Team:Heidelberg/Project
From 2008.igem.org
(→Project Idea) |
(→Project Realization) |
||
| (114 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
| - | <link | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | <style> | |
| + | h1.firstHeading { display: none; } | ||
| + | |||
| + | p {text-align: justify;} | ||
| + | |||
| + | a:link { color: #00b0e6; text-decoration: none} | ||
| + | a:visited { color:#00b0e6; text-decoration: none} | ||
| + | a:hover { color:#f29400; text-decoration: none} | ||
| + | a:active { color:#f29400; text-decoration: none} | ||
| + | |||
| + | #bodyContent { padding: 10px auto; width: 910px; margin: auto; clear: none; } | ||
| + | |||
| + | table#team_members { text-align: justify; border: 0; } | ||
| + | table#team_members h2, table#team_members h3 { clear: both; } | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | /*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li ul.DropDownMenu { | ||
| + | display: none; /* Hides all drop-down menus. */ | ||
| + | |||
| + | } | ||
| + | /* | ||
| + | li:hover works in IE7 and FF2. | ||
| + | a:hover works in IE6 and FF2. | ||
| + | a:hover breaks li:hover in FF2. | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li ul.SideMenu, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a ul.SideMenu { | ||
| + | display: none; /* Hides all side menus. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | /*------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Menu Bar */ | ||
| + | div.MenuBar { | ||
| + | font: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; | ||
| + | height: 30px; | ||
| + | width: 910px; | ||
| + | /*width: 100%*/ | ||
| + | margin: 0; | ||
| + | border-top: 0; | ||
| + | border-right: 0; | ||
| + | border-left: 0; | ||
| + | padding: 0; | ||
| + | background: black; | ||
| + | |||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul { | ||
| + | font: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; | ||
| + | text-align: center; | ||
| + | list-style-type: none; | ||
| + | margin: 0.5em auto; | ||
| + | border: 0; | ||
| + | padding: 0; | ||
| + | background: black; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li { | ||
| + | font: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; | ||
| + | display: block; | ||
| + | padding: 0; | ||
| + | margin: 0; | ||
| + | font-size: 1.3em; | ||
| + | float: left; | ||
| + | background: black; | ||
| + | text-align: center; | ||
| + | width: 107px; | ||
| + | position: relative; /* Sets the positioning context for each drop-down menu. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a { | ||
| + | font: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; | ||
| + | display: block; | ||
| + | background: black; | ||
| + | height: 22px; /* Keep height + padding-top + padding-bottom sync with the menu bar height. */ | ||
| + | color: #ffffff; | ||
| + | padding-top: 4px; | ||
| + | padding-bottom: 4px; | ||
| + | padding-left: 1em; /* Sets the left space between top-level items. */ | ||
| + | padding-right: 1em; /* Sets the right space between top-level items. */ | ||
| + | text-decoration: none; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | /*------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Drop-Down Menus */ | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu { | ||
| + | display: block; | ||
| + | width: 10em; /* Drop-down menu width. | ||
| + | Use MenuTailor.css to customize. */ | ||
| + | height: 1em; | ||
| + | padding: 1px; /* Sets the drop-down menu "effective border" width. */ | ||
| + | position: absolute; | ||
| + | top: 23px; /* Places the drop-down menu under the menu bar. | ||
| + | Keep it sync with the menu bar height. */ | ||
| + | left: 0; /* Aligns the drop-down menu to its top-level item. */ | ||
| + | background-color: black; /* Selected item. */ | ||
| + | color: #FFFFFF; | ||
| + | |||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a { | ||
| + | width: 10em; /* Keep it sync with the drop-down menu width. | ||
| + | Use MenuTailor.css to customize. */ | ||
| + | height: 1em; | ||
| + | padding-left: 0; | ||
| + | padding-right: 0; | ||
| + | background-color: black; /* Selected item. */ | ||
| + | color: #FFFFFF; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | ul.DropDownMenu li a span { | ||
| + | display: block; | ||
| + | padding-left: 0.75em; /* Sets the left space of each drop-down menu item. */ | ||
| + | padding-right: 0.25em; /* Sets the right space of each drop-down menu item. */ | ||
| + | text-align: right; /* Aligns the >> symbol to the right. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | ul.DropDownMenu li a span span { | ||
| + | float: left; /* Aligns the text (back) to the left. */ | ||
| + | font: 12px arial, helvetica, sans-serif; /* Required for IE55. */ | ||
| + | height: 20px; | ||
| + | color: #FFFFFF; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | /*----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Side Menus */ | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover ul.SideMenu, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover ul.SideMenu { | ||
| + | display: block; | ||
| + | width: 11em; /* Side menu width. | ||
| + | Use MenuTailor.css to customize. */ | ||
| + | padding: 1px; /* Sets the side menu "effective border" width. */ | ||
| + | position: absolute; | ||
| + | top: -1px; /* Aligns the side menu to its drop-down menu item. | ||
| + | Keep it sync with the side menu "effective border" width. */ | ||
| + | left: 13em; /* Places the side menu to the right of the drop-down menu. | ||
| + | Keep it sync with the drop-down menu width. | ||
| + | Use MenuTailor.css to customize. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover ul.SideMenu li a, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover ul.SideMenu li a { | ||
| + | width: 11em; /* Keep it sync with the side menu width. | ||
| + | Use MenuTailor.css to customize. */ | ||
| + | font: 12px arial, helvetica, sans-serif; /* Required for IE55. */ | ||
| + | left: 13em; /* Places the side menu to the right of the drop-down menu. | ||
| + | Keep it sync with the drop-down menu width. | ||
| + | Use MenuTailor.css to customize. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li ul.DropDownMenu li ul.SideMenu li a span { | ||
| + | padding-left: 1.5em; /* Sets the left space of each side menu item. */ | ||
| + | padding-right: 0.5em; /* Sets the right space of each side menu item. */ | ||
| + | text-align: left; | ||
| + | font: 12px arial, helvetica, sans-serif; /* Required for IE55. */ | ||
| + | left: 13em; /* Places the side menu to the right of the drop-down menu. | ||
| + | Keep it sync with the drop-down menu width. | ||
| + | Use MenuTailor.css to customize. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | /*----------------------------------------------------------------------------- Browser Specific */ | ||
| + | * html div.MenuBar ul li a { | ||
| + | float: left; /* Required for IE55 and IE6. | ||
| + | Breaks O9. | ||
| + | Hidden (* html) from non-IE browsers. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | * html ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover { | ||
| + | cursor: hand; /* Required for IE55. | ||
| + | Hidden (* html) from non-IE browsers. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover { | ||
| + | cursor: pointer; /* Required for IE6 and IE7. | ||
| + | Hidding it (* html) from non-IE browsers breaks IE7! | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | * html div.MenuBar a:hover { | ||
| + | text-decoration: none; /* Required for IE55 and IE6. | ||
| + | Hidden (* html) from non-IE browsers. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | * html div.MenuBar ul li table, | ||
| + | * html div.MenuBar ul li table td { | ||
| + | border: 0; /* Required for IE55 and IE6. | ||
| + | Hidden (* html) from non-IE browsers. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | /*------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Default Colors */ | ||
| + | div.MenuBar { | ||
| + | background-color: Menu; | ||
| + | border-bottom: 1px solid ButtonShadow; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar a { | ||
| + | background-color: Menu; /* Top-level unselected items. */ | ||
| + | color: MenuText; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover a, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover { | ||
| + | color: #ea7f16; | ||
| + | background-color: Highlight; /* Top-level selected item. */ | ||
| + | color: HighlightText; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | /*...............................................................................................*/ | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu { | ||
| + | background-color: ButtonShadow; /* Sets the drop-down menu "effective border" color. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a { | ||
| + | background-color: Menu; Drop-down menu unselected items. | ||
| + | Sets the drop-down menu "effective background" color. */ | ||
| + | color: MenuText; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover a, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover { | ||
| + | background-color: Highlight; /* Drop-down menu selected item. */ | ||
| + | color: HighlightText; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | /*...............................................................................................*/ | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover ul.SideMenu, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover ul.SideMenu { | ||
| + | background-color: ButtonShadow; /* Sets the side menu "effective border" color. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover ul.SideMenu li a, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover ul.SideMenu li a { | ||
| + | background-color: Menu; /* Side menu unselected items. | ||
| + | Sets the side menu "effective background" color. */ | ||
| + | color: MenuText; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover ul.SideMenu li a:hover, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover ul.SideMenu li a:hover { | ||
| + | background-color: Highlight; /* Side menu selected item. */ | ||
| + | color: HighlightText; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | /*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ | ||
| + | /*Script-Free 3-Level Menu 1.2 Tailor | ||
| + | www.CesarDaniel.info | ||
| + | /*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- General */ | ||
| + | body { | ||
| + | background: white; | ||
| + | color: black; | ||
| + | margin: 0; | ||
| + | border: 0; | ||
| + | padding: 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | div.MenuBar { | ||
| + | font: 13px arial, helvetica, sans-serif; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul { | ||
| + | font: 13px arial, helvetica, sans-serif; /* Required for IE55. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | /*--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Colors */ | ||
| + | div.MenuBar { | ||
| + | background-color: black; /* Selected item. */ | ||
| + | color: #FFFFFF; | ||
| + | border-bottom: 1px solid ButtonShadow; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar a, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover ul.SideMenu li a, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover ul.SideMenu li a { | ||
| + | background-color: black; /* Selected item. */ | ||
| + | color: #FFFFFF; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover a, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover a, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover ul.SideMenu li a:hover, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover ul.SideMenu li a:hover { | ||
| + | background-color: #00b0e6; /* Selected item. */ | ||
| + | color: #FFFFFF; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover ul.SideMenu, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover ul.SideMenu { | ||
| + | background-color: ButtonShadow; /* Sets the drop-down and side menus "effective border" color. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | /*--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Widths */ | ||
| + | /* | ||
| + | |||
| + | /* | ||
| + | Menu Bar 1 | ||
| + | Drop-Down Menu #2 | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu#MB1-DDM4, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu#MB1-DDM4, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu#MB1-DDM4 li a, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu#MB1-DDM4 li a { | ||
| + | width: 11em; /* Drop-down menu width. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu#MB1-DDM5, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu#MB1-DDM5, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu#MB1-DDM5 li a, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu#MB1-DDM5 li a { | ||
| + | width: 12em; /* Drop-down menu width. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | /*...............................................................................................*/ | ||
| + | /* | ||
| + | Menu Bar 1 | ||
| + | Drop-Down Menu #2 | ||
| + | Side Menu #1 | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM1, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM1 { | ||
| + | left: 15.5em !important; /* Places the side menu to the right of the drop-down menu. | ||
| + | Keep it sync with the drop-down menu width. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM1, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM1, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM1 li a, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM1 li a { | ||
| + | width: 10em; /* Side menu width. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | /*...............................................................................................*/ | ||
| + | /* | ||
| + | Menu Bar 1 | ||
| + | Drop-Down Menu #2 | ||
| + | Side Menu #2 | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM2, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM2 { | ||
| + | left: 15.5em !important; /* Places the side menu to the right of the drop-down menu. | ||
| + | Keep it sync with the drop-down menu width. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM2, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM2, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM2 li a, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM2 li a { | ||
| + | width: 10em; /* Side menu width. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | /*...............................................................................................*/ | ||
| + | /* | ||
| + | Menu Bar 1 | ||
| + | Drop-Down Menu #2 | ||
| + | Side Menu #3 | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM3, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM3 { | ||
| + | left: 15.5em !important; /* Places the side menu to the right of the drop-down menu. | ||
| + | Keep it sync with the drop-down menu width. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM3, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM3, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li:hover ul.DropDownMenu li:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM3 li a, | ||
| + | div.MenuBar#navi ul li a:hover ul.DropDownMenu li a:hover ul.SideMenu#MB1-DDM2-SM3 li a { | ||
| + | width: 10em; /* Side menu width. */ | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | /*...............................................................................................*/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | </style> | ||
| + | |||
<body> | <body> | ||
| Line 91: | Line 432: | ||
<!--[if lte IE 6]></td></tr></table></a><![endif]--> | <!--[if lte IE 6]></td></tr></table></a><![endif]--> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
| - | <li><a href="https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Notebook/ | + | <li><a href="https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Notebook/visualization"><span><span>Visualization</span></span></a> |
<li><a href="https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Notebook/material"><span><span>Material & Methods</span></span></a> | <li><a href="https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Notebook/material"><span><span>Material & Methods</span></span></a> | ||
<li><a href="https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Notebook/team_meetings"><span><span>Team Meetings</span></span></a> | <li><a href="https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Notebook/team_meetings"><span><span>Team Meetings</span></span></a> | ||
| Line 133: | Line 474: | ||
<div class="blocksatz"> | <div class="blocksatz"> | ||
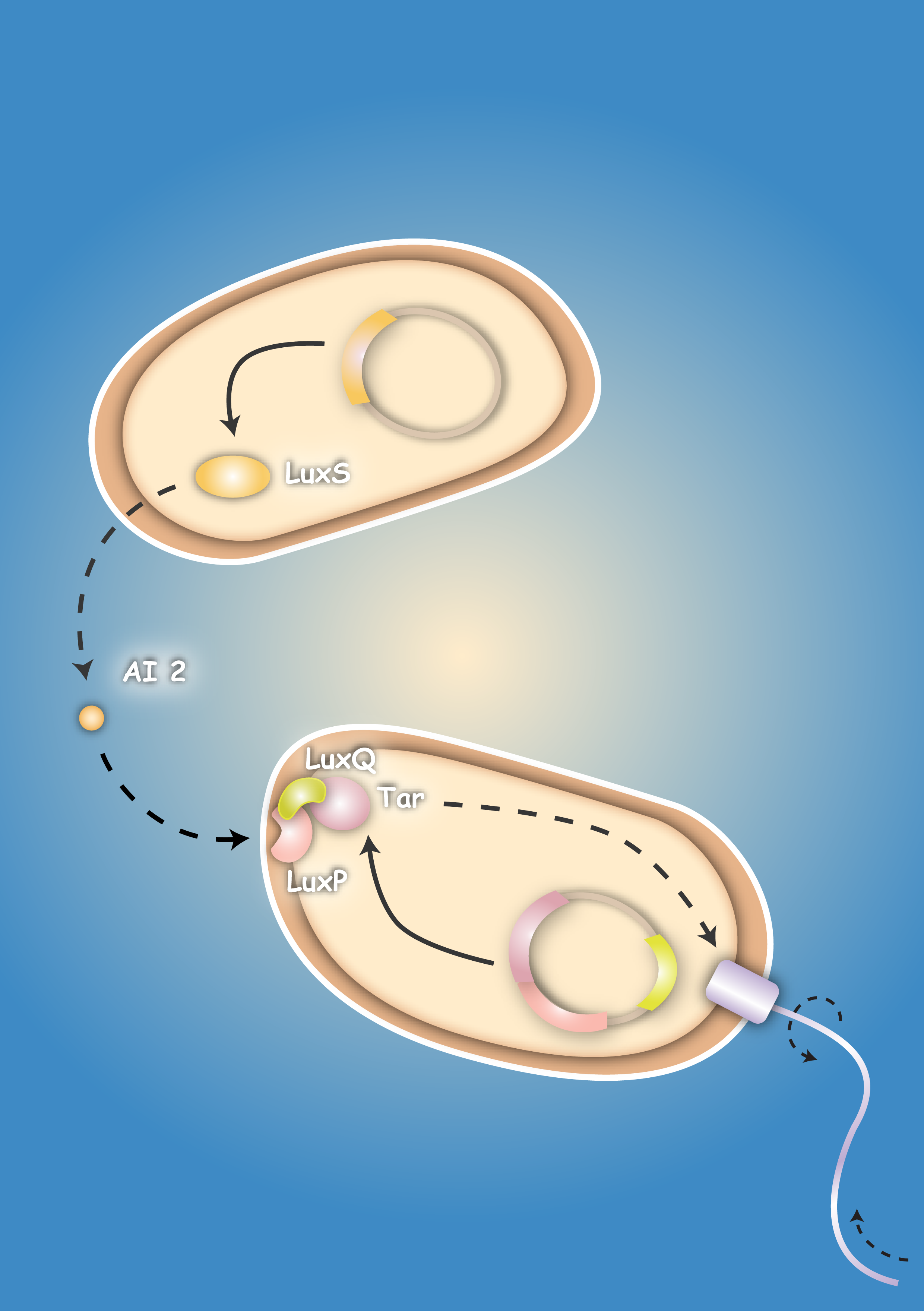
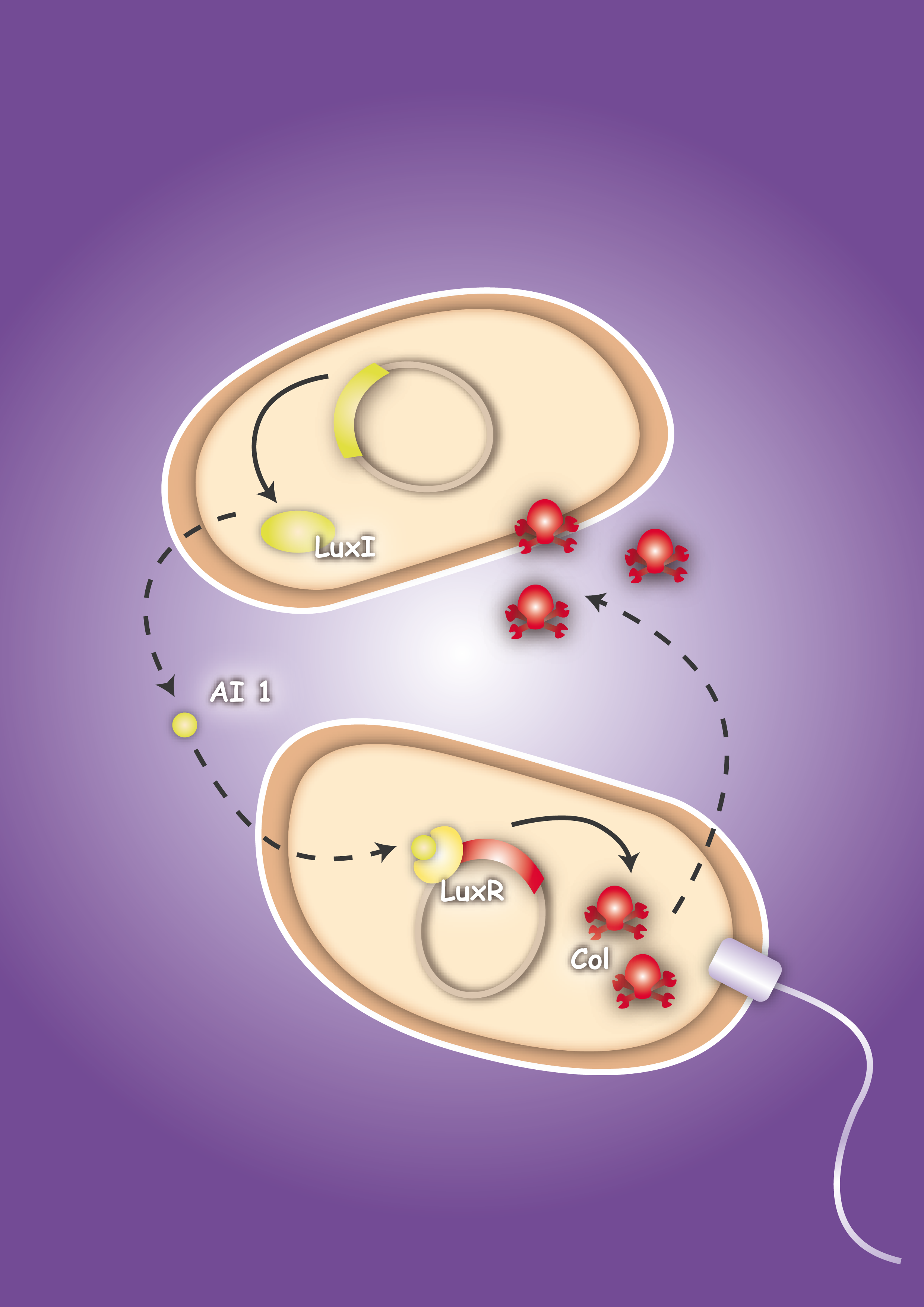
| - | Pathogenic microorganisms represent a major challenge to both medicine and industry. Microbial communities known as biofilms prove to be particularly resistant to conventional therapies and demonstrate the need for alternative methods to fight bacterial growth. The formation of biofilms, as well as other processes such as virulence, antibiotic production, and sporulation, are regulated by communication circuits that depend on small signalling molecules called autoinducers. Our aim is to exploit this communication mechanism by engineering synthetic [[Team:Heidelberg/Project/General_information#Bacteria – general introduction|bacteria]] that are able to target potentially harmful autoinducer-secreting species and kill them. Working with E. coli as a model system, we plan to engineer separate “killer” and “prey” cells, and divide our project into two complementary modules. The “sensing module” comprises the modification of E. coli’s [[Team:Heidelberg/Project/General_information#Chemotaxis|chemotaxis]] system to make killer cells move towards prey cells. | + | Pathogenic microorganisms represent a major challenge to both medicine and industry. Microbial communities known as biofilms prove to be particularly resistant to conventional therapies [1] and demonstrate the need for alternative methods to fight bacterial growth. The formation of biofilms, as well as other processes such as virulence, antibiotic production, and sporulation, are regulated by communication circuits that depend on small signalling molecules called autoinducers. Our aim is to exploit this communication mechanism by engineering synthetic [[Team:Heidelberg/Project/General_information#Bacteria – general introduction|bacteria]] that are able to target potentially harmful autoinducer-secreting species and kill them. Working with E. coli as a model system, we plan to engineer separate “killer” and “prey” cells, and divide our project into two complementary modules. The “sensing module” comprises the modification of E. coli’s [[Team:Heidelberg/Project/General_information#Chemotaxis|chemotaxis]] [2] system to make killer cells move towards prey cells. |
This requires the engineering of a “sensing module” which propagates a prey-specific stimulus to the downstream signalling cascades, prompting the cells to swim towards the gradient of such a stimulus. The directed swimming stops only in the region where the stimulus is maximal, i.e. in the vicinity of the prey. The “killing module” ensures that once in the vicinity of the prey, a bacteriocidal mechanism is activated. Computer models will show how both modules behave in concert and probe the efficiency of the system in defined spatial environments. Future directions, which are beyond the scope of this project, include the modification of the sensory and killing modules, adjusting the range of targets to real pathogens, but also other organisms, specific cell types or even cancer cells. | This requires the engineering of a “sensing module” which propagates a prey-specific stimulus to the downstream signalling cascades, prompting the cells to swim towards the gradient of such a stimulus. The directed swimming stops only in the region where the stimulus is maximal, i.e. in the vicinity of the prey. The “killing module” ensures that once in the vicinity of the prey, a bacteriocidal mechanism is activated. Computer models will show how both modules behave in concert and probe the efficiency of the system in defined spatial environments. Future directions, which are beyond the scope of this project, include the modification of the sensory and killing modules, adjusting the range of targets to real pathogens, but also other organisms, specific cell types or even cancer cells. | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| - | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| - | + | |- | |
| - | + | | [[Image:HD_Sensing.png|left|thumb|300px| Fig. 1: A killer cell senses the specific signal of autoinducer-2 secreted by prey cells and chases them with chemotaxis]] || [[Image:Fig_0-System.png|left|thumb|300px|Fig. 2: Once the preys are caught the killer cells are induced by a second specific signal, autoinducer-1, to activate a killer mechanism.]] | |
| - | + | |- | |
| - | + | |} | |
| + | [[https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Project back]] | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| + | You are very interested in this exciting project, but did not understand all details? Well then come on with me on my guiding tour [[Team:Heidelberg/Human_Practice/Phips_the_Phage/General_Backround|'''... follow phips to step 3''']] [[Image:Phips_3.png|middle|50px]] [ [[Team:Heidelberg/Team| ''... back to step 2'']] ] | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <div> ''Deutsche Übersetzung:'' | ||
| - | + | '''Ecolizenz zum Töten: Eine ''E. coli''-Konstruktion zum gezielten Angriff auf pathogene Mikroorganismen''' | |
| - | + | Pathogene Mikroorganismen stellen eine große Herausforderung sowohl für die Medizin als auch für die Industrie dar. Gemeinschaften aus Mikroorganismen, die in der Fachsprache als Biofilme bezeichnet werden, haben sich als äußerst resistent gegenüber konventionellen Therapien erwiesen [1]. Um deren Wachstum zu bekämpfen bedarf es daher alternativen Ansätzen. Die Entstehung von Biofilmen, genauso wie die der Virulenz, die Produktion von Antibiotika oder die Bildung von Sporen werden durch Kommunikations-Schaltkreise reguliert, die auf kleinen Signalmolekülen - den sogennanten Autoinduzierern (AI) - basieren. Unser Ziel ist es, diese Kommunikationsmechanismen in der Weise zu integrieren, dass synthetische Bakterien potenziell gefährliche, AI-ausschüttende Spezies aufspüren und töten können. Mit ''E. coli'' als Modellorganismus beabsichtigen wir zwei separate Stämme - einen Killer- und einen Beutestamm - zu entwerfen. Das Projekt gliedert sich in zwei ergänzende Module: Die Signalerkennung umfasst die Modifizierung des Chemotaxis-Systems von E. coli [2], um Killer-Zellen zu den Beute-Zellen schwimmen zu lassen. Dafür ist es notwendig, dass ein Erkennungsmodul einen Beute-spezifischen Stimulus an die Signalkaskade für Chemotaxis weiterleitet, so dass die Killer-Zellen entgegen des Gradienten des Stimulus schwimmen. Das gerichtete Schwimmen kommt nur zum Erliegen, wenn sich die Killer-Zellen in der unmittelbaren Umgebung der Beute-Zellen befinden - dort, wo die Stimuluskonzentration maximal ist. Das Killer-Modul gewährt, dass - einmal in der Nähe der Beute angekommen - ein bakterizider Mechanismus aktiviert wird. Computermodelle werden ergänzend zeigen, wie sich die beiden Modelle im Zusammenspiel verhalten, und wie die Effizienz des Gesamtsystems in seiner räumlichen Umgebung einzuschätzen ist. In Zukunft - sicherlich außerhalb der Reichweite unseres Projekts - könnte die Spezifität auf relevante Pathogene, genauso wie auf andere Organismen, Gewebe oder sogar Krebszellen erweitert werden. </div> | |
| + | [[https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Project back]] | ||
| - | + | == Project Realization== | |
| + | Have you ever wondered, why numbers of iGEM team members are limited to a maximum of twelve students? Apart from financial resources, this limit is only natural: efficient work with larger team sizes requires a subtle organization and project management, in particular when the team is yet green! On top, team formation and project work have to be conducted within a short time interval and under liabilities to the academic curriculum - both on the student and the advisor sides. The social abilities for reliable team formation, in particular communication, team integration, and consequence to work towards common team goals, must therefore be substantial and dedicated to compensate these circumstances. When you visit our portraits, however, you will realize that we are not really green and that each of us has an active past often intricately connected with scientific work. In our project description we provide a sincere answer to the apparent question, if 16 "greenhorns" can push forward in only four months to contribute research on an international level! | ||
| - | + | In order to streamline our horse-power, we divide the project into four columns, which are simultaneously developed by us and can merge in the end with a synergistic effect to a complex population system (modeling inclusive). At the same time the global progress is robust towards each column, consequently a delay or failure in one column will not lead to a breakdown of the overall project. In accordance with current scientific standards demanded in systems and synthetic biology, we pursue an interdisciplinary approach combining mathematics, experimental, and quantitative biology [3]. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | The first column ([[2008.igem.org:Team_Heidelberg/Project/Sensing|Project - Sensing]]) comprises the design and development of a sensing module. Chemotaxis is a very effective mechanism of bacteria to move towards nutrients. Using the natural signals for bacterial quorum communication, we re-design a chemotactic receptor for detection of the quorum signal (AI-2) and its transmission to the chemotaxis signaling network. A prey strain, which is to be found via the sensing mechanism, will be engineered to secrete two prey specific quorum signals (AI-1 and AI-2). We dedicate two columns to the development of a killing mechanism to secure a higher implementation confidence: In one column, the second ([[2008.igem.org:Team_Heidelberg/Project/Killin_I|Project - Killing I/Phages]]), a killing mechanism is developed based on bacteriophages, which are conjugated into prey cells, once the killers are in their vicinity. In prey cells, however, the phage becomes lytic due to the missing regulation of the cI transcription factor; the phage is thereby released and infects other prey cells in a domino effect. The killing module in the third column ([[2008.igem.org:Team_Heidelberg/Project/Killing_II|Project - Killing II/Colicins]]) can be considered as a mechanism for recognition of molecular exudation patterns. Once killer cells are in the vicinity of preys, they detect the specific signal molecule AI-1, which leads to the production and release of colicins. The bactericide substance, to which the producing host is resistant, will then eliminate the prone prey. In a fourth column ([[2008.igem.org:Team_Heidelberg/Modeling|Modeling]]) we model the system behavior of these two bacterial strains - the killer and the prey - in a 2D landscape. One approach is based on partial differential equations and simulates chemotaxis and the colicin killing mechanism; the second approach, based on delay differential equations, analyzes the killing dynamics of conjugated bacteriophages. [[2008.igem.org:Team_Heidelberg/Project/Visualization|Visualization]] - the architrave - with microscopy is finally employed to quantify bacterial density landscapes in space and time - allowing a phenotypic connection and comparison with our modeling work. An experimental engagement would these days of course not be appreciable without the active responsibility towards the sake of the community under ethical considerations. We therefore actively engage in [https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Human_Practice/Project_Overview human practice] ... and the pupils are enthusiastic! | |
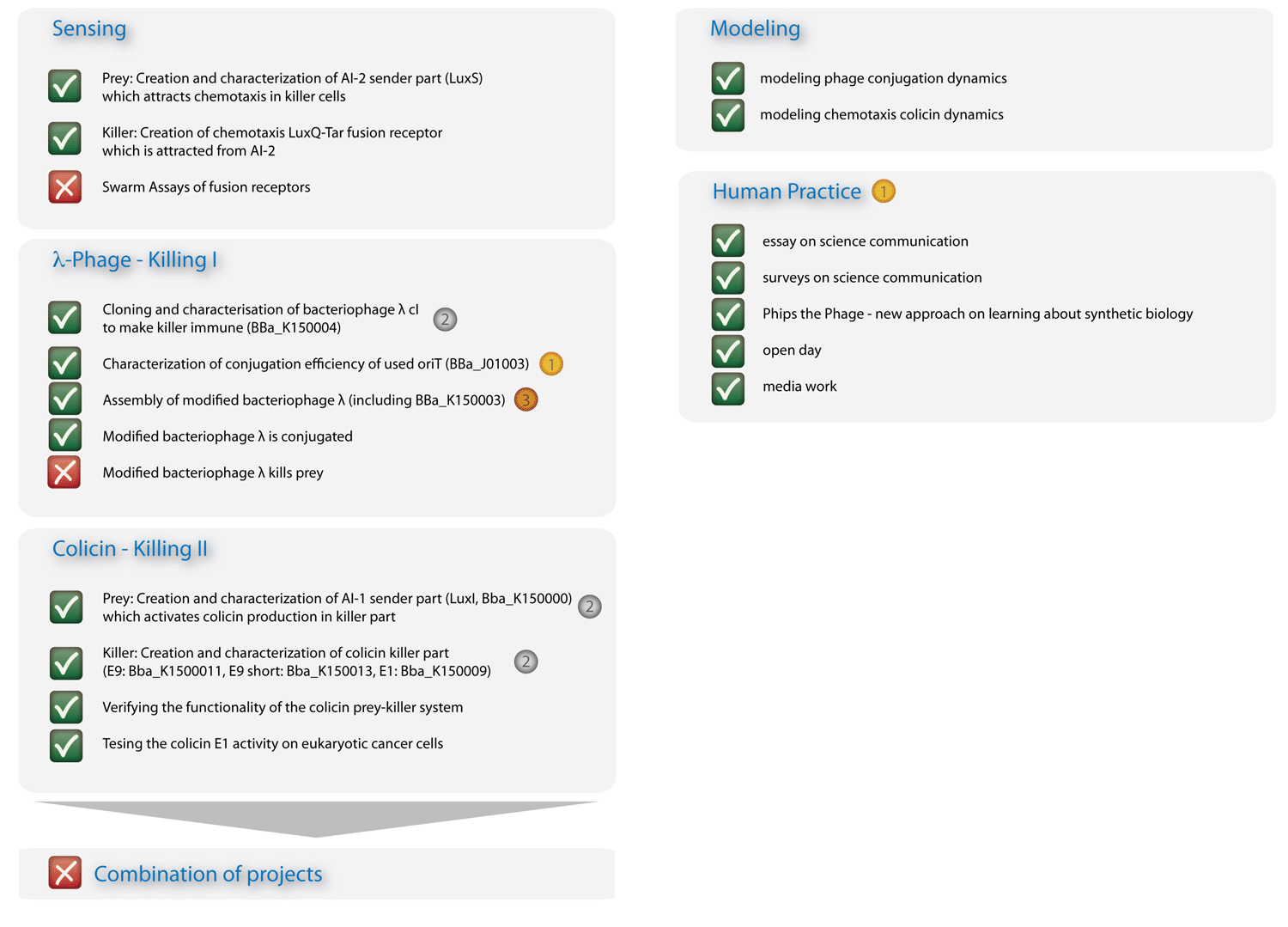
| - | + | In Figure 3 you can see the essence of our project: The sensing column could be advanced significantly, though efficient chemotaxis towards AI-2 could not be established. The phages are conjugated efficiently, though a killing of the prey could not yet be experimentally implemented. The colicin column and the modeling, however, worked out in all respects, and the human practice work has found enthusiastic resonance. With seven new standardized Biobrick parts, all of them have been shown to work, four characterized new parts and one characterized old part, we will run a high pace for the hottest awards at the championship jamboree in one week! | |
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | [[Image:HD_overview2_klein.png|left|650px|thumb|Fig. 3: Overview on project advancements. The colicin, the modeling, and the human practice columns are immaculate.]] | |
| - | + | ||
| + | [[https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Project back]] | ||
| - | + | == Project Perspectives== | |
| - | + | This project is supposed to be a wet model for a mechanism of specific target finding and elimination, in particular of cancer cells. There is clear evidence that bacteria accumulate in tumor areas [4, 5]. One reason might be the immunosuppressive effect of the tumor. The possibility to discriminate cancer patients from breath samples [6, 7, 8] gives rise to the idea to use bacterial receptors for the recognition of specific molecular exudation patterns. The effect of bacterial accumulation might in this way be enhanced by the engineering of a pattern sensitive chemotaxis mechanism. Furthermore bacteria could be induced very specifically in the near environment of the tumor to metabolize a pre-curser into a tumor suppressive molecule. Both mechanisms, increased accumulation at tumor sites and tumor located drug metabolism, would lead to a potentiated selectivity for the elimination of cancer cells. If the toxin is then also cancer cell specific - as could be shown by Pastan ''et al.'' [9] - then three strong effects would fulminate into ... of course, all this is still music of the future - but we are sure: it will be the future! | |
| - | [[ | + | [[https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Project back]] |
| - | + | == Literature == | |
| - | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| + | |- valign=top | ||
| + | |[1] || width=500px |K. Brenner ''et al.'', Engineered bidirectional communication mediates a consensus in a microbial biofilm consortium, ''PNAS'', Vol. 104 (44), pp. 17300-17304 (2007) | ||
| + | |- valign=top | ||
| + | |[2] || G. H. Wadhams and J. P. Armitage, Making sense of it all: bacterial chemotaxis, ''Nat. Rev. Mol. Cel. Bio.'', Vol. 5, pp. 1024-1037 (2004) | ||
| + | |- valign=top | ||
| + | |[3] || N. Wingreen and D. Botstein, Back to future: education for systems-level biologists, ''Nat. Rev. Mol. Cel. Bio.'', Vol. 7(11), pp. 829-832 | ||
| + | |- valign=top | ||
| + | |[4] || J. M. Pawelek ''et al.'', Bacteria as tumour-targeting vectors, ''The Lancet Oncology'', Vol. 4, pp. 548-546 (2003) | ||
| + | |- valign=top | ||
| + | |[5] || H. Loessner ''et al.'', Remote control of tumour-targeted ''Salmonella enterica'' serovar Typhimurium by the use of L-arabinose as inducer of bacterial gene expression ''in vivo'', ''Cellular Microbiology'', Vol 9 (6), pp. 1529-1537 (2007) | ||
| + | |- valign=top | ||
| + | |[6] || C. M. Willis ''et al.'', Olfactory detection of human bladder cancer by dogs: proof of principle study, ''Biomedical Journal'', Vol. 329 (2009) | ||
| + | |- valign=top | ||
| + | |[7] || M. Phillips ''et al.'', Detection of Lung Cancer with Volatile Markers in the Breath, ''Chest'', Vol. 123, pp. 2115-2123 (2003) | ||
| + | |- valign=top | ||
| + | |[8] || M. Phillips ''et al.'', Volatile organic compounds in breath as markers of lung cancer: a cross-sectional study, ''The Lancet'', Vol. 353, pp. 1930-1934 (1999) | ||
| + | |- valign=top | ||
| + | |[9] || I. Pastan and D. Fitzgerald, Recombinant Toxins for Cancer Treatment, ''Science'', Vol. , pp. 1173-1177 (1991) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| - | [[ | + | [[https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Project back]] |
| - | + | |width="250px"| | |
| - | | | + | [[image:Phips_phage.PNG|middle|200px|Phips the Phage]] |
| + | |||
| + | Hi, you are new here and hear about synthetic Biology for the first time? Perfect! I am Phips the Phage and will be your guide to this exciting field of biological research and if you like I will explain the background synthetic biology and gentic engineering as well as of this project to you. Just follow me[[Team:Heidelberg/Human_Practice/Phips_the_Phage/|'''... follow Phips''']] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:52, 29 October 2008


Project IdeaEcolicence to kill: Engineering E.coli for targeting pathogenic microorganisms Pathogenic microorganisms represent a major challenge to both medicine and industry. Microbial communities known as biofilms prove to be particularly resistant to conventional therapies [1] and demonstrate the need for alternative methods to fight bacterial growth. The formation of biofilms, as well as other processes such as virulence, antibiotic production, and sporulation, are regulated by communication circuits that depend on small signalling molecules called autoinducers. Our aim is to exploit this communication mechanism by engineering synthetic bacteria that are able to target potentially harmful autoinducer-secreting species and kill them. Working with E. coli as a model system, we plan to engineer separate “killer” and “prey” cells, and divide our project into two complementary modules. The “sensing module” comprises the modification of E. coli’s chemotaxis [2] system to make killer cells move towards prey cells. This requires the engineering of a “sensing module” which propagates a prey-specific stimulus to the downstream signalling cascades, prompting the cells to swim towards the gradient of such a stimulus. The directed swimming stops only in the region where the stimulus is maximal, i.e. in the vicinity of the prey. The “killing module” ensures that once in the vicinity of the prey, a bacteriocidal mechanism is activated. Computer models will show how both modules behave in concert and probe the efficiency of the system in defined spatial environments. Future directions, which are beyond the scope of this project, include the modification of the sensory and killing modules, adjusting the range of targets to real pathogens, but also other organisms, specific cell types or even cancer cells. [back] You are very interested in this exciting project, but did not understand all details? Well then come on with me on my guiding tour ... follow phips to step 3
Deutsche Übersetzung:
Ecolizenz zum Töten: Eine E. coli-Konstruktion zum gezielten Angriff auf pathogene Mikroorganismen Pathogene Mikroorganismen stellen eine große Herausforderung sowohl für die Medizin als auch für die Industrie dar. Gemeinschaften aus Mikroorganismen, die in der Fachsprache als Biofilme bezeichnet werden, haben sich als äußerst resistent gegenüber konventionellen Therapien erwiesen [1]. Um deren Wachstum zu bekämpfen bedarf es daher alternativen Ansätzen. Die Entstehung von Biofilmen, genauso wie die der Virulenz, die Produktion von Antibiotika oder die Bildung von Sporen werden durch Kommunikations-Schaltkreise reguliert, die auf kleinen Signalmolekülen - den sogennanten Autoinduzierern (AI) - basieren. Unser Ziel ist es, diese Kommunikationsmechanismen in der Weise zu integrieren, dass synthetische Bakterien potenziell gefährliche, AI-ausschüttende Spezies aufspüren und töten können. Mit E. coli als Modellorganismus beabsichtigen wir zwei separate Stämme - einen Killer- und einen Beutestamm - zu entwerfen. Das Projekt gliedert sich in zwei ergänzende Module: Die Signalerkennung umfasst die Modifizierung des Chemotaxis-Systems von E. coli [2], um Killer-Zellen zu den Beute-Zellen schwimmen zu lassen. Dafür ist es notwendig, dass ein Erkennungsmodul einen Beute-spezifischen Stimulus an die Signalkaskade für Chemotaxis weiterleitet, so dass die Killer-Zellen entgegen des Gradienten des Stimulus schwimmen. Das gerichtete Schwimmen kommt nur zum Erliegen, wenn sich die Killer-Zellen in der unmittelbaren Umgebung der Beute-Zellen befinden - dort, wo die Stimuluskonzentration maximal ist. Das Killer-Modul gewährt, dass - einmal in der Nähe der Beute angekommen - ein bakterizider Mechanismus aktiviert wird. Computermodelle werden ergänzend zeigen, wie sich die beiden Modelle im Zusammenspiel verhalten, und wie die Effizienz des Gesamtsystems in seiner räumlichen Umgebung einzuschätzen ist. In Zukunft - sicherlich außerhalb der Reichweite unseres Projekts - könnte die Spezifität auf relevante Pathogene, genauso wie auf andere Organismen, Gewebe oder sogar Krebszellen erweitert werden.[back] Project RealizationHave you ever wondered, why numbers of iGEM team members are limited to a maximum of twelve students? Apart from financial resources, this limit is only natural: efficient work with larger team sizes requires a subtle organization and project management, in particular when the team is yet green! On top, team formation and project work have to be conducted within a short time interval and under liabilities to the academic curriculum - both on the student and the advisor sides. The social abilities for reliable team formation, in particular communication, team integration, and consequence to work towards common team goals, must therefore be substantial and dedicated to compensate these circumstances. When you visit our portraits, however, you will realize that we are not really green and that each of us has an active past often intricately connected with scientific work. In our project description we provide a sincere answer to the apparent question, if 16 "greenhorns" can push forward in only four months to contribute research on an international level! In order to streamline our horse-power, we divide the project into four columns, which are simultaneously developed by us and can merge in the end with a synergistic effect to a complex population system (modeling inclusive). At the same time the global progress is robust towards each column, consequently a delay or failure in one column will not lead to a breakdown of the overall project. In accordance with current scientific standards demanded in systems and synthetic biology, we pursue an interdisciplinary approach combining mathematics, experimental, and quantitative biology [3]. The first column (Project - Sensing) comprises the design and development of a sensing module. Chemotaxis is a very effective mechanism of bacteria to move towards nutrients. Using the natural signals for bacterial quorum communication, we re-design a chemotactic receptor for detection of the quorum signal (AI-2) and its transmission to the chemotaxis signaling network. A prey strain, which is to be found via the sensing mechanism, will be engineered to secrete two prey specific quorum signals (AI-1 and AI-2). We dedicate two columns to the development of a killing mechanism to secure a higher implementation confidence: In one column, the second (Project - Killing I/Phages), a killing mechanism is developed based on bacteriophages, which are conjugated into prey cells, once the killers are in their vicinity. In prey cells, however, the phage becomes lytic due to the missing regulation of the cI transcription factor; the phage is thereby released and infects other prey cells in a domino effect. The killing module in the third column (Project - Killing II/Colicins) can be considered as a mechanism for recognition of molecular exudation patterns. Once killer cells are in the vicinity of preys, they detect the specific signal molecule AI-1, which leads to the production and release of colicins. The bactericide substance, to which the producing host is resistant, will then eliminate the prone prey. In a fourth column (Modeling) we model the system behavior of these two bacterial strains - the killer and the prey - in a 2D landscape. One approach is based on partial differential equations and simulates chemotaxis and the colicin killing mechanism; the second approach, based on delay differential equations, analyzes the killing dynamics of conjugated bacteriophages. Visualization - the architrave - with microscopy is finally employed to quantify bacterial density landscapes in space and time - allowing a phenotypic connection and comparison with our modeling work. An experimental engagement would these days of course not be appreciable without the active responsibility towards the sake of the community under ethical considerations. We therefore actively engage in human practice ... and the pupils are enthusiastic! In Figure 3 you can see the essence of our project: The sensing column could be advanced significantly, though efficient chemotaxis towards AI-2 could not be established. The phages are conjugated efficiently, though a killing of the prey could not yet be experimentally implemented. The colicin column and the modeling, however, worked out in all respects, and the human practice work has found enthusiastic resonance. With seven new standardized Biobrick parts, all of them have been shown to work, four characterized new parts and one characterized old part, we will run a high pace for the hottest awards at the championship jamboree in one week!
[back] Project PerspectivesThis project is supposed to be a wet model for a mechanism of specific target finding and elimination, in particular of cancer cells. There is clear evidence that bacteria accumulate in tumor areas [4, 5]. One reason might be the immunosuppressive effect of the tumor. The possibility to discriminate cancer patients from breath samples [6, 7, 8] gives rise to the idea to use bacterial receptors for the recognition of specific molecular exudation patterns. The effect of bacterial accumulation might in this way be enhanced by the engineering of a pattern sensitive chemotaxis mechanism. Furthermore bacteria could be induced very specifically in the near environment of the tumor to metabolize a pre-curser into a tumor suppressive molecule. Both mechanisms, increased accumulation at tumor sites and tumor located drug metabolism, would lead to a potentiated selectivity for the elimination of cancer cells. If the toxin is then also cancer cell specific - as could be shown by Pastan et al. [9] - then three strong effects would fulminate into ... of course, all this is still music of the future - but we are sure: it will be the future! [back] Literature
[back] |
Hi, you are new here and hear about synthetic Biology for the first time? Perfect! I am Phips the Phage and will be your guide to this exciting field of biological research and if you like I will explain the background synthetic biology and gentic engineering as well as of this project to you. Just follow me... follow Phips |
 "
"