Team:Newcastle University/Notebook
From 2008.igem.org
Riachalder (Talk | contribs) |
Riachalder (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 874: | Line 874: | ||
* Plasmid was [[isolated]] from 2mL of each of the 6 ON cultures. pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colonies 7 + 11 were [[restricted]] using 7.5μl plasmid and 0.5μl each enzyme (EcoRI and NheI) in 15μl total volume: | * Plasmid was [[isolated]] from 2mL of each of the 6 ON cultures. pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colonies 7 + 11 were [[restricted]] using 7.5μl plasmid and 0.5μl each enzyme (EcoRI and NheI) in 15μl total volume: | ||
| - | * iGEMgfp colony 7.1 was [[prepared for microscopy]]. This showed no difference between the subtilin-induced and the control cultures. Also, only some cells expressed ''gfp'' whilst others did not. However, it was noticed that every cell that did flouresce was also undergoing sporulation, possibly indicating that the insert promotor may be under the control of the sporulation factor. | + | * iGEMgfp colony 7.1 was [[induced with subtilin]] and [[prepared for microscopy]]. This showed no difference between the subtilin-induced and the control cultures. Also, only some cells expressed ''gfp'' whilst others did not. However, it was noticed that every cell that did flouresce was also undergoing sporulation, possibly indicating that the insert promotor may be under the control of the sporulation factor. |
Revision as of 12:06, 19 September 2008
</style> </html>
Newcastle University
GOLD MEDAL WINNER 2008
| Home | Team | Original Aims | Software | Modelling | Proof of Concept Brick | Wet Lab | Conclusions |
|---|
Home >> Wet Lab
Introduction
- We finally started in the labs today so we will start updating the wiki with what's been happening and the progress we are making.
Fig 1 shows the construct which contains:
- spaRK promotor
- rrnB - rRNA binding site
- spaR (subtilin peptide antibiotic Regulation) - the 220 amino acid product of this gene usually regulates the downstream production of subtilin antibiotic. It has an N-terminal domain that can be phosphorylated and a C-terminal domian that has DNA binding properties [http://http://aem.asm.org/cgi/reprint/59/1/296.pdf]
- spaK (subtilin peptide antibiotic Kinase) - this gene codes for a 325 amino acid histadine kinase peptide that phosphorylates the N-terminus of spaR [http://http://aem.asm.org/cgi/reprint/59/1/296.pdf]. This activates the DNA binding ability of the C-terminus of spaR, which in turn initiates transcription of the downstream gene. In the case of our construct, this gene is gfp.
- gfp (green fluorescence protein) - the marker being used to show activation of the spaRK system and therefore diagnosis of gram-positive bacteria by B. Subtilis
- spaS promotor - a strong promotor inducible by upstream activation of spaRK. It can be placed in front any gene to regulate its activity.
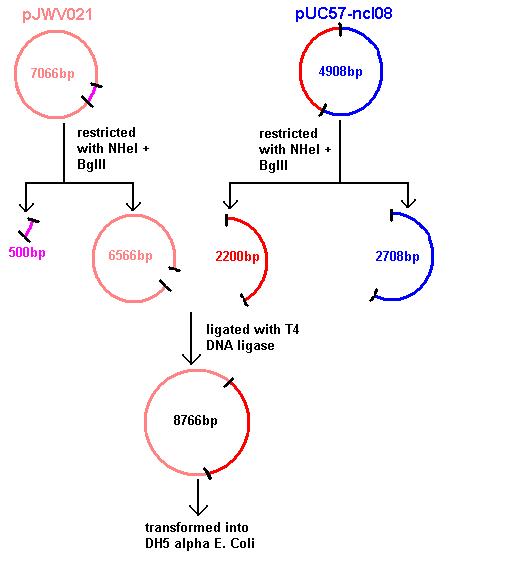
Aim 1: clone the spaRK system from pUC57 into pJWV021 and transform into DH5 alpha competent E. coli
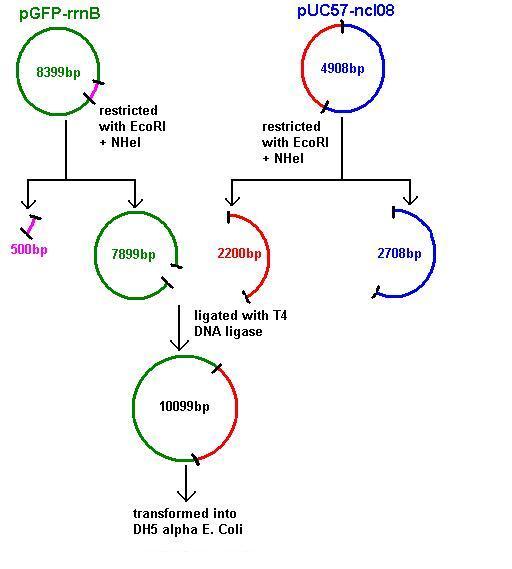
Aim 2: clone the spaRK system from pUC57 into pGFP-rrnB and transform into TOP10 competent E. coli
- The 2.2kb fragment (ncl08) contains the spaRK system and promotor-less gfp linked to this. This means that when spaR is activated, its positive regulatory effect on spaK will in turn activate gfp.
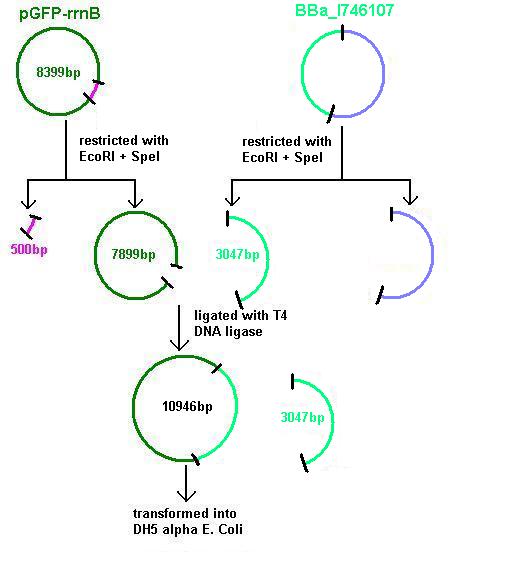
Aim 3: clone the agr system from the plasmid vector into pGFP-rrnB and transform into DH5 alpha competent E. coli
- BBa_I647107 contains a partial agr operon, which includes agrC and A but has agrB and D deleted. This allows coding for the receptor (C/A) but not for production of the quorum peptides themselves (B/D). Eventually this will be linked to the spaRK system in a B. subtilis vector.
Monday 4th August
- All 5 of us (Megan, Mark, Nina, Ria and Jess) went into the lab today to decide on a plan of action for the weeks to come.
- We used Agarose Gel Electrophoresis to check for the presence of plasmids (pGFPrrnB - our plasmid with the gfp gene, and pJWV021 - with the mCherry gene). Our gel was inconclusive, so we decided to re-run it the following day to confirm our results.
- In the afternoon we attempted to transform TOP10 competent E. coli cells with DNA from the registry (from source plate 1010 well 4A and 1018 7A). See Transforming into DH5α or TOP10 E. coli
- We followed the extraction method outlined in the green folder and for each DNA spot we plated two agar dishes: one with a larger volume of DNA (4μl) and one with a smaller volume (2μl) to make colony counting easier. (See Making Agar Plates.) We plated the following and incubated at 37˚C overnight:
Plate 1: +ve control (isolated plasmid plus TOP10 cells)
Plate 2: -ve control (TOP10 cells only, no plasmid)
Plate 3: Large 1010 4A
Plate 4: Small 1010 4A
Plate 5: Large 1018 7A
Plate 6: Small 1018 7A
Tuesday 5th August
- Today we re-ran the gel of pGFP-rrnB and pJWV021 to check correct plasmid size and sufficient plasmid quantity. Results showed this to be true and the expected plasmid sizes of 8399bp for pGFP-rrnB and 7066bp for pJWV021.
Wednesday 6th August
- Analyses of results from Monday’s transformation showed no colony growth except for the positive control. We decided to try another transformation into TOP10 E. coli using different spots from the registry. This time we used 1018 7A and 1004 6G.
- We noticed that Cambridge, who had also been having problems, had adapted the extraction method. So we tried their improved method, with a couple of minor differences:
1) Warm 50μl of H20 in an Eppendorf tube at 50˚C
2) Add 4 punched-out spots from the registry
3) Keep at 50˚C for 20 minutes
4) Centrifuge at 13,300g for 3 minutes
5) Warm for a further 10 minutes at 50˚C
6) Centrifuge at 13,300g for 3 minutes
7) Pipette out the supernatant which should (hopefully!) contain the DNA
- To see the original modified method, go to Cambridge’s OpenWetWare page:
http://openwetware.org/wiki/IGEM:Cambridge/2008/Protocols
Thursday 7th August
- Unfortunately none of the plates showed any colonies. However, further incubation overnight of the plates at 37˚C from Monday 4th August produced 5 colonies on Plate 4 (2μl 1010 4A). These colonies were individually incubated overnight at 37˚C in 10μl LB. (See Making Overnight Cultures from Agar Colonies.)
Friday 8th August
- The 5 colonies from Thursday 7th August cultured in LB were pooled and the plasmid purified (see Isolating Plasmid from Cells (Miniprep)). When the sample was run on gel no band appeared, showing that the colonies were not E. coli and must have resulted from contamination.
Monday 11th August
- Plasmids were isolated from pUc57-ncl08 (the ncl08 fragment contains the spaRK 2-part component system). We aim to clone this into pGFP-rrnB and pJWV021 vectors.
- Restrictions of pGFP-rrnB and pJWV021 carried out using 10μl plasmid and 0.5μl in 50μl total reaction volume (see Restricting Plasmids (Double Restriction)). pJWV021 was restricted in a 2-step reaction as we beleived that the enzymes were incompatible in the same buffer. The second restriction of this plasmid used 48μl of the purified plasmid mixture in a total volume of 100μl. pGFP-rrnB was restricted using EcoRI and NHeI. pJWV021 was restricted firstly with NHeI and secondly with BglII.
These were purified and stored overnight at -25˚C.
Tuesday 12th August
- pGFPrrnB and pJWV021 were restricted using 10μl plasmid and 0.5μl each enzyme in 50μl total reaction volume:
- pGFPrrnB restricted with EcoRI + NheI
- pJWV021 restricted with NheI then BglII in a 2 step reaction (the second step used 48μl purified plasmid in 100μl total reaction volume).
Running the samples on a gel showed only partial restriction had occurred and that there was very little pJWV021.
Wednesday 13th August
- pGFPrrnB and pJWV021 were restricted using 10μl plasmid and 0.5μl each enzyme in 50μl total reaction volume:
- pGFPrrnB restricted with EcoRI + NheI
- pJWV021 restricted with NheI then BglII in a 2 step reaction (the second step used 48μl purified plasmid in 100μl total reaction volume). These were stored overnight at -25˚C.
- BBa_I746101 (from Plate 1018 Spot 7A) and BBa_I746107 (containing the agr 2-component system) were received as cell stocks from the iGEM Registry.
Thursday 14th August
- BBa_I746101 and BBa_746107 were isolated and run on a gel together with the 4 restrictions performed 13.08.08.
Lane 1: 1kb ladder
Lane 2: empty
Lane 3: pGFPrrnB restricted with EcoRI + NheI
Lane 4: pJWV021 restricted with NheI + BglII
Lane 5: pUC57-ncl08 restricted with EcoRI + NheI
Lane 6: pUC57-ncl08 restricted with NheI + BglII
Lane 7: BBa_746101
Lane 8: BBa_746107
The gel showed that there was very little pGFPrrnB (restricted with EcoRI + NheI) and no pJWV021. It was concluded that the 2 step restriction and purification method reduced the plasmid yield significantly. As it was later discovered that this method was unnecessary (as NheI and BglII are compatible using buffer M), it was decided to perform the restriction as a single step in future.
The gel also showed successful restrictions of the pUC57-ncl08 plasmid and lots of the two BioBrick samples.
- The 2.2kb fragments from the pUC57-ncl08 restrictions were cut out of the gel using a UV light box and scalpel blade (see Cutting a Specific Band from Agarose Gel). The resulting gel slices were then purified to remove all gel and enzymes (see Purifying DNA from Gel Slices).
Friday 15th August
pGFPrrnB, pJWV021 and BBa_I746107 were restricted using 20μl plasmid and 1μl each enzyme in 40μl total reaction volume: - pGFPrrnB restricted with EcoRI + NheI
- pJWV021 restricted with NheI + BglII
- pGFPrrnB restricted with EcoRI + SpeI
- BBa_I746107 restricted with EcoRI + SpeI
These were incubated at 37˚C for 1 hour and run on a gel. The gel showed that pGFPrrnB and pJWV021 had restricted well with EcoRI + NheI and Nhe +BglII respectively, but pGFPrrnB and BBa_I746107 restricted with EcoRI + SpeI had only partially restricted.
Monday 18th August
- The gel slices containing the 2.2kb ncl08 fragment were purified and a small amount run on a gel to check for correct restriction. Unfortunately it appeared that due to a pipetting error the solution was too dilute and thereofre not enough of the plasmid had been loaded on the gel to see.
Wednesday 20th August
- The dilute 2.2kb fragment was concentrated by repeated rounds of heating and cooling. This was purified to see if any plasmid had been obtained. As the sample was in 500μl buffer, it was split into 5 x 100μl aliquots. Each was purified separatly and then the samples pooled afterwards to maximise the yield of DNA. This was then run on a gel.
- The gel showed no pGFPrrnB (restricted with EcoRI and NheI) and only a small amount of pGFPrrnB (restricted with EcoRI). Therefore pGFPrrnB and pUC57-ncl08 were restricted using EcoRI and NheI (as this also showed as absent on the gel).
- Following these restrictions, the samples were run on gel which again showed them to be absent.
Thursday 21st August
- pJWV021 and pUC57-ncl08 were restricted using a different method:
pJWV021 stock
- 48μl MillQ H2O
- 8μl buffer M
- 20μl pJWV021
- Tube 1 = 19μl stock solution + 1μl NheI + 1μl BglII
- Tube 2 = 19μl stock solution + 1μl NheI
- Tube 3 = 19μl stock solution + 1μl BglII
- Tube 4 = 19μl stock solution
pJWV021 and pUC57-ncl08 were restricted using a different method:
pJWV021 stock
- 48μl MillQ H2O
- 8μl buffer M
- 20μl pJWV021
- Tube 5 = 19μl stock solution + 1μl NheI + 1μl BglII
- Tube 6 = 19μl stock solution + 1μl NheI
- Tube 7 = 19μl stock solution + 1μl BglII
- Tube 8 = 19μl stock solution
Friday 22nd August
- Stock pGFPrrnB from -80˚C was plated onto ampicillin, spectinomycin and normal agar (control) and incubated overnight at 37˚C.
- 2μl pUC57-ncl08 and pJWV021 were run on gel to check quantity. This showed large quantities of both plasmids and therefore pUC57-ncl08 was restricted with EcoRI + NHeI and NHeI + BglII. Controls (buffer A and buffer M without enzyme) were used for both restrictions.
Tuesday 26th August
- Due to unforeseen circumstances, restriction mixtures were put in the fridge on Friday 22.08.08. Therefore the restriction was allowed to run for a further 1.5 hours before running on a gel.
Lane 1: 1kb ladder
Lane 2: empty
Lane 3: pUC57-ncl08 restricted with EcoRI + NHeI
Lane 4: pUC57-ncl08 restricted with NHeI and BglII
Lane 5: pUC57-ncl08 buffer A control
Lane 6: pUC57-ncl08 buffer M control
Lane 7: pure pJWV021
Results from overnight (ON) agar cultures:
- pGFPrrnB (amp) - no colonies
- pGFPrrnB (spec) - colonies present
- pGFPrrnB (no antibiotic) - colonies present
- ON cultures were made:
- pGFP-rrnB grown on ampicillin
- pJWV021 grown on ampicillin
- pUC57-ncl08 grown on ampicillin
Wednesday 27th August
- ON cultures were analysed:
- pGFP-rrnB grown on ampicillin - cells had lysed (medium was clear with large bubbles at the surface).
- pJWV021 grown on ampicillin - frozen glycerol stock made (see protocol).
- pUC57-ncl08 grown on ampicillin - frozen glycerol stock made.
- A colony stab was taken of pGFP-rrnB using 10μl spectinomycin in 10mL LB as the culture medium.
Thursday 28th August
- New frozen glycerol stock of cells made to be kept at -80˚C.
- Isolated plasmid from overnight culture of pGFP-rrnB. For this the 10mL culture was divided into 5 x 2mL plastic tubes and pelleted by centrifugation for 10 minutes. The supernatent was discarded and follwing the isolation procedure the product was pooled.
- Restrictions of pUC57-ncl08 and pJWV021 were carried out.
Lane 1: 1kb ladder
Lane 2: pUC57-ncl08 restricted with EcoRI
Lane 3: pUC57-ncl08 restricted with BglII
Lane 4: pUC57-ncl08 restricted with EcoRI and NHeI
Lane 5: pUC57-ncl08 restricted with NHeI and BglII
Lane 6: pUC57-ncl08 control (no enzyme)
Lane 7: pJWV021 restricted with NHeI and BglII
Lane 8: pure pGFPrrnB
- This gel shows that only partial restrictions of the plasmids had occurred. It was subsequently discovered that an incorrect quantity of buffer was being used. This was rectified in further restriction reactions.
Friday 29th August
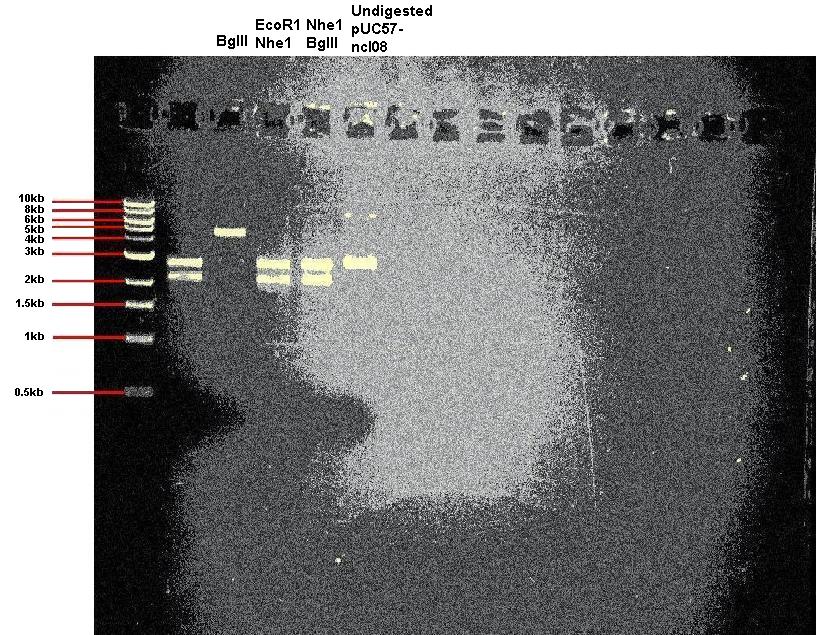
- Today we restricted our pUC57-ncl08 plasmid. In one reaction we used EcoR1 and Nhe1, and in other we used BglII and Nhe1. We also carried out a restriction with just BglII to check for the correct sized linear DNA. In addition we ran unrestricted plasmid on the gel.
Expected band sizes:
* For digestion with BglII only: ~ 4.9kb
* For digestion with Nhe1 and EcoR1: ~ 2.2kb and 2.7kb
* For digestion with Nhe1 and BglII: ~ 2.2kb and 2.7kb
- As you can see, the restrictions appear successful.
Monday 1st September
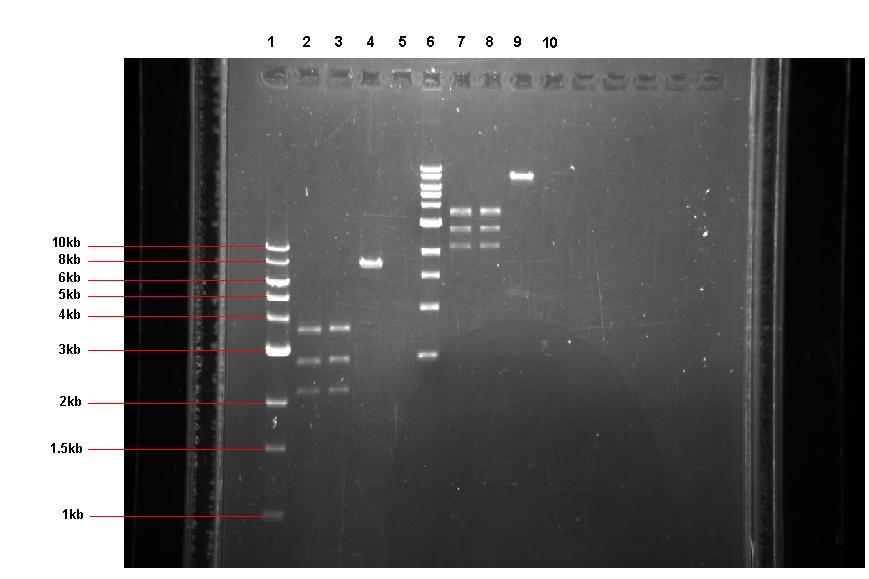
- To obtain a large enough volume for our ligations, we carried out all 4 restrictions again (i.e. of our pUC57-ncl08, pGFP-rrnB and pJWV021). We used a total volume of 100μl per reaction (using 2μl of each enzyme and 20μl of plasmid). These were incubated for 1 1/2 hours at 37˚C.
- 4μl of each reaction was then run on a gel for 1 hour @ 70V- See the gel below (Tuesday the 2nd)
Lane 1: 1kb ladder
Lane 2: pUC57-ncl08 restricted with EcoR1 and Nhe1 (1 hour 30 mins)
Lane 3: pUC57-ncl08 restricted with BglII and Nhe1(1 hour 30 mins)
Lane 4: pGFP-rrnB restricted with EcoR1 and Nhe1(1 hour 30 mins)
Lane 5: pJWV021 restriced with BglII and NHe1(1 hour 30 mins)
Lane 6: 1kb ladder
Lane 7: pUC57-ncl08 restricted with EcoR1 and Nhe1 (2 hours 30 mins)
Lane 8: pUC57-ncl08 restricted with BglII and Nhe1(2 hours 30 mins)
Lane 9: pGFP-rrnB restricted with EcoR1 and Nhe1(2 hours 30 mins)
Lane 10: pJWV021 restriced with BglII and NHe1(2 hours 30 mins)
Expected band sizes:
* Lane 2: ~ 2.2kb and 2.7kb
* Lane 3: ~ 2.2kb and 2.7kb
* Lane 4: ~ 7.9kb and 0.5kb
* Lane 5: ~ 6.6kb and 0.5kb
- The gel shows partial restrictions in lanes 2 and 3. In Lane 4, the larger fragment is the correct size, but the observed smaller fragment is larger than expected. Lane 5 shows that no pJWV021 is present, so we will need to re-isolate this tomorrow.
- The samples were incubated for a further 1 hour, and run on a gel again. Unfortunately, there was no change, so we decided to re-isolate all 3 plasmids tomorrow.
- We made ON cultures using 10μl ampicillin in 10ml of LB for pUC57-ncl08 and pJWV021, and 5μl of spectinomycin in 10ml LB for pGFP-rrnB. These were incubated overnight at 37˚C.
Tuesday 2nd September
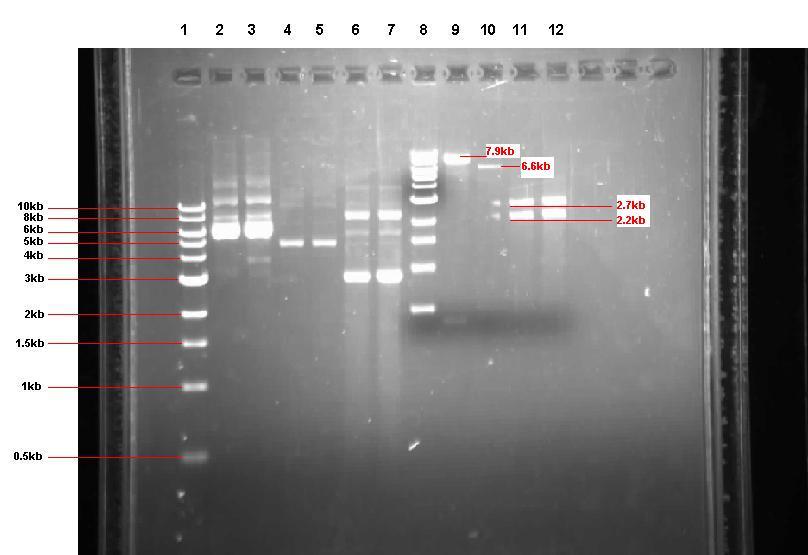
- The 3 ON cultures were isolated by dividing each 20ml tube into 2 x 5ml tubes. These were centrifuged for 10 minutes to pellet.
- Once isolated, we ran 5μl of each sample on a gel to check for the presence of plasmid. As you can see from lanes 1-7 on the gel below, there was plenty of pGFP-rrnB but not much of pJWV021. Also, the pUC57-ncl08 samples look 'dirty' (see grey smears).
- As a result, for the restrictions we decided to use more of the pUC57-ncl08 and pJWV021 (in a total volume of 100µl for the restrictions, we used 40µl of plasmid for the pUC57-ncl08 restriction, 30µl for the pJWV021 restriction and 20µl for the pGFP-rrnB restriction).
- After incubation, we ran the restriction products on a gel.
Expected band sizes:
* Lane 9: ~ 7.9kb and 0.5kb
* Lane 10: ~ 6.6kb and 0.5kb
* Lane 11: ~ 2.2kb and 2.7kb
* lane 12: ~ 2.2kb and 2.7kb
Lane 1: 1kb ladder
Lane 2: Unrestricted pGFP-rrnB sample 1
Lane 3: ‘’ ‘’ sample 2
Lane 4: Unrestricted pJWV021 sample 1
Lane 5: ‘’ ‘’ sample 2
Lane 6: Unrestricted pUC57-ncl08 sample 1
Lane 7: ‘’ ‘’ sample 2
Lane 8: 1kb ladder
Lane 9: pGFP-rrnB restricted with EcoR1 and Nhe1
Lane 10: pJWV021 restricted with BglII and Nhe1
Lane 11: pUC57-ncl08 restricted with EcoR1 and Nhe1
Lane 12: pUC57-ncl08 restricted with BglII and Nhe1
The gel showed that our restrictions were successful. Before we moved on to ligating, we purified the 4 restricted samples using the PCR DNA purification kit to remove the enzymes.
For the ligations we made each reaction mixture to 25µl (using 1.5µl of T4 ligase and 2.5µl of 10x ligase buffer). We incubated our samples for 1 hour in a 27˚C water bath.
Wednesday 3rd September
- Today our aim was to transform our ligated plasmids into DH5-aplha E.coli competent cells.
- For each transformation, we added 100µl of DH5-alpha E.coli competent cells to 12.5µl of the ligation mixtures from yesterday.
- So in total we carried out 6 transformations, preparing them all on ice:
T1) Transforming pGFP-rrnB containing the 2.2kb fragment from pUC57-ncl08 into DH5-alpha
T2) Transforming pGFP-rrnB minus the 2.2kb fragment from pUC57-ncl08 into DH5-alpha
T3) Transforming pJWV021 containing the 2.2kb fragment from pUC57-ncl08 into DH5-alpha
T4) Transforming pJWV021 minus the 2.2kb fragment from pUC57-ncl08 into DH5-alpha
T5) Positive control: DH5-alpha cells plus pGFP-rrnB
T6) Negative control: DH5-alpha cells only
- The transformations were then plated onto antibiotic agar:
T1 : +spec
T2 : +spec (small and large volume plated)
T3 : +amp and +kan
T4 : +amp +kan
T5 : +spec
T6 : +spec
Thursday 4th September
- The plates from 03.09.08 showed expected colony growth and therefore overnight cultures were made from individual colonies on Plates 1, 2 and 9. The culture media were made using 10mL of LB in 15mL plastic tubes together with the correct volume of the relavent antibiotic. This was 5μl spectinomycin for the GFP-rrnB colonies and 4μl kanomycin for the pJWV021 colonies. Cultures were taken as follows:
GFP-rrnB - pUC57 ligation (grown on spec)
- 9 white colonies (1-9) (Plate 1)
- 1 green colony (10) (Plate 1)
- 2 white colonies (11,12) (Plate 2)
pJWV021 - pUC57 ligation (grown on kan)
- 10 white colonies (13-22) (Plate 9)
- 1 pink colony (23) (Plate 9)
- 1 bright white colony (24) (Plate 9) (this is likely to a be contaminant non-E.coli colony)
- All 24 culture tubes were incubated at 37˚C whilst shaking for ~20 hours. This large quantity of cultures should ensure that we obtain at least 2 cultures (one GFP-rrnB and one pJWV021) that have taken up the ncl08 insert. The plates were kept at room temperature in case fulrther stab cultures needed to be made.
Friday 05th September
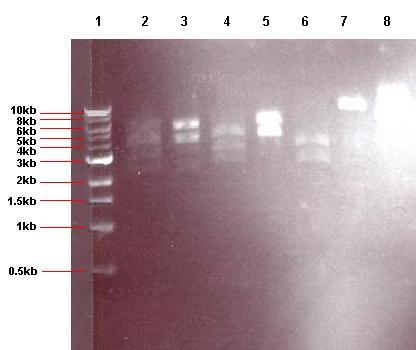
- 4μl of each of the 24 overnight cultures was centrifuged and the plasmid isolated from the resulting pellets. The isolated plasmid was then restricted to see if the plasmid had taken up the insert. All pGFPrrnB-nvl08 plasmids were restricted using EcoRI and NheI and pJWV021-ncl08 plasmids restricted with NheI and BglII. The restrictions were carried out in using 7.5μl plasmid in a total volume of 15μl. Samples were run on gel.
Lane 1: 1kb ladder
Lane 2: pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 1 (white colony, 25μl plate)
Lane 3: pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 2 (white colony, 25μl plate)
Lane 4: pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 3 (white colony, 25μl plate)
Lane 5: pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 4 (white colony, 25μl plate)
Lane 6: pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 5 (white colony, 25μl plate)
Lane 7: pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 6 (white colony, 25μl plate)
Lane 8: pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 7 (white colony, 25μl plate)
Lane 9: pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 8 (white colony, 25μl plate)
Lane 10: pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 9 (white colony, 25μl plate)
Lane 11: pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 10 (white colony, 250μl plate)
Lane 12: pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 11 (white colony, 250μl plate)
Lane 13: pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 12 (green colony, 25μl plate)
Lane 1: 1kb ladder
Lane 2: pJWV021-ncl08 colony 1 (white colony)
Lane 3: pJWV021-ncl08 colony 2 (white colony)
Lane 4: pJWV021-ncl08 colony 3 (white colony)
Lane 5: pJWV021-ncl08 colony 4 (white colony)
Lane 6: pJWV021-ncl08 colony 5 (white colony)
Lane 7: pJWV021-ncl08 colony 6 (white colony)
Lane 8: pJWV021-ncl08 colony 7 (white colony)
Lane 9: pJWV021-ncl08 colony 8 (white colony)
Lane 10: pJWV021-ncl08 colony 9 (white colony)
Lane 11: pJWV021-ncl08 colony 10 (white colony)
Lane 12: pJWV021-ncl08 colony 11 (white colony)
Lane 13: pJWV021-ncl08 colony 12 (white colony)
- The gels showed correct insert fragments (2.2kb) in lanes 8 (colony 7) and 12 (colony 11) for pGFPrrnB and lanes 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9 and 10 (colonies 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 20 and 21 respectively) for pJWV021.
- Unrestricted plasmid from colonies 7 + 11 (pGFPrrnB) and 13 + 14 (pJWV021) were transformed into Bacillus subtilis (see Transforming into Bacillus subtilis).
- Plasmid renamed once transformed into B. subtilis to avoid confusion with plasmid in E. coli:
- pGFPrrnB-ncl08 (E. coli) = iGEMgfp (B. subtilis)
- pJWV021-ncl08 (E. coli) = iGEMcherry (B. subtilis)
- Agar cultures were also made from the same colony cultures:
- iGEMgfp (chloramphenicol) colony 7
- iGEMgfp (chloramphenicol) colony 11
- iGEMgfp (chloramphenicol) negative control
- iGEMcherry (kanomycin) colony 13
- iGEMcherry (kanomycin) colony 14
- iGEMcherry (kanomycin) negative control
Monday 08th September
- Results from the agar cultures:
- iGEMgfp (chloramphenicol) colony 7 - many colonies
- iGEMgfp (chloramphenicol) colony 11 - many colonies
- iGEMgfp (chloramphenicol) negative control - no colonies
- iGEMcherry (kanomycin) colony 13 - a few colonies
- iGEMcherry (kanomycin) colony 14 - 3 colonies (plus 'background' contaminants)
- iGEMcherry (kanomycin) negative control - no colonies (some 'background' contaminants)
- Agar stabs were taken from the following colonies and streaked onto agar to obtain isolated colonies:
- iGEMgfp colonies 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6
- iGEMgfp colonies 11.1, 11.2, 11.3, 11.4, 11.5, 11.6
- iGEMcherry colonies 13.1, 13.2, 13.3
B. subtilis wild type strain ATCC6633 was also streaked onto agar.
- Overnight (ON) cultures were made by JW of iGEMgfp 7.1, iGEMgfp colonies 11.1, iGEMcherry 13.1 and 13.2.
The following cultures were then made and incubated at 37˚C whilst shaking for 3 hours. Dilute (dil) cultures were made by adding 500μl ON culture to 10mL LB. After 3 hours ATCC6633 supernatent was obtained by centrifuging ON ATCC6633 culture and 250μl of this added to the + ATCC6633 tubes.
- iGEMgfp ON + ATCC6633
- iGEMgfp ON - ATCC6633
- iGEMgfp dil + ATCC6633
- iGEMgfp dil - ATCC6633
- iGEMcherry ON + ATCC6633
- iGEMcherry ON - ATCC6633
- iGEMcherry dil + ATCC6633
- iGEMcherry dil - ATCC6633
- These were left to incubate at 37˚C for a further 2 hours to allow gfp and mCherry induction by the subtilin contained in the ATCC6633 supernatent. Those wiothout supernatent were positive controls.
- The B. subtilis cells were prepared for microscopy (see protocol) and viewed:
- iGEMgfp ON + ATCC6633 - some cells expressed gfp
- iGEMgfp ON - ATCC6633 - some cells expressed gfp (although less than in the presence of subtilin)
- iGEMgfp dil + ATCC6633 - some cells expressed gfp
- iGEMgfp dil - ATCC6633 - some cells expressed gfp (although less than in the presence of subtilin)
- iGEMcherry ON + ATCC6633 - very few celled expressed mCherry
- iGEMcherry ON - ATCC6633 - very few celled expressed mCherry
- iGEMcherry dil + ATCC6633 - very few celled expressed mCherry
- iGEMcherry dil - ATCC6633 - very few celled expressed mCherry
- There appeared to be a difference in the GFP intensities between iGEMgfp with and without subtilin but this microscopy was not sufficient to confirm this.
- Starch, sucrose and glucose agar plates were made (see protocol) and the following colonies streaked:
- iGEMgfp 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6, 11.1, 11.2, 11.3, 11.4, 11.5, 11.6 streaked onto starch agar
- iGEMcherry 13.1, 13.2, 13.3 streaked onto both glucose and sucrose
- iGEMgfp should be able to grow on starch but will have no 'halo' surrounding the colonies (the halo is digested starch). This is becuase the insert should have integrated into amyE and the bacteria therefore cannot make amylase to digest starch.
iGEMcherry should not be able to grow on sucrose as the insert should have integrated into sacA. The bacterium therefore cannot make sucrase to digest sucrose and consequently will have no carbon source. The glucose plates act as controls.
- Overnight cultures were also made of iGEMgfp 7.1 and 11.1 and iGEMcherry 13.1 and 13.2.
Tuesday 9th September
- Half of the overnight cultures iGEMgfp 7.1 and iGEMcherry 13.1 were diluted (by adding 500μl ON culture to 10mL LB) to make the following cultures. These were incubated at 37˚C whilst shaking for 3 hours. 250μl ATCC6633 supernatent was then added to the + ATCC6633 tubes and the mixtures left to incubate for 2 hours at 37˚C.
- Glycerol stocks made (see protocol) of iGEMgfp 7.1 and 11.1 and iGEMcherry 13.1 and 13.2.
- Microscopy of the cultures showed similar results to yesterday with again only a possible difference between the iGEMgfp with and without subtilin.
- BBa_I746107 and pGFPrrnB restricted using 20μl plasmid and 2μl of each enzyme (EcoRI and SpeI) in 100μl total reaction volume. These were run on a gel at 70V for 1 hour.
Lane 1 = 1kb ladder
Lane 2 = pGFP restricted with EcoRI and SpeI
Lane 3 = BBa_I746107 restricted with EcoRI and SpeI
- This showed successful restriction of both plasmids which were then purified and ligated overnight using 6μl plasmid and 1.5μl enzyme (T4 ligase) in 25μl total reaction volume.
Wednesday 10th September
- Overnight ligation mixtures transformed into competent DH5α E. coli cells (see protocol).
- 12.5μl pGFPrrnB-BBa_746107 + 100μl DH5α cells - 12.5μl pGFPrrnB + 100μl DH5α cells (positive control) - 100μl DH5α cells (negative control)
- All transformants were then plated onto spectinomycin agar in both 25μl and 250μl volumes and incubated overnight at 37˚C.
Thurday 11th September
- Single colonies of iGEMcherry were streaked from the overnight kanamycin plates onto sucrose and glucose plates.
- Stab cultures were taken from the overnight 25μl and 250μl pGFP-BBa_I7045898 plates (grown on spectinomycin) and grown in 10mL LB:
- 25μl plate white colony 1
- 25μl plate white colony 2
- 25μl plate white colony 3
- 25μl plate white colony 4
- 25μl plate white colony 5
- 25μl plate white colony 6
- 250μl plate white colony 1
- 250μl plate white colony 2
- 250μl plate white colony 3
- 250μl plate white colony 4
- 250μl plate white colony 5
- 250μl plate green colony 6
These were incubated overnight at 37˚C whilst shaking.
- iGEMgfp was diluted by adding 250μl of the overnight culture to 10mL LB in a sterile shake flask. This was incubated at 37˚C whilst shaking for a further 2 hours to give the cells fresh nutrients and allow them to multiply. This culture was then divided into 3 tubes (3mL in each) and subtilin added in the following concentrations:
- 0% induction (3mL dilute iGEMgfp)
- 1% induction (3mL dilute iGEMgfp + 30μl subtilin)
- 10% induction (30mL dilute iGEMgfp + 300μl subtilin)
These were incubated whilst shaking for 1 hour at 37°C. Flow cytometry was then performed on the samples.
- Overnight cultures were made from glycerol stocks pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 7 and pJWV021-ncl08 colony 13 (see protocol). The plasmid from these cultures are to be checked for the 2.2kb fragment before being sent for sequencing.
Friday 12th September
- The ON cultures of iGEMgfp and Bs168 were diluted by adding 250μl ON culture to 10mL LB and incubating at 37°C whilst shaking for 2 hours. The two diluted cultures were then each split into 5 x 2mL aliquots and subtilin added in the following concentrations:
- 0% induction (2mL dilute culture)
- 0.1% induction (2mL dilute culture + 2μl subtilin)
- 0.5% induction (2Ml dilute culture + 10μl subtilin)
- 1% induction (2mL dilute culture + 20μl subtilin)
-10% induction (2mL dilute culture + 200μl subtilin)
The five Bs168 tubes acted as controls. These were incubated at 37°C whilst shaking for 1 hour to allow the subtilin to induce gfp expression.
- Plasmid was isolated from the 12 pGFPrrnB-BB107 ON cultures 9see protocol). Unfortunately plasmid from colony 4 (25μl plate) and colony 4 (250μl plate) were lost due to human error.
- pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 7 and pJWV021 colony 13 isolated from overnight cultures (see protocol).
- All isolated plasmid was restricted using 7.5μl plasmid and 0.5μl each enzyme in 15μl total volume:
- pGFPrrnB-BB107 restrited with EcoRI and SpeI.
- pGFPrrnB-ncl08 restricted with EcoRI and NheI
- pJWV021-ncl08 restricted with NheI and BglII
These restrictions were run on gels.
Lane 1: 1kb ladder
Lane 2: pGFPrrnB-BB107 colony 1
Lane 3: pGFPrrnB-BB107 colony 2
Lane 4: pGFPrrnB-BB107 colony 3
Lane 5: pGFPrrnB-BB107 colony 5
Lane 6: pGFPrrnB-BB107 colony 6
Lane 7: pGFPrrnB-BB107 colony 7
Lane 8: pGFPrrnB-BB107 colony 8
Lane 9: pGFPrrnB-BB107 colony 9
Lane 10: pGFPrrnB-BB107 colony 10
Lane 11: pGFPrrnB-BB107 colony 11
Lane 1: 1kb ladder
Lane 2: pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 7
Lane 3: pJWV021-ncl08 colony 13
Lane 4: pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 7 control (no enzyme)
Lane 5: pJWV021-ncl08 colony 13 control (no enzyme)
Monday 15th September
- ON cultures were made from glycerol stocks of pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colonies 7 + 11 and pGFPrrnB-BB107 colonies 3 + 5.
- ON culture made from B. subtilis ON culture:
Tuesday 16th September
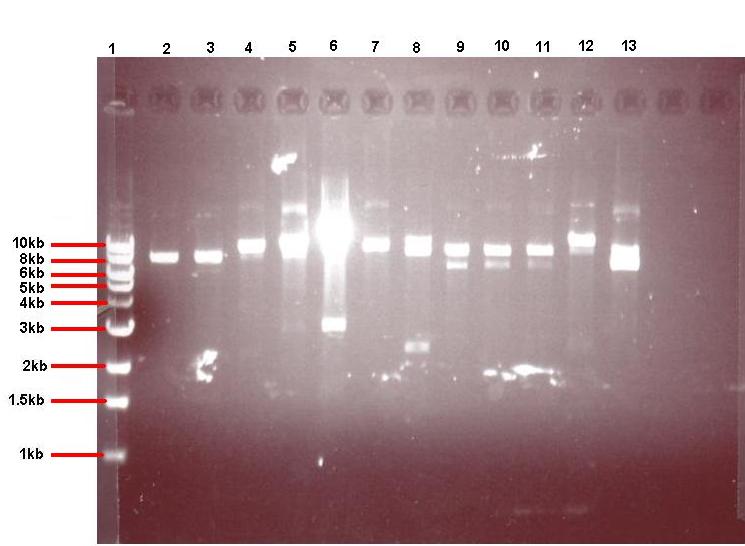
- Plasmid isolated from pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colonies 7 + 11 and pGFPrrnB-BB107 colonies 3 + 5 ON cultures.
- A Sample of each of the 4 isolated plasmids were restricted using 7.5μl plasmid and 0.5μl each enzyme in 15μl total volume:
- pGFPrrnB-ncl08 restricted with EcoRI + NheI
- pGFPrrnB-BB107 restricted with EcoRI + SpeI
Gel:
Expected band sizes:
* Lane 2: ~ 8.4kb and 2.2kb
* Lane 3: ~ 8.4kb and 2.2kb
* Lane 4: ~ 8.4kb and 3.2kb
* lane 5: ~ 8.4kb and 3.2kb
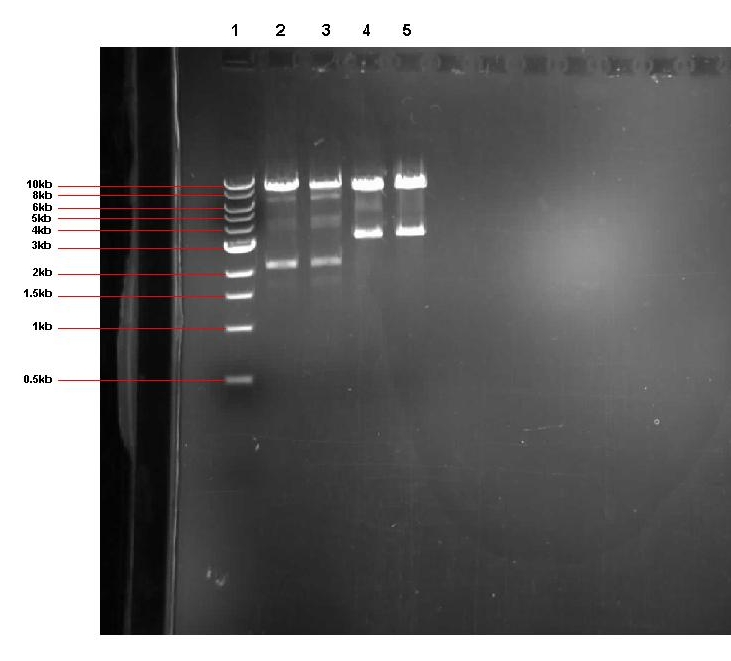
Lane 1: 1kb ladder
Lane 2: pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 7 restricted with EcoR1 and Nhe1
Lane 3: pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 11 restricted with EcoR1 and Nhe1
Lane 4: pGFPrrnB-BBa_I746107 colony 3 restricted with EcoR1 and Spe1
lane 5: pGFPrrnB-BBa_I746107 colony 5 restricted with EcoR1 and Spe1
As you can see from our gel, all 4 restrictions yielded the expected sized bands, indicating that the ligations had been successful. The remainder of the unrestricted plasmid from pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 7 was stored in the -20°C freezer ready to be sent off for sequencing. The two unrestricted pGFPrrnb-BBa_I746107 plasmid samples were then transformed into B.subtilis 168.
Agar plates made:
- pGFPrrnB-BBa_I746107 colony 3 (chloramphenicol)
- pGFPrrnB-BBa_I746107 colony 5 (chloramphenicol)
- B. subtilis 168 (negative control) (chloamphenicol)
Wednesday 17th September
- Results of ON agar plate cultures:
- pGFPrrnB-BBa_I746107 colony 3 (chloramphenicol) = ~100 colonies
- pGFPrrnB-BBa_I746107 colony 5 (chloramphenicol) = ~80 colonies
- B. subtilis 168 (negative control) (chloamphenicol) = O colonies
These colonies show that the BBa_I746107 insert has successfully transformed into the B. subtilis chromosomal DNA. To avoid confusion between E. coli and B. subtilis, it was decided to rename the insert from pGFPrrnB-ncl08 (in E. coli) to iGEMBioBrick (in B. subtilis). It was important to then check that only this insert had integrated (and not the rest of the vector plasmid) and that it had integrated in the correct place. Therefore the following agar plate cultures were made:
- iGEMBioBrick colony 3 (starch + chloramphenicol)
- iGEMBioBrick colony 3 (spectinomycin)
- iGEMBioBrick colony 3 (chloramphenicol)
- iGEMBioBrick colony 5 (starch + chloramphenicol)
- iGEMBioBrick colony 5 (spectinomycin)
- iGEMBioBrick colony 5 (chloramphenicol)
- ON cultures were made from glycerol stocks to check for correct insert (in 3mL LB):
- pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 7
- pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colony 11
- iGEMgfp colony 7.1
- iGEMgfp colony 11.1
- iGEMcherry colony 13.1
- iGEMcherry colony 13.2
Thursday 18th September
- Plasmid was isolated from 2mL of each of the 6 ON cultures. pGFPrrnB-ncl08 colonies 7 + 11 were restricted using 7.5μl plasmid and 0.5μl each enzyme (EcoRI and NheI) in 15μl total volume:
- iGEMgfp colony 7.1 was induced with subtilin and prepared for microscopy. This showed no difference between the subtilin-induced and the control cultures. Also, only some cells expressed gfp whilst others did not. However, it was noticed that every cell that did flouresce was also undergoing sporulation, possibly indicating that the insert promotor may be under the control of the sporulation factor.
 "
"