order to concentrate more energy into making β-carotene.
Directly involved genes from P. ananatis
- Geranyl diphosphate synthase (crtE) converts the substrates farnesyl diphosphate and isopentyl diphosphate into geranyl geranyl diphosphate.
- Geranyl geranyl diphosphate is then converted into phytoene by phytoene synthase (crtB).
- Lycopene is produced from phytoene by phytoene desaturase (crtI).
- Finally, lycopene β-cyclase (crtY) cyclises lycopene to produce β-carotene.
Indirectly involved genes from E. coli
Overview
- In blue are the genes which we manipulated.
 "
"