Team:Heidelberg/Project/Visualization
From 2008.igem.org
(→Killing - Colicin) |
(→Microscopic Scanning and Quantification of 2D bacterial landscapes) |
||
| (82 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 467: | Line 467: | ||
==Killing - Colicin== | ==Killing - Colicin== | ||
| - | Time series of killer and prey bacteria over 48 hours. Killer cells are marked with mCherry (red) and prey bacteria are marked with GFP (green). The intial ratio is 1:1, which can be recognized on the second and third frame (8h and 12h, respectively). Many prey and killer bacteria are grown after | + | Time series of killer and prey bacteria over 48 hours. Killer cells are marked with mCherry (red) and prey bacteria are marked with GFP (green). The intial ratio is 1:1, which can be recognized on the second and third frame (8h and 12h, respectively). Many prey and killer bacteria are grown after 38 hours (last three image frames). However, the faint green fluorescence (it is sharp!) indicates the weak prey metabolism due to the toxin. Toxin production and excretion is activated in killer bacteria by the signaling molecule autoinducer-1 (visit [https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Project/Killing_II Project - Colicins] for more biological information). |
<html> | <html> | ||
| Line 475: | Line 475: | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
| - | To see separate images click [[2008.igem.org/Team Heidelberg/timeseriescolicin| here]] | + | For viewing this video, the [http://www.apple.com/quicktime/download/| QickTime Player] (free on apple.com) is required. To see separate images click [[2008.igem.org/Team Heidelberg/timeseriescolicin| here]]. |
| + | |||
| + | [[https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Project/Visualization back]] | ||
== Microscopic Scanning and Quantification of 2D bacterial landscapes == | == Microscopic Scanning and Quantification of 2D bacterial landscapes == | ||
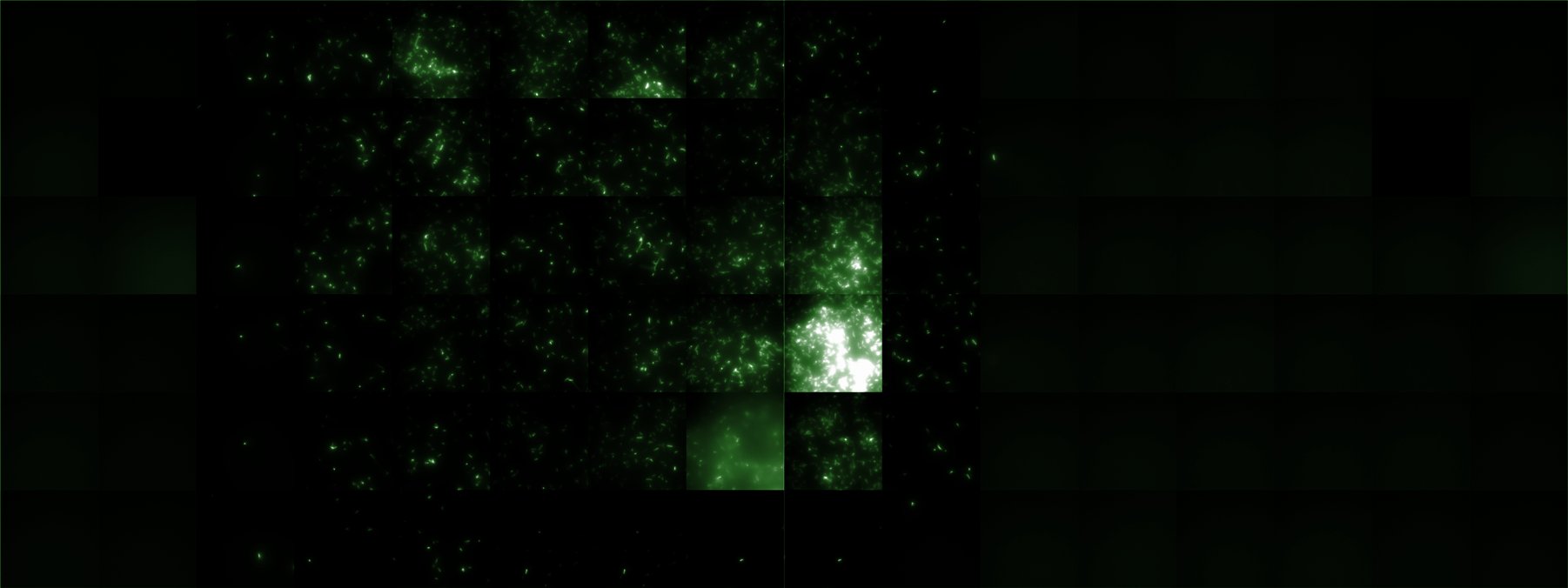
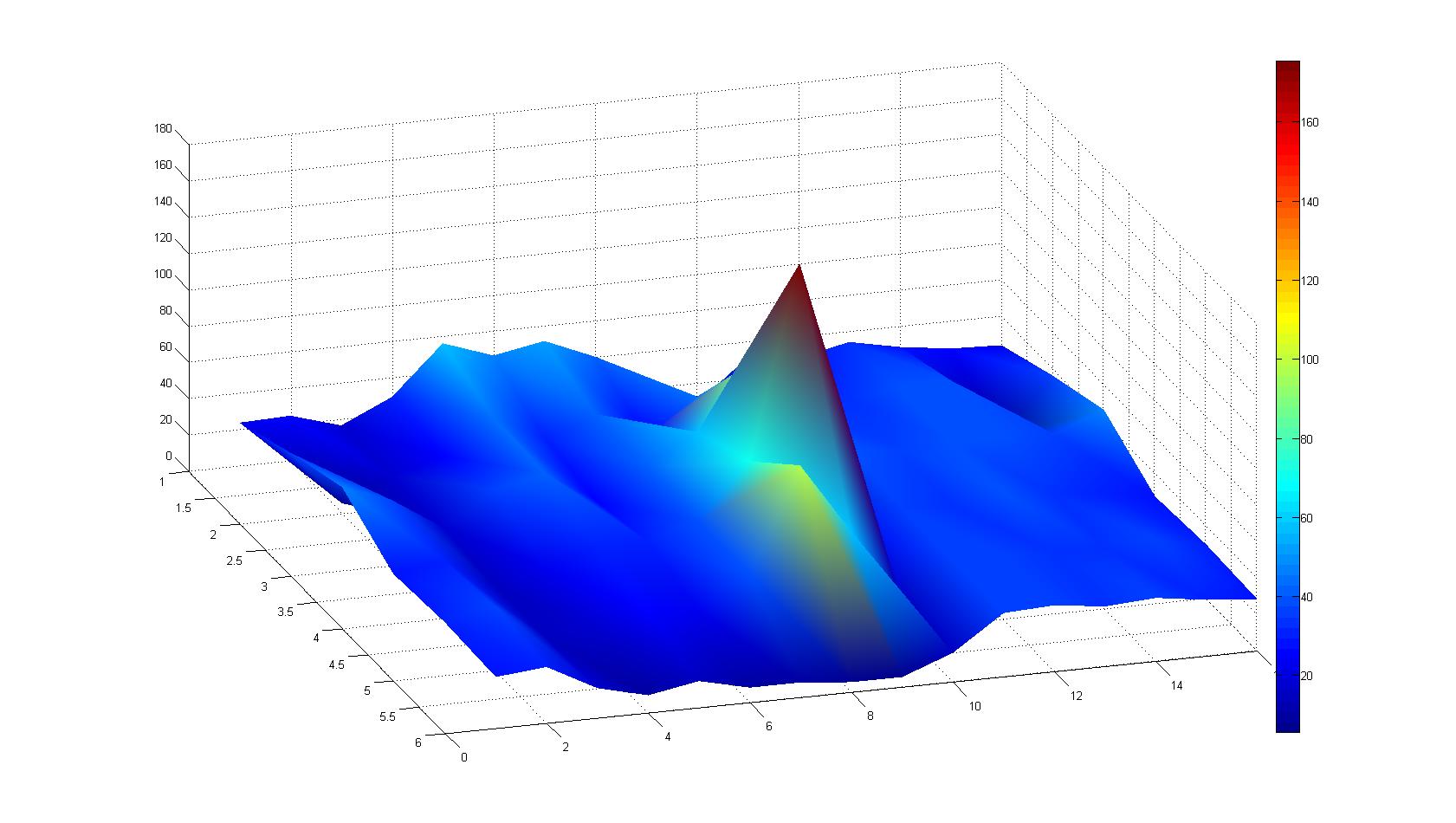
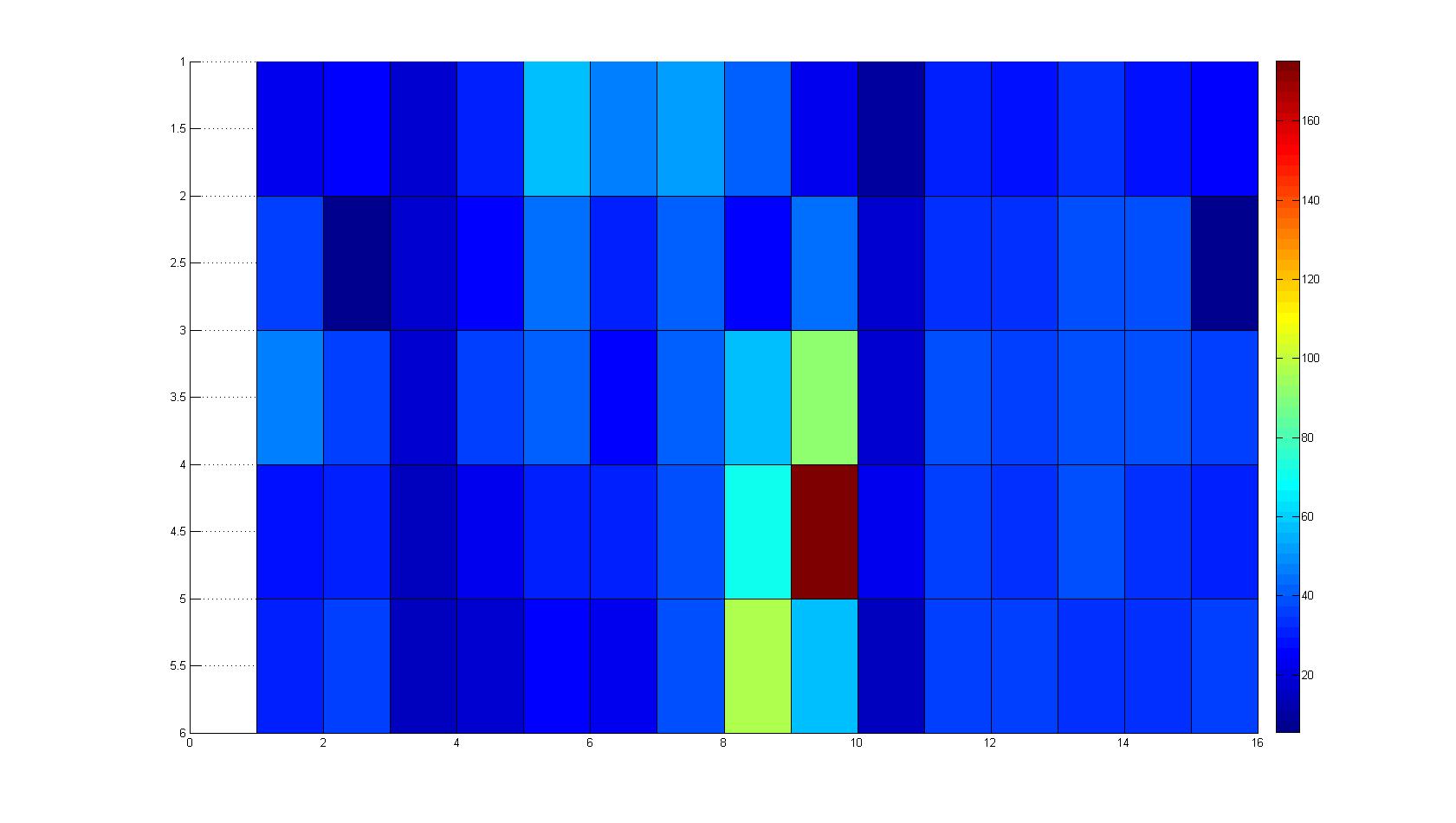
| - | A scan of the bacterial density in soft agar chamber (visit [https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Notebook/visualization Notebook - Visualization] for more technical information). For a proof of principle the chemotactic ''E. coli'' strain HCB33 is applied in the middle of the chamber. On the left side of the chamber is a 2% agar plug containing 10% of casamino acids. | + | A scan of the bacterial density in a soft agar chamber (visit [https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Notebook/visualization Notebook - Visualization] for more technical information). For a proof of principle the chemotactic ''E. coli'' strain HCB33 is applied in the middle of the chamber. On the left side of the chamber is a 2% agar plug containing 10% of casamino acids. |
| - | After | + | After 21 hours the bacteria accumulate around the plug, because they sense the established gradient of amino acids. Calculation of the mean of each image and subtraction of the background leads to a quantitative 2D representation of the bacterial density landscape. This data can be compared to the 2D chemotactic modeling results based on a system of partial differential equations (visit [https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Modeling/Chemotaxis Modeling - Chemotaxis/Colicins)]. In simulations the chemotaxis velocity is approximately 1mm per 10 min, which is about six times faster than the experimental oberservation. Experimental feedback can therefore be used to fine-tune the chemotaxis model parameters. |
Remark: The scans are taken from two different experiments with equal settings due to the difficult adjustment of a constant focus. | Remark: The scans are taken from two different experiments with equal settings due to the difficult adjustment of a constant focus. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === After 3 hours === | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | + | |width=450px | [[Image:landscape1.jpg|800px|left|thumb|Fig. 1: Microscopic Scan of the 2D density landscape three hours after addition of chemotactic bacteria in the center of the chamber. On the left end of the chamber a 2% agar plug containing 10% casamino acids is fixed.]] || | |
| - | + | ||
| - | |width=450px | [[Image:landscape1.jpg| | + | |
|- | |- | ||
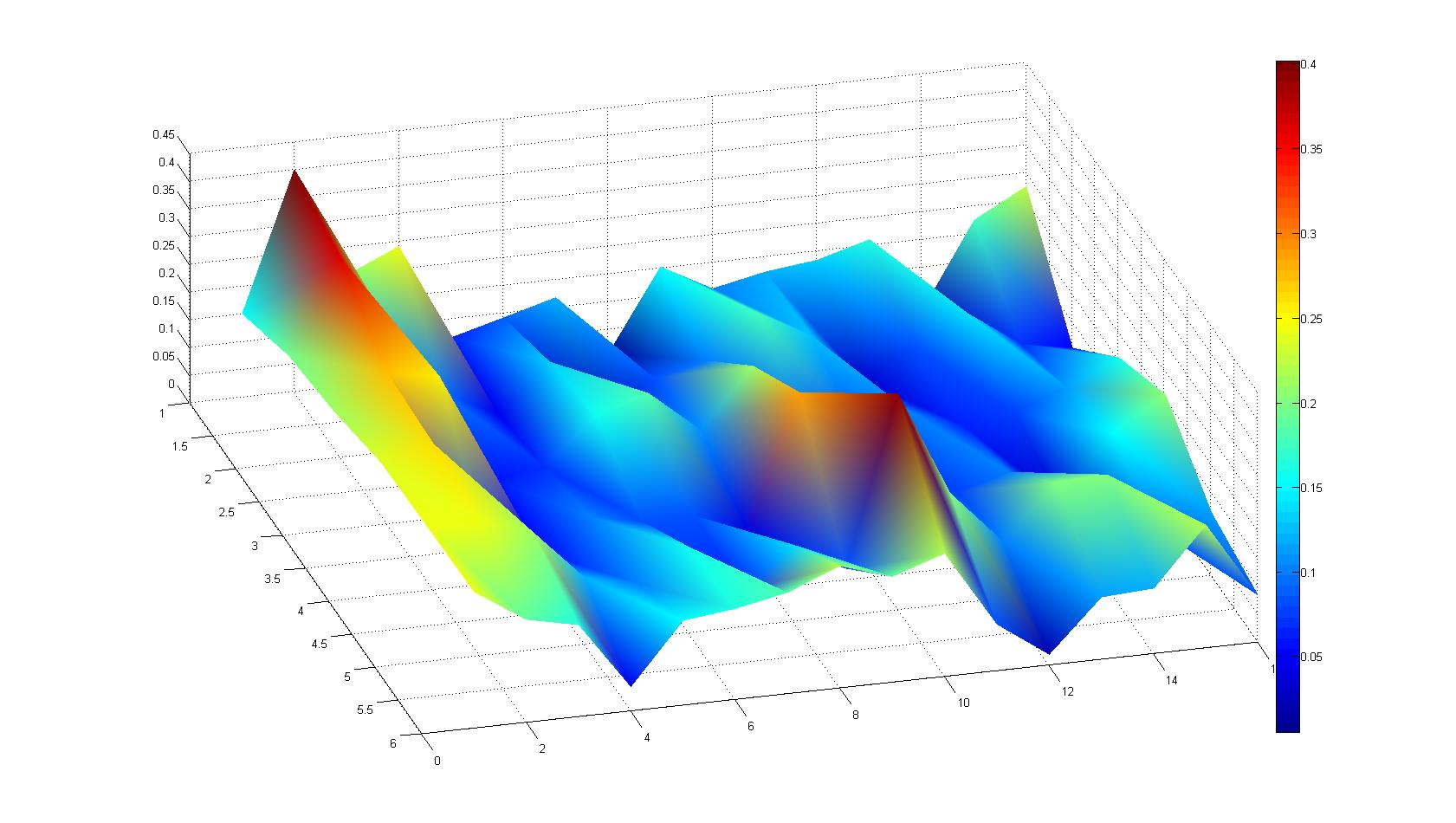
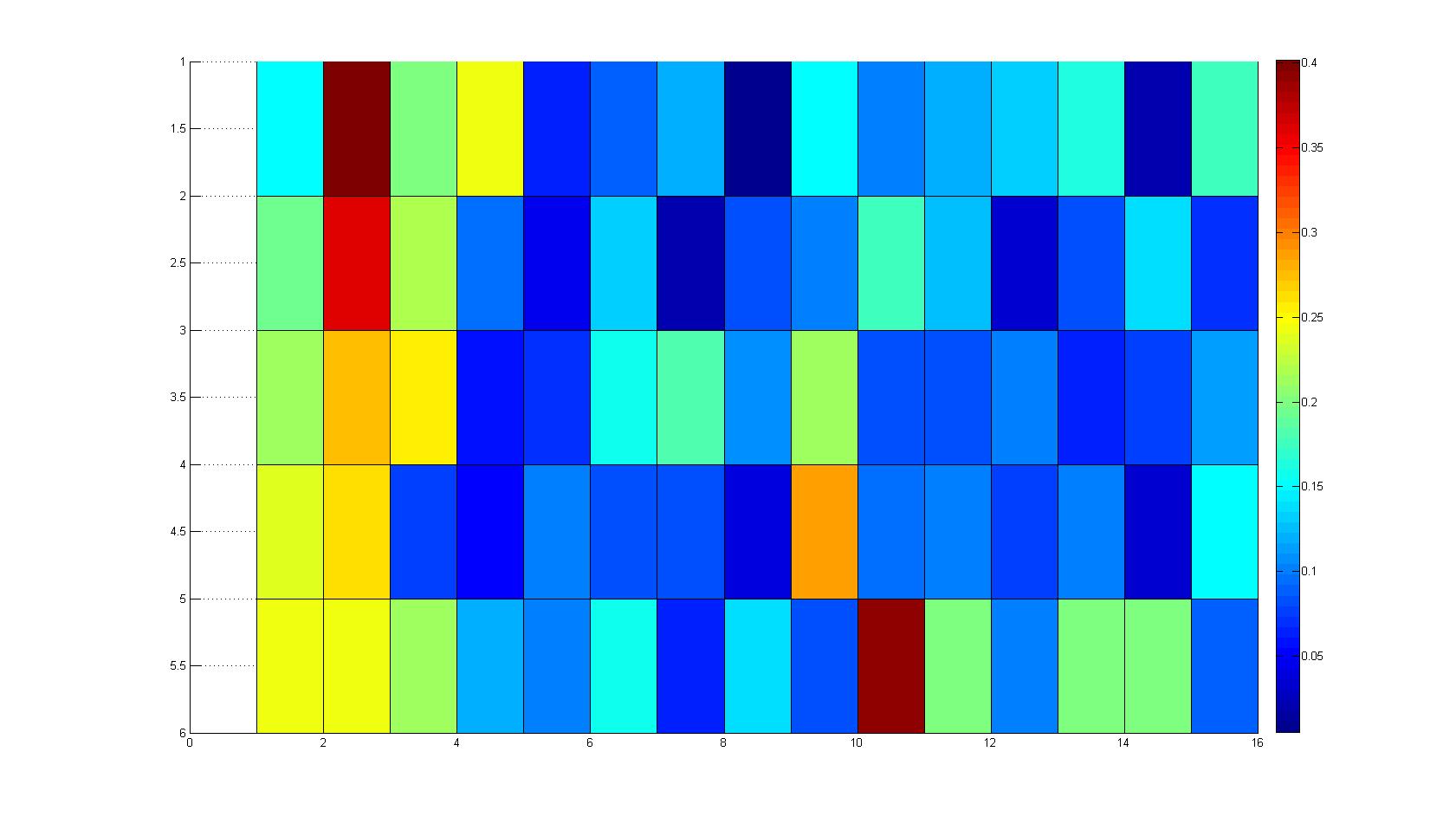
| - | |width=450px | [[Image:graph11.jpg| | + | |width=450px | [[Image:graph11.jpg|350px|left|thumb|Fig. 2: Bird view of microscopic scan after 0 hours. Quantification of each image from Figure 1 is done by calculation of the image mean minus the background.]] [[Image:graph12.jpg|350px|left|thumb|Fig. 3: Top view of Figure 2.]] |
|- | |- | ||
| - | |After | + | |} |
| + | |||
| + | === After 21 hours === | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | |width=450px | [[Image:Landscape2.jpg| | + | |width=450px | [[Image:Landscape2.jpg|800px|left|thumb|Fig. 4: Microscopic scan of density distribution after 21 hours. The bacteria accumulate around the plug (dark image in second left column).]] || |
|- | |- | ||
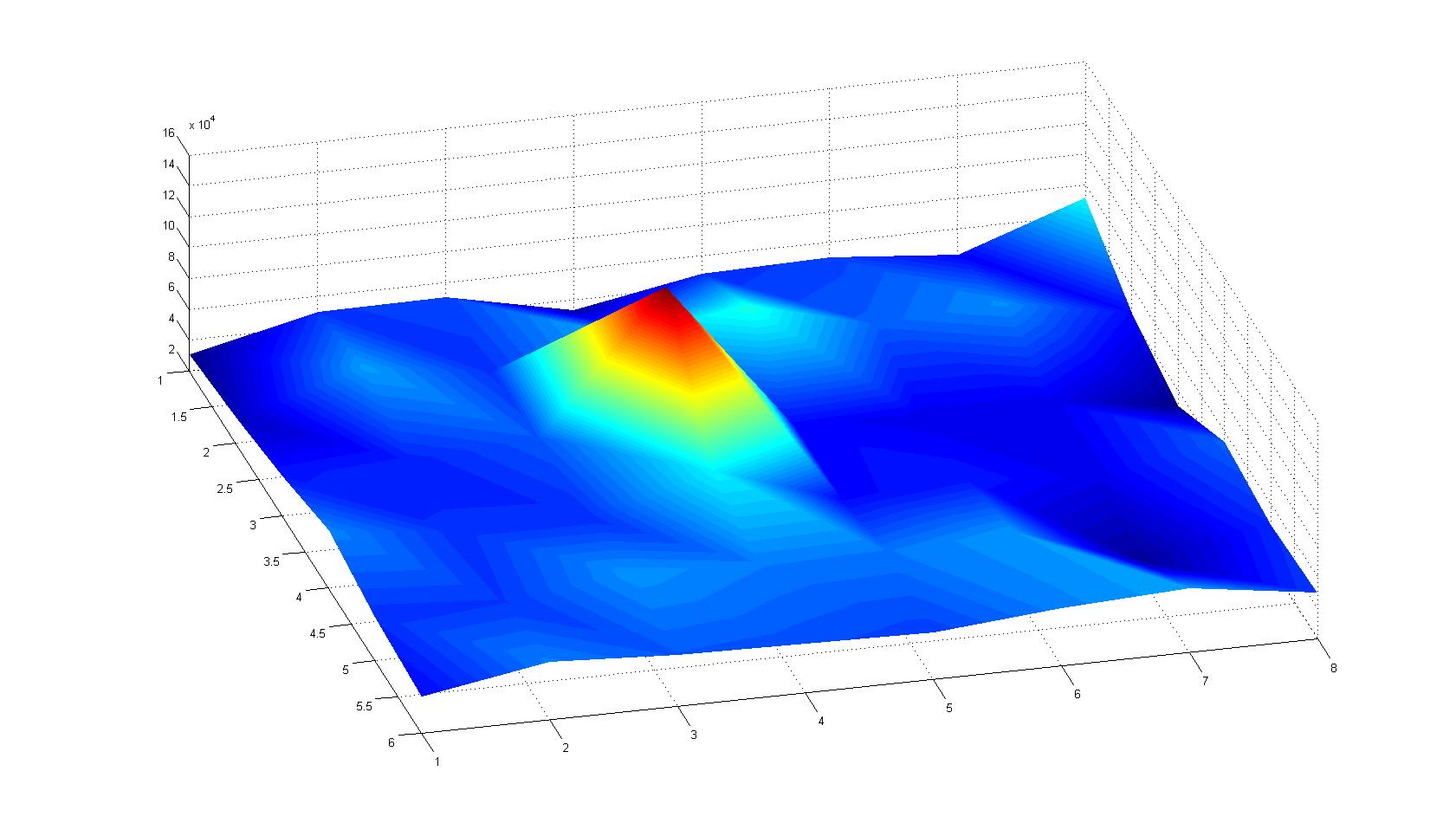
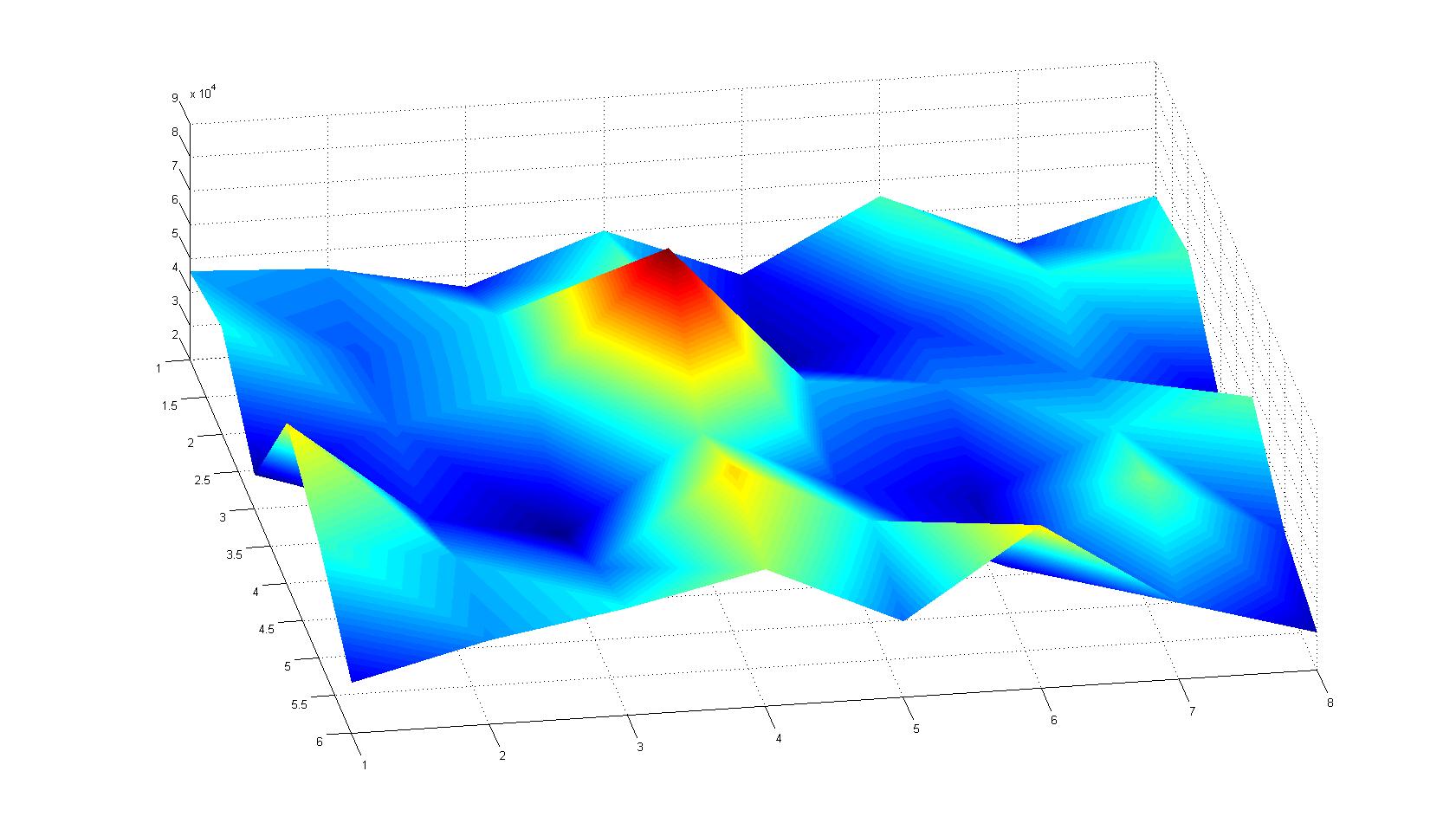
| - | |width=450px | [[Image:graph21.jpg| | + | |width=450px | [[Image:graph21.jpg|350px|left|thumb|Fig. 5: Bird view of microscopic scan in Figure 4.]] [[Image:graph22.jpg|350px|left|thumb|Fig. 6: Top View. Compare to Figure 5.]] |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | [[https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Project/Visualization back]] | ||
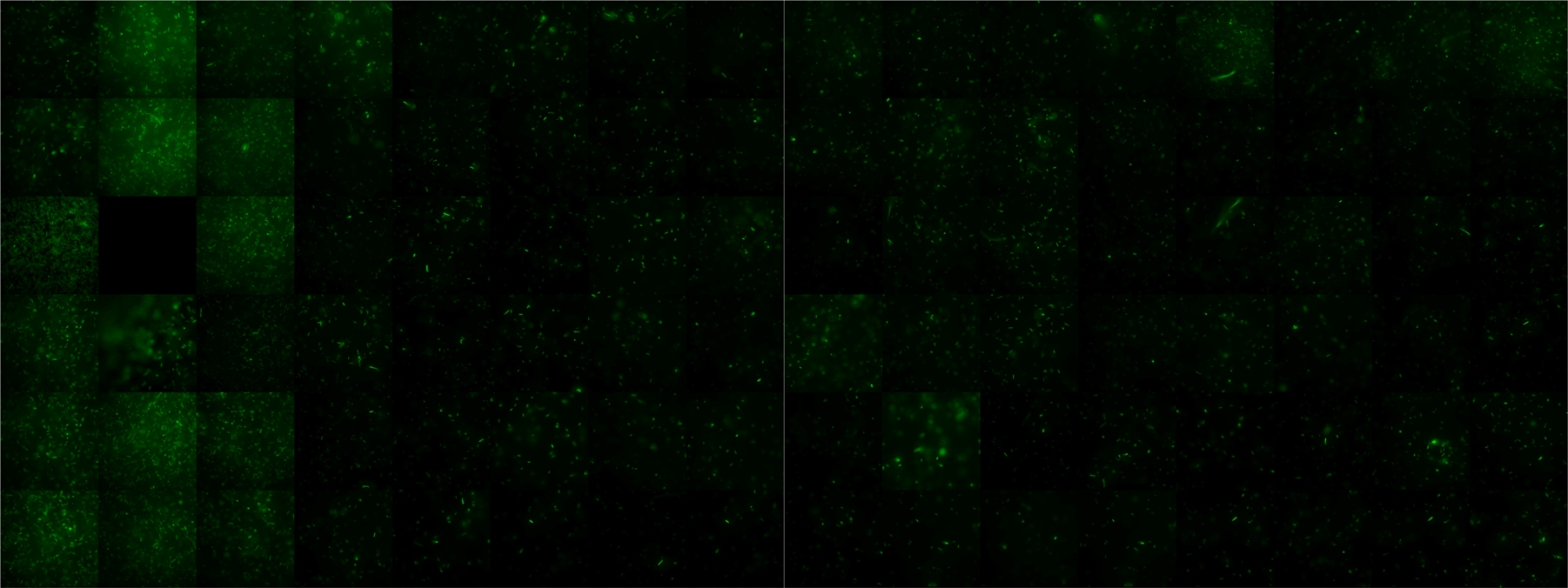
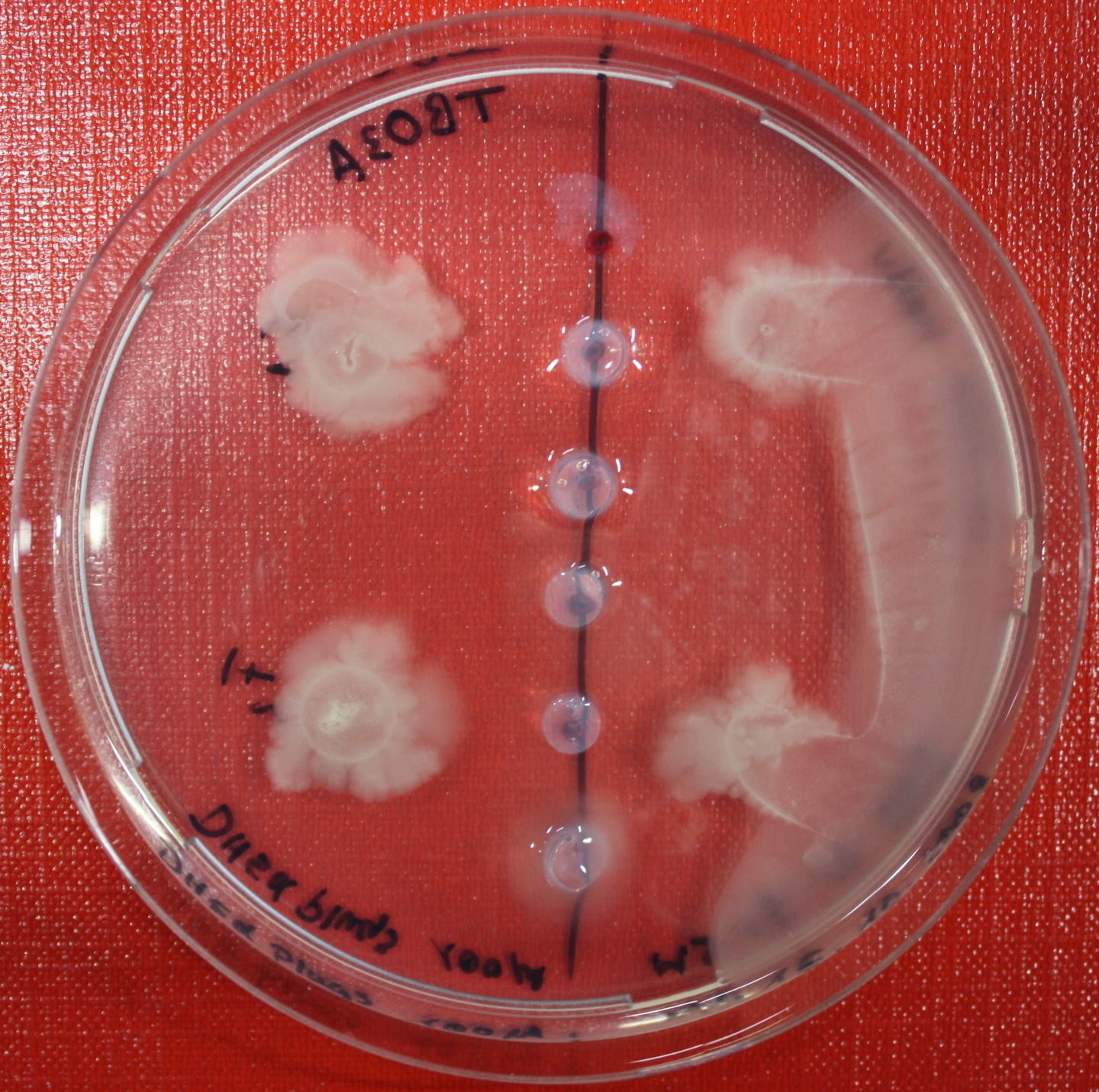
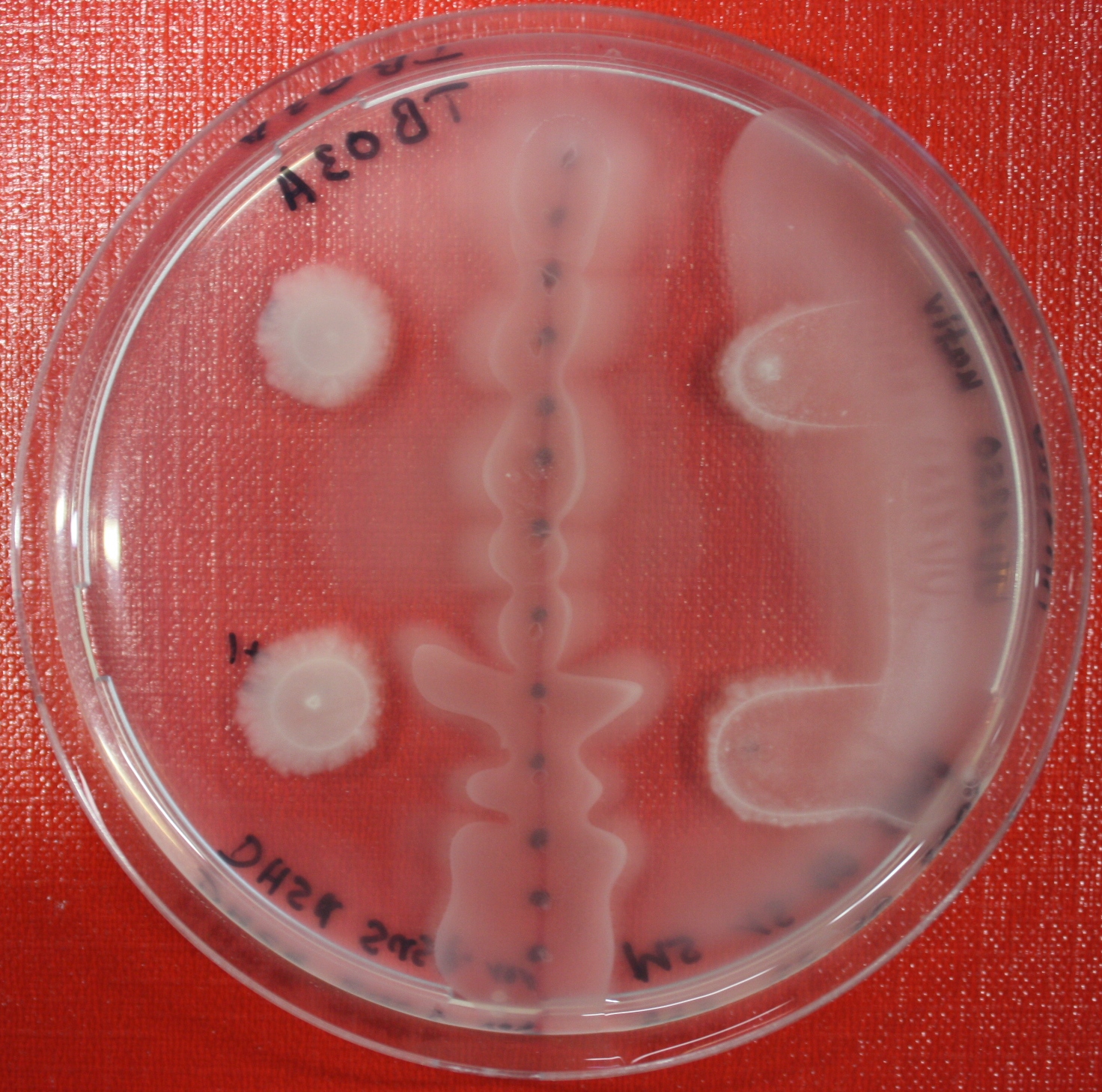
== Sensing test of Fusion Receptor with 2D Microscopy == | == Sensing test of Fusion Receptor with 2D Microscopy == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sensitivity of fusion constructs to AI-2 is analyzed in fluorescent UU1250 (lacking all natural chemotaxis receptors) and HCB33 strains. Images are taken on a wide-field Delta-Vision microscope in LabTek chambers with minimal medium containing 0.2% agar (2 ml). As attractant either 3 µl of AI-2 producing cells (strain DH5alpha, OD=0.4, induced with 100 nM IPTG), are spotted at the left side of the chamber. A gradient is established during incubation for 12-16 hours at 4 °C. Afterwards either fusion receptor expressing UU1250 cells (0.01% arabinose induced overnight) are spotted at the center of the chamber. The chamber is then incubated for three hours at 30 °C. In this setting no chemotactic efficiency can be observed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === After 0 hours === | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |width=450px | [[Image:Landscape3.jpg|400px|left|thumb|Fig. 7: UU1250 cells expressing fusion receptors. On the left side of the image]]|| width=450px | [[Image:graph31.jpg|350px|left|thumb|Fig. 8: Bird view of microscopic scan in Figure 7.]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | === After 3 hours === | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |width=450px | [[Image:Landscape4.jpg|400px|left|thumb|Fig. 10]]||width=450px | [[Image:graph41.jpg|350px|left|thumb|Fig. 11: Bird view of microscopic scan in Figure 10.]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Project/Visualization back]] | ||
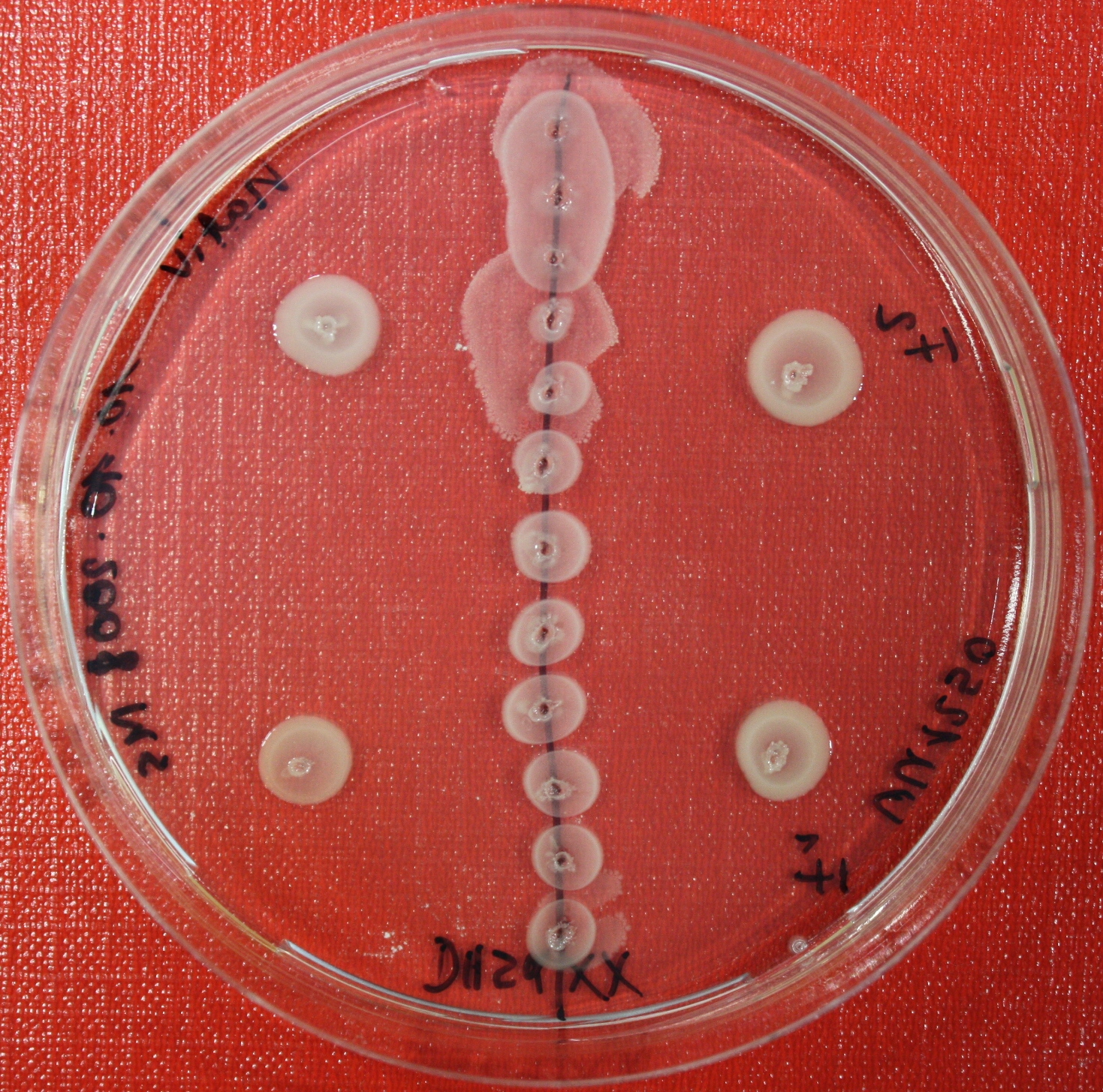
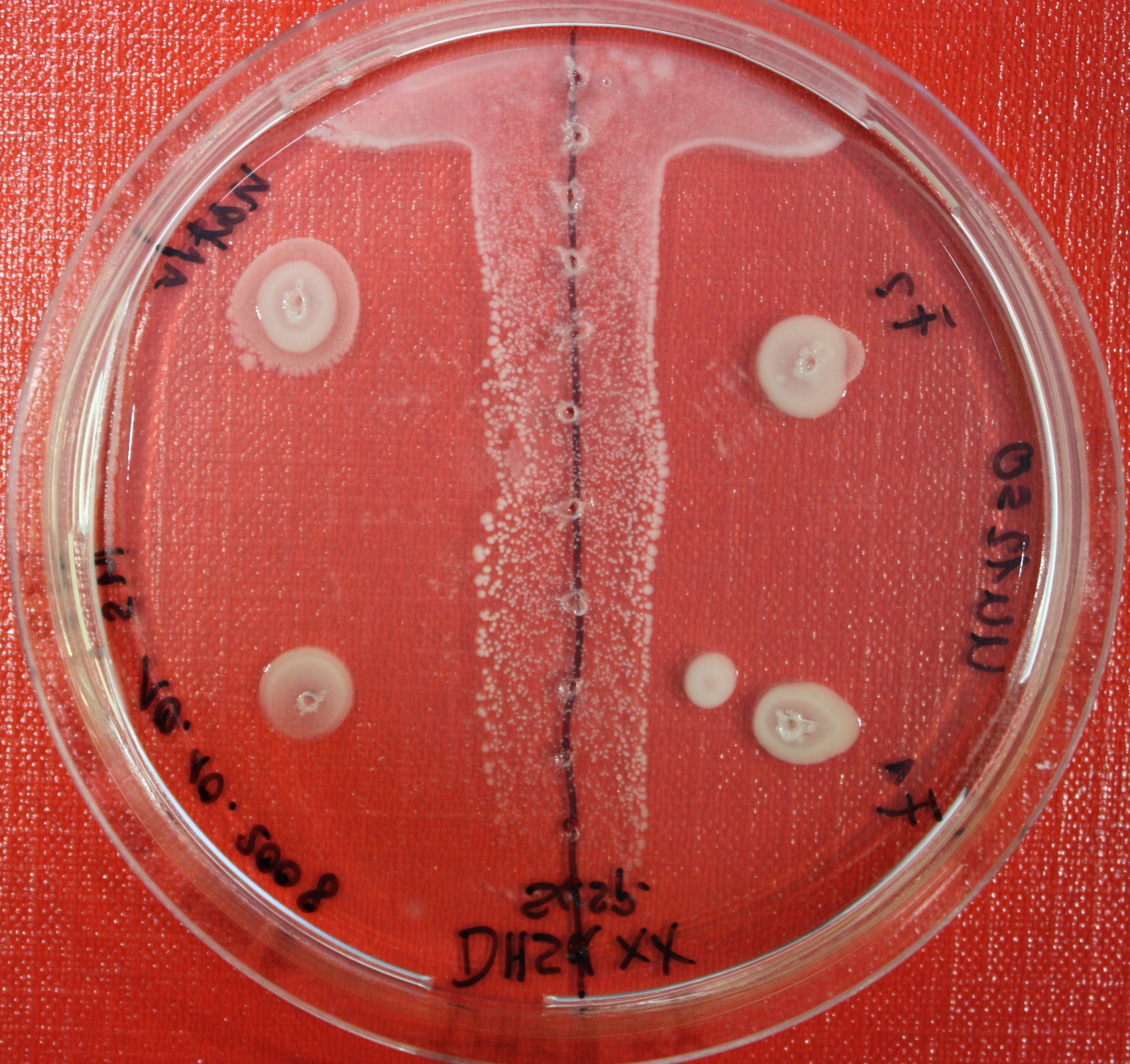
== Sensing test of Fusion Receptor with Swarm Plates == | == Sensing test of Fusion Receptor with Swarm Plates == | ||
| + | |||
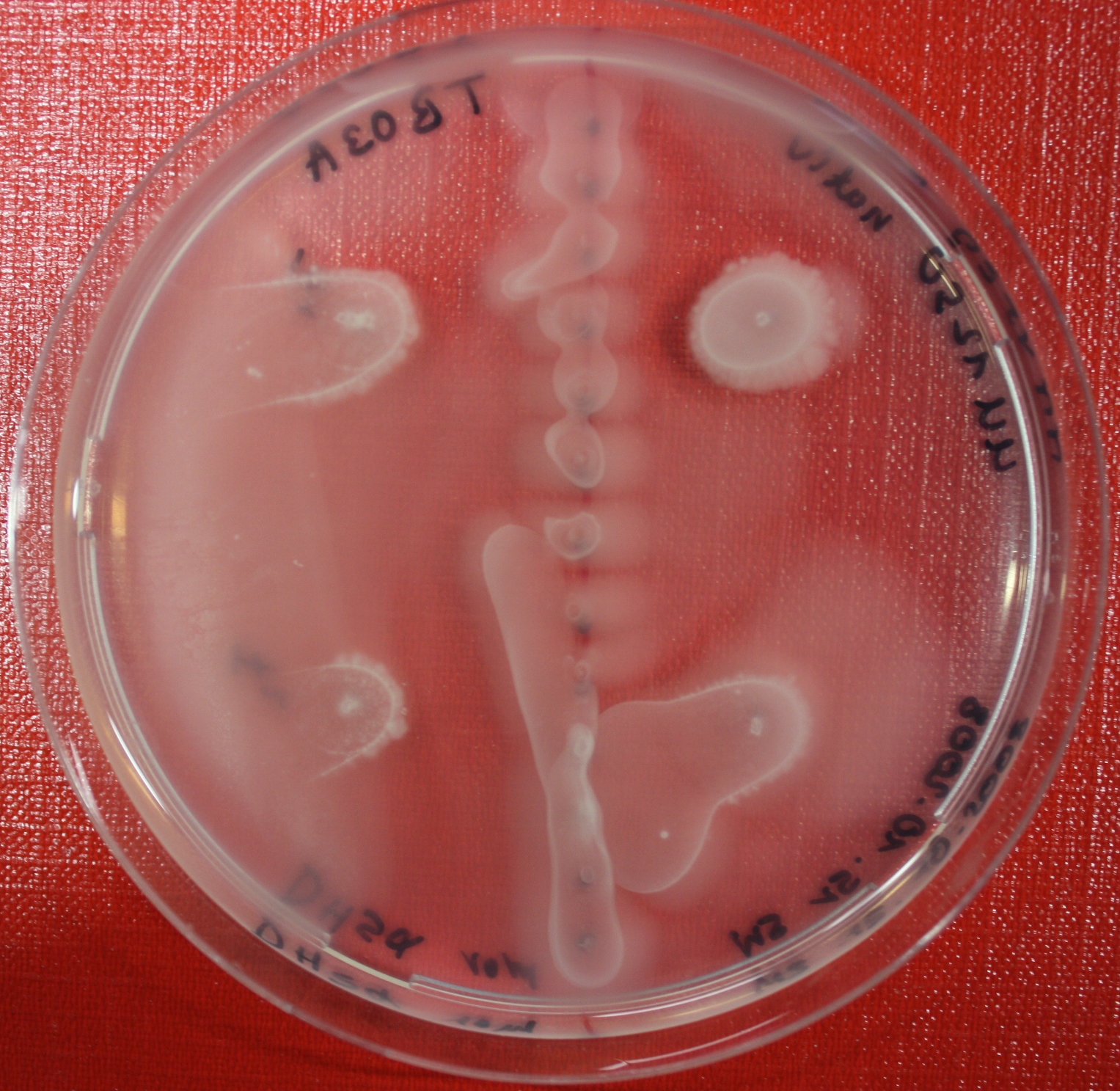
| + | Swarm assays are done to test the sensitivity of the fusion receptor to AI-2. Two different strains are used: UU1250 and HCB33. The assays are conducted in TB medium containing 0.2% or 0.3% agar. As attractant either 3 µl of AI-2 producing cells (strain DH5alpha, OD=0.4), induced with 100 nM IPTG, or 10 µl supernatant from those cells are spotted 13 times on the plate to create a center line. The gradient of AI-2 is established within 12-16 hours during incubation at 4 °C. The fusion receptor expressing UU1250 cells (induced with 0.01% arabinose overnight) as well as non-chemotactic reference strains were spotted at a distance of 3-3.5 cm from the attractant line. Swarm plates were incubated at 30 °C and pictures taken after 24 or 72 hours. Chemotactic efficiency can not be observed yet. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:sensing_swarmassay1.JPG| 150px | thumb| Fig. 12: Swarm Assay after 24 hours. On the right side UU1250 expressing the fusion receptor, on the left side native UU1250, both against AI-2 producing cells. Agar concentration 0.3%. ]] | ||
| + | |[[Image:sensing_swarmassay2.JPG| 150px | thumb| Fig. 13: Swarm assay after 24 hours. On the right side UU1250 expressing the fusion receptor on the left side UU1250 native, both against supernatant of AI-2 producing cells.]] | ||
| + | |[[Image:sensing_swarmassay3.JPG| 150px | thumb| Fig. 14: Swarm assay after 72 hours. On the left side UU1250 expressing the fusion receptor on the right side UU1250 native, both against AI-2 producing cells. ]] | ||
| + | |[[Image:sensing_swarmassay4.JPG| 150px | thumb| Fig. 15: Swarm assay after 72 hours. On the left side UU1250 expressing the fusion receptor on the right side UU1250 native, both against AI-2 producing cell ]] | ||
| + | |[[Image:sensing_swarmassay5.JPG| 150px | thumb| Fig. 16: Swarm assay after 72 hours. On the left side UU1250 with fusion receptor and on the right side native UU1250, center attractant AI-2 plugs (100 µl AI-2)]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | [[https://2008.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Project/Visualization back]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:17, 29 October 2008


Contents |
Killing - Colicin
Time series of killer and prey bacteria over 48 hours. Killer cells are marked with mCherry (red) and prey bacteria are marked with GFP (green). The intial ratio is 1:1, which can be recognized on the second and third frame (8h and 12h, respectively). Many prey and killer bacteria are grown after 38 hours (last three image frames). However, the faint green fluorescence (it is sharp!) indicates the weak prey metabolism due to the toxin. Toxin production and excretion is activated in killer bacteria by the signaling molecule autoinducer-1 (visit Project - Colicins for more biological information).
For viewing this video, the [http://www.apple.com/quicktime/download/| QickTime Player] (free on apple.com) is required. To see separate images click here.
[back]
Microscopic Scanning and Quantification of 2D bacterial landscapes
A scan of the bacterial density in a soft agar chamber (visit Notebook - Visualization for more technical information). For a proof of principle the chemotactic E. coli strain HCB33 is applied in the middle of the chamber. On the left side of the chamber is a 2% agar plug containing 10% of casamino acids. After 21 hours the bacteria accumulate around the plug, because they sense the established gradient of amino acids. Calculation of the mean of each image and subtraction of the background leads to a quantitative 2D representation of the bacterial density landscape. This data can be compared to the 2D chemotactic modeling results based on a system of partial differential equations (visit Modeling - Chemotaxis/Colicins). In simulations the chemotaxis velocity is approximately 1mm per 10 min, which is about six times faster than the experimental oberservation. Experimental feedback can therefore be used to fine-tune the chemotaxis model parameters.
Remark: The scans are taken from two different experiments with equal settings due to the difficult adjustment of a constant focus.
After 3 hours
| |
After 21 hours
[back]
Sensing test of Fusion Receptor with 2D Microscopy
Sensitivity of fusion constructs to AI-2 is analyzed in fluorescent UU1250 (lacking all natural chemotaxis receptors) and HCB33 strains. Images are taken on a wide-field Delta-Vision microscope in LabTek chambers with minimal medium containing 0.2% agar (2 ml). As attractant either 3 µl of AI-2 producing cells (strain DH5alpha, OD=0.4, induced with 100 nM IPTG), are spotted at the left side of the chamber. A gradient is established during incubation for 12-16 hours at 4 °C. Afterwards either fusion receptor expressing UU1250 cells (0.01% arabinose induced overnight) are spotted at the center of the chamber. The chamber is then incubated for three hours at 30 °C. In this setting no chemotactic efficiency can be observed.
After 0 hours
After 3 hours
[back]
Sensing test of Fusion Receptor with Swarm Plates
Swarm assays are done to test the sensitivity of the fusion receptor to AI-2. Two different strains are used: UU1250 and HCB33. The assays are conducted in TB medium containing 0.2% or 0.3% agar. As attractant either 3 µl of AI-2 producing cells (strain DH5alpha, OD=0.4), induced with 100 nM IPTG, or 10 µl supernatant from those cells are spotted 13 times on the plate to create a center line. The gradient of AI-2 is established within 12-16 hours during incubation at 4 °C. The fusion receptor expressing UU1250 cells (induced with 0.01% arabinose overnight) as well as non-chemotactic reference strains were spotted at a distance of 3-3.5 cm from the attractant line. Swarm plates were incubated at 30 °C and pictures taken after 24 or 72 hours. Chemotactic efficiency can not be observed yet.
[back]
 "
"