Team:Freiburg Transfection and Synthetic Receptor
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<font face="Arial Rounded MT Bold" style="color:#010369">_transfection and synthetic receptor activation </font></div> | <font face="Arial Rounded MT Bold" style="color:#010369">_transfection and synthetic receptor activation </font></div> | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| - | + | <h2>Introduction>/h2> | |
The functionality of our parts was analyzed in three steps. First, we tested the transfection protocol and checked the utility of the transfectionvector-CMV construct for expressing proteins in eucaryotic cells. Second, we analyzed protein expression level and cellular localization. Third, cotransfections were performed to show that clustering of two receptors leads to an assembly of the intracellular splitfluorophores/-enzymes resulting in a functional protein. | The functionality of our parts was analyzed in three steps. First, we tested the transfection protocol and checked the utility of the transfectionvector-CMV construct for expressing proteins in eucaryotic cells. Second, we analyzed protein expression level and cellular localization. Third, cotransfections were performed to show that clustering of two receptors leads to an assembly of the intracellular splitfluorophores/-enzymes resulting in a functional protein. | ||
| - | + | <h2>Methods</h2> | |
| - | + | <h4>Transfection of 293T cells</h4> | |
One day before transfection cells were counted in the Neubauer chamber and 6*10^4 cells/cm² were seeded in 6 well plates. Approximately 1 hour before transfection cells were washed with 1xPBS and fresh DMEM medium was added. For transfection 2µg of DNA were mixed with 25µl CaCl2 and ddH2O was filled up to 250µl. After an incubation on ice for 20 min 250µl BBS (2x) were added. This mixture was given to the cells and after 4-12 hours cells were washed and fresh medium was added.<br> | One day before transfection cells were counted in the Neubauer chamber and 6*10^4 cells/cm² were seeded in 6 well plates. Approximately 1 hour before transfection cells were washed with 1xPBS and fresh DMEM medium was added. For transfection 2µg of DNA were mixed with 25µl CaCl2 and ddH2O was filled up to 250µl. After an incubation on ice for 20 min 250µl BBS (2x) were added. This mixture was given to the cells and after 4-12 hours cells were washed and fresh medium was added.<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | + | <h4>ONPG (o-Nitrophenyl-ß-D-galactopyranosid) Test</h4><br> | |
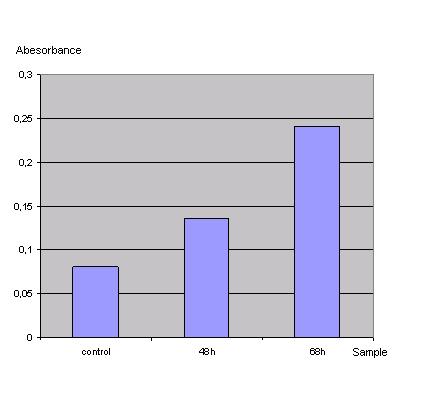
Transfection was performed with a lac z gene using the transfection protocol described above. After 48h one part of the cells was harvested by washing them in PBS and scraping them off. Then the cells were centrifuged at 13000rpm for 2 min and the PBS was replaced by 500µl lysisbuffer (1x). Incubation took place at -80°C for 20min. After thawing the solution was vortexed, spun down and the supernatant was frozen at -20°C. The same procedure was done with the rest of the cells one day later (68h). Then 20µl of each lysate was given to 130µl reactionbuffer (incl. ONPG) letting the mixture incubate for 1h at 37°C. Measurement was done using the ELISA-reader at 405nm.<br> | Transfection was performed with a lac z gene using the transfection protocol described above. After 48h one part of the cells was harvested by washing them in PBS and scraping them off. Then the cells were centrifuged at 13000rpm for 2 min and the PBS was replaced by 500µl lysisbuffer (1x). Incubation took place at -80°C for 20min. After thawing the solution was vortexed, spun down and the supernatant was frozen at -20°C. The same procedure was done with the rest of the cells one day later (68h). Then 20µl of each lysate was given to 130µl reactionbuffer (incl. ONPG) letting the mixture incubate for 1h at 37°C. Measurement was done using the ELISA-reader at 405nm.<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | + | <h2>Results</h2> | |
| - | <h4> | + | <h4>Testing the transfection protocol</h4> |
In order to check if the transfection protocol (Ca2+ precipitation) is suitable to transfect 293T cells a 'test'transfection with a lac z gene (Test-vector from Katja Arndt's lab) was done and the β-galactosidase was detected with an ONPG test.<br> | In order to check if the transfection protocol (Ca2+ precipitation) is suitable to transfect 293T cells a 'test'transfection with a lac z gene (Test-vector from Katja Arndt's lab) was done and the β-galactosidase was detected with an ONPG test.<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
Due to the results of the ONPG assay the Ca2+ precipitation proofed to be a very simple and effective method to transfect the 293t cells.<br> | Due to the results of the ONPG assay the Ca2+ precipitation proofed to be a very simple and effective method to transfect the 293t cells.<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | <h4> | + | <h4>Testing the transfectionvector-CMV promoter construct</h4> |
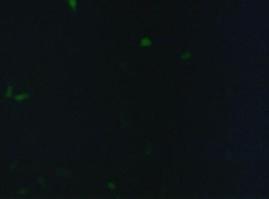
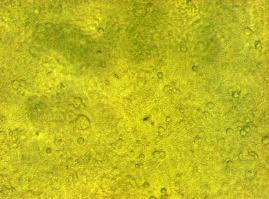
To test the functionality of the transfectionvector and the CMV-promoter (BBa_K157040), YFP was cloned behind the promoter and the plasmid was brought into 293T cells. The detection of YFP took place 1 day later under a microscope with YFP filter.<br> | To test the functionality of the transfectionvector and the CMV-promoter (BBa_K157040), YFP was cloned behind the promoter and the plasmid was brought into 293T cells. The detection of YFP took place 1 day later under a microscope with YFP filter.<br> | ||
The transfected cells show fluorescence by excitation of 510-520nm while the untransfected remain dark at this wavelength demonstrating the capability of the transfectionvector-CMV construct to induce protein expression in eucaryotic cells.<br> | The transfected cells show fluorescence by excitation of 510-520nm while the untransfected remain dark at this wavelength demonstrating the capability of the transfectionvector-CMV construct to induce protein expression in eucaryotic cells.<br> | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
''Figure 1_Transfection: Transfected 293T cells (left), untransfected cells (middle) and transfected cells transmitted light (right)''<br> | ''Figure 1_Transfection: Transfected 293T cells (left), untransfected cells (middle) and transfected cells transmitted light (right)''<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | <h4> | + | <h4>Localization at the cell membrane</h4> |
To show the localization of the constructs at the cell membrane transfection of the construct signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-betaLactamase1-YFP was performed.<br> | To show the localization of the constructs at the cell membrane transfection of the construct signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-betaLactamase1-YFP was performed.<br> | ||
Figure 2_Transfection shows the model of the protein structure based on PDB files. Anti-fluorescein Anticalin (BBa_K157004) is the extracellular part of the construct. The transmembrane region is identical to that of the EGF-receptor erbb1 (BBa_K157002). Split-beta-Lactamase (BBa_I757011), the intracellular part is labeled to the yellow fluorescent protein to detect membrane localization.<br> | Figure 2_Transfection shows the model of the protein structure based on PDB files. Anti-fluorescein Anticalin (BBa_K157004) is the extracellular part of the construct. The transmembrane region is identical to that of the EGF-receptor erbb1 (BBa_K157002). Split-beta-Lactamase (BBa_I757011), the intracellular part is labeled to the yellow fluorescent protein to detect membrane localization.<br> | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
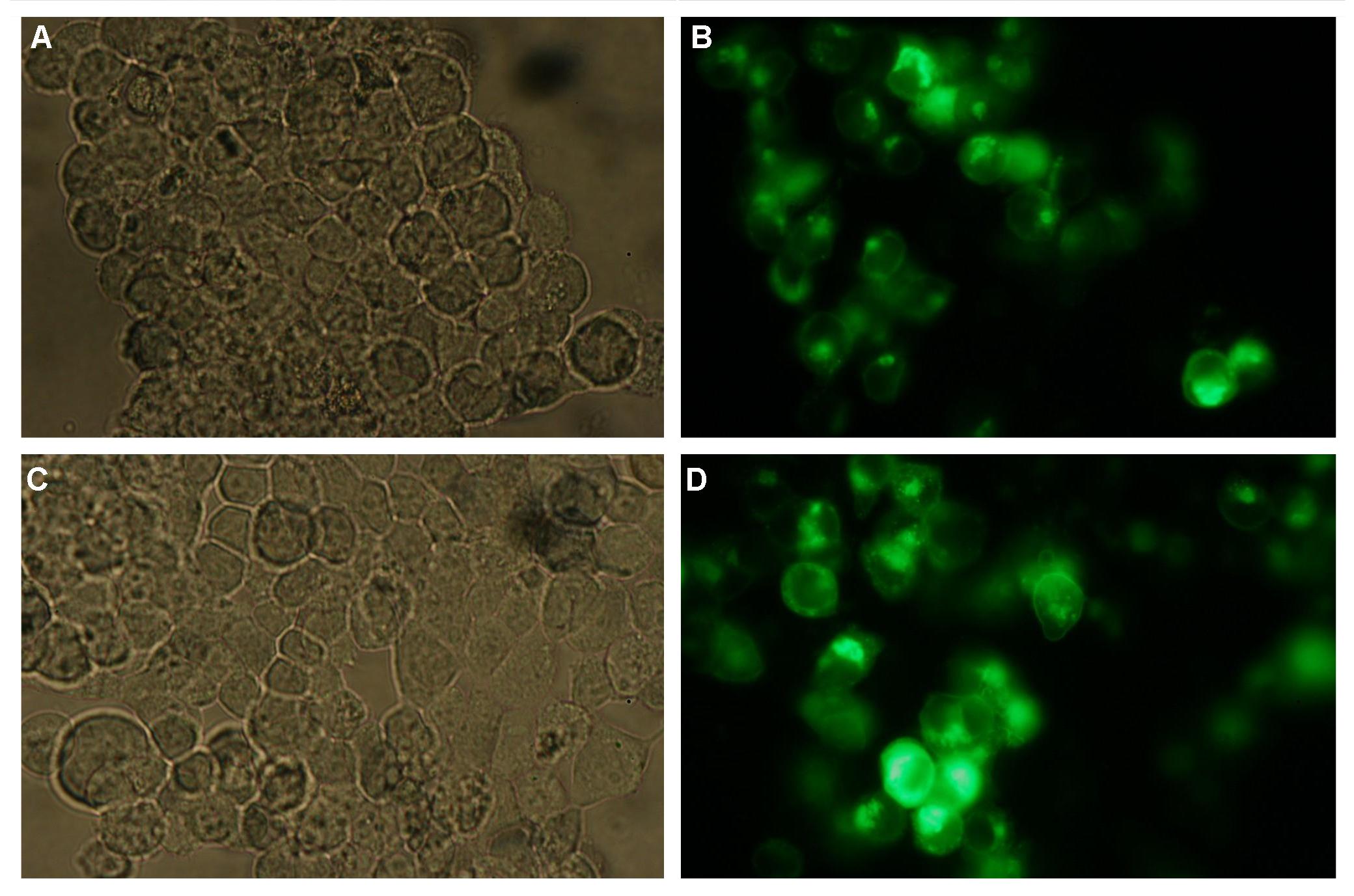
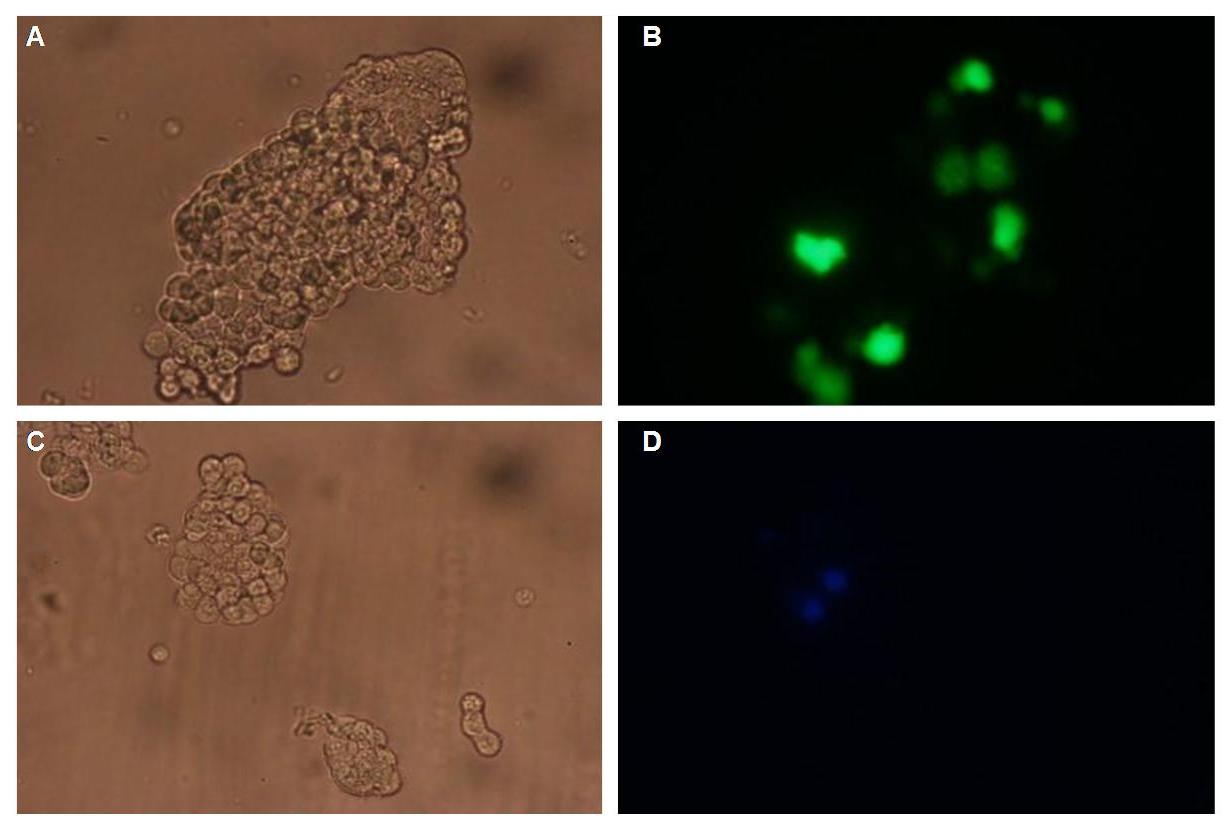
'''Figure 4_Transfection: 293T cells transfected with transfectionvector-CMV-YFP (A and B); 293T cells transfected with transfectionvector-CMV-CFP (C and D)<br>Fluorescence is uniformly distributed all over the cell and not restricted to the cell membrane'''<br> | '''Figure 4_Transfection: 293T cells transfected with transfectionvector-CMV-YFP (A and B); 293T cells transfected with transfectionvector-CMV-CFP (C and D)<br>Fluorescence is uniformly distributed all over the cell and not restricted to the cell membrane'''<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | <h4> | + | <h4>Cotransfections with Splitfluorophor-/Splitenzyme-constructs</h4> |
Figure 5_Transfection gives the model of the Anticalin fused to the GGGSlinker, the transmembrane domain and the N-terminal part of Cerulean CFP or the C-terminal part of Cerulean CFP. To achieve more flexibility and to support the assembly of the two splitfluorophore parts a fluolinker is fused in between the transmembrane region and the C-terminal part of the splitfluorophores. The signalpeptide is not displayed. <br> | Figure 5_Transfection gives the model of the Anticalin fused to the GGGSlinker, the transmembrane domain and the N-terminal part of Cerulean CFP or the C-terminal part of Cerulean CFP. To achieve more flexibility and to support the assembly of the two splitfluorophore parts a fluolinker is fused in between the transmembrane region and the C-terminal part of the splitfluorophores. The signalpeptide is not displayed. <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 19:28, 29 October 2008
 "
"