Team:Rice University
From 2008.igem.org
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
<font color="navy"> | <font color="navy"> | ||
== '''Welcome to Rice University's 2008 iGEM wiki page.''' == | == '''Welcome to Rice University's 2008 iGEM wiki page.''' == | ||
| - | Our project for this year is BIOBEER, where we are genetically engineering the biosynthetic pathway for resveratrol production into a brewing yeast strain. Resveratrol has been shown to have a plethora of health benefits, including anti-cancer and anti-viral activity, cardio- and neuro-protective effects, modulation of diabetes, and anti-aging effects. Although research has been done previously to produce resveratrol in various organisms, no one to date has developed a yeast strain able to synthesize resveratrol in a de novo manner. We are going one step further, characterizing resveratrol production during anaerobic fermentation with the intent of creating a beer that contains all the health benefits of wine. Get ready for resveratrol in a fizzy ready-to-consume beverage! | + | Our project for this year is BIOBEER, where we are genetically engineering the biosynthetic pathway for resveratrol production into a brewing yeast strain. Resveratrol has been shown to have a plethora of health benefits, including anti-cancer and anti-viral activity, cardio- and neuro-protective effects, modulation of diabetes, and anti-aging effects. Although research has been done previously to produce resveratrol in various organisms, no one to date has developed a yeast strain able to synthesize resveratrol in a ''de novo'' manner. We are going one step further, characterizing resveratrol production during anaerobic fermentation with the intent of creating a beer that contains all the health benefits of wine. Get ready for resveratrol in a fizzy ready-to-consume beverage! |
</font> | </font> | ||
<BR><BR> | <BR><BR> | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
[[Image:RSV-health.jpg|left|thumb|300px|Resveratrol has been shown to provide a wealth of health benefits.]] | [[Image:RSV-health.jpg|left|thumb|300px|Resveratrol has been shown to provide a wealth of health benefits.]] | ||
=== '''Health Benefits''' === | === '''Health Benefits''' === | ||
| - | :* '''Improved cardiovascular function''': resveratrol has been shown to have cardioprotective effects such as the suppression of atherosclerosis, inhibition of platelet aggregation, vasorelaxation promotion, and modulation of triglyceride blood levels, in a wide variety of in vitro and in vivo models. [1-4] | + | :* '''Improved cardiovascular function''': resveratrol has been shown to have cardioprotective effects such as the suppression of atherosclerosis, inhibition of platelet aggregation, vasorelaxation promotion, and modulation of triglyceride blood levels, in a wide variety of ''in vitro'' and ''in vivo'' models. [1-4] |
:* '''Inhibition of carcinogenesis''': one well-documented effect of resveratrol is the ability to induce cell death specifically in cancerous cells. This property of resveratrol has been shown for a wide variety of cancers, including colon cancer [5-7], pancreatic cancer [8], prostate cancer [9,10], breast cancer [11,12], and skin cancer [13,14]. In fact, several phase I human clinical trials are investigating the administration of resveratrol as a cancer therapy [15,16] | :* '''Inhibition of carcinogenesis''': one well-documented effect of resveratrol is the ability to induce cell death specifically in cancerous cells. This property of resveratrol has been shown for a wide variety of cancers, including colon cancer [5-7], pancreatic cancer [8], prostate cancer [9,10], breast cancer [11,12], and skin cancer [13,14]. In fact, several phase I human clinical trials are investigating the administration of resveratrol as a cancer therapy [15,16] | ||
:* '''Upregulates the antioxidant systems of cells''', such as SuperOxide Dismutase and glutathione, and these cells are protected against oxidative damage [16,17]. | :* '''Upregulates the antioxidant systems of cells''', such as SuperOxide Dismutase and glutathione, and these cells are protected against oxidative damage [16,17]. | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
-->Dark and anaerobic conditions required for fermentation improve resveratrol stability. | -->Dark and anaerobic conditions required for fermentation improve resveratrol stability. | ||
| + | <BR><BR><BR><BR><BR> | ||
| - | The Rice 2008 Synthetic BiOWLogists | + | == '''The Rice 2008 Synthetic BiOWLogists''' == |
[[Image:iGEM-2008-Splash.jpg|400px|right]] | [[Image:iGEM-2008-Splash.jpg|400px|right]] | ||
Revision as of 23:31, 27 October 2008
Contents |
Welcome to Rice University's 2008 iGEM wiki page.
Our project for this year is BIOBEER, where we are genetically engineering the biosynthetic pathway for resveratrol production into a brewing yeast strain. Resveratrol has been shown to have a plethora of health benefits, including anti-cancer and anti-viral activity, cardio- and neuro-protective effects, modulation of diabetes, and anti-aging effects. Although research has been done previously to produce resveratrol in various organisms, no one to date has developed a yeast strain able to synthesize resveratrol in a de novo manner. We are going one step further, characterizing resveratrol production during anaerobic fermentation with the intent of creating a beer that contains all the health benefits of wine. Get ready for resveratrol in a fizzy ready-to-consume beverage!
BioBeer: Producing Resveratrol During Beer Fermentation
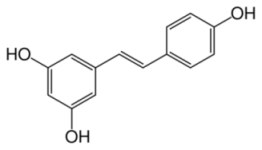
Resveratrol
- First identified as the active component in C. quinquangulata (cinnamon) extract responsible for anti-inflammatory properties.
- Normally used as a defense mechanism in plants in response to fungal pathogens and UV irradiation.
- Main source in human diet is red wine, but significant amounts are also found in grape juice, peanuts, cranberry juice, and other sources.
- There is a tremendous interest in the potential of resveratrol for various health benefits. A PubMed search for 'resveratrol' returns 2,470 scientific articles.
- First identified as the active component in C. quinquangulata (cinnamon) extract responsible for anti-inflammatory properties.
Resveratrol and Yeast
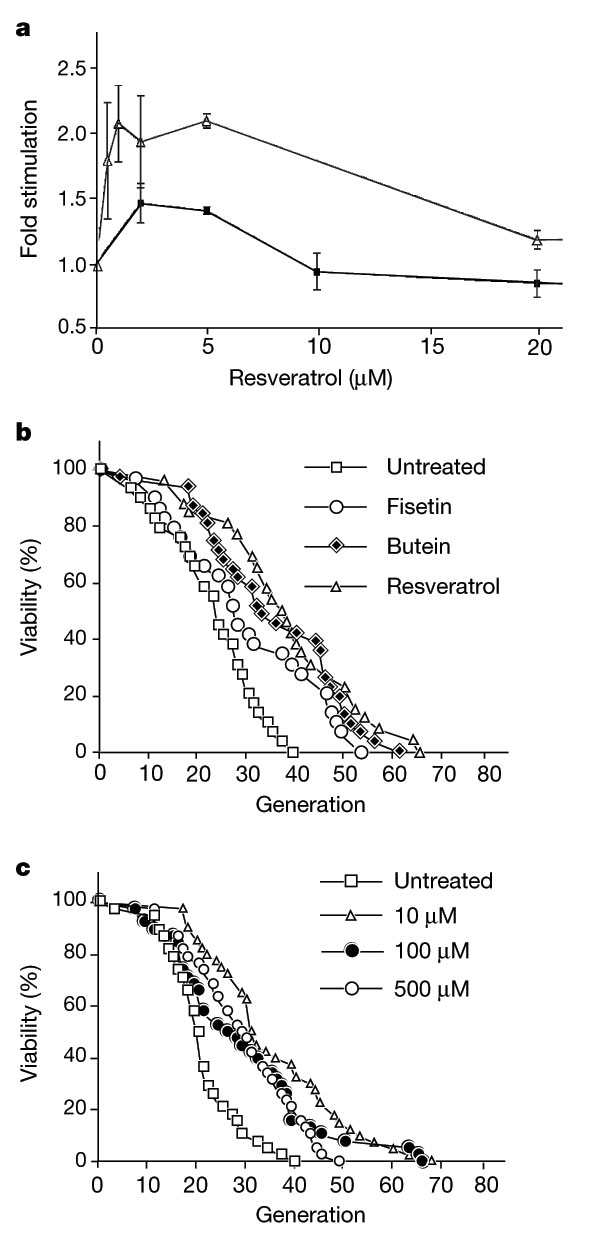
- Resveratrol has been extensively investigated in the Saccharomyces cerevesiae model system. In August 2003, Sinclair and Scherer reported 70% increase in yeast lifespan after induction with 10uM resveratrol.
- "In the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, calorie restriction extends lifespan by increasing the activity of Sir2, a member of the conserved sirtuin family of NAD+-dependent protein deacetylases2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Included in this family are SIR-2.1, a Caenorhabditis elegans enzyme that regulates lifespan7, and SIRT1, a human deacetylase that promotes cell survival by negatively regulating the p53 tumour suppressor. the potent activator resveratrol, a polyphenol found in red wine, lowers the Michaelis constant of SIRT1 for both the acetylated substrate and NAD+, and increases cell survival by stimulating SIRT1-dependent deacetylation of p53."
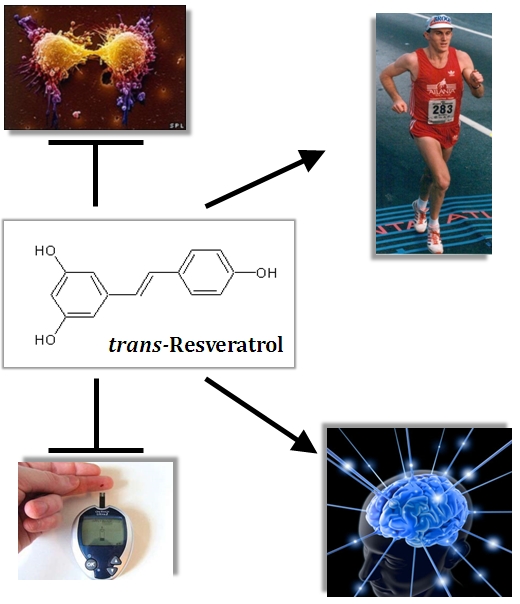
Health Benefits
- Improved cardiovascular function: resveratrol has been shown to have cardioprotective effects such as the suppression of atherosclerosis, inhibition of platelet aggregation, vasorelaxation promotion, and modulation of triglyceride blood levels, in a wide variety of in vitro and in vivo models. [1-4]
- Inhibition of carcinogenesis: one well-documented effect of resveratrol is the ability to induce cell death specifically in cancerous cells. This property of resveratrol has been shown for a wide variety of cancers, including colon cancer [5-7], pancreatic cancer [8], prostate cancer [9,10], breast cancer [11,12], and skin cancer [13,14]. In fact, several phase I human clinical trials are investigating the administration of resveratrol as a cancer therapy [15,16]
- Upregulates the antioxidant systems of cells, such as SuperOxide Dismutase and glutathione, and these cells are protected against oxidative damage [16,17].
- Resveratrol decreases several modes of inflammation [18-21].
- Maintenance of neural pathways: mouse models of Alzheimers and Parkinsons demonstrate the potential of resveratrol as a neuroprotective agent in degenerative neural diseases [22,23]. Experiments with rats, mice, and gerbils show that resveratrol administration protects against brain damage following ischemic stroke [24-26].
- Improves insulin sensitivity: resveratrol has been shown as a potent therapeutic for type 2 diabetes [27]. Pharmaceuticals based on resveratrol-like compounds for the treatment of diabetes are currently in Phase I clinical trials [28].
- Mimics caloric restriction in mammals and is proven to extend lifespans in invertebrates [29,30], a fish model [31] and is shown to reduce the genetic changes associated with aging in a mammalian mouse model [4,32].
Why resveratrol in beer?
-Beer made up 85.8% of all alcoholic beverage consumption (in total volume) in 2005.
-->Annual per capita consumption of Beer (2005) = ~20 gallons
-->Annual per capita consumption of Wine (2005) = ~2.5 gallons
-If resveratrol can be produced during fermentation, it provides an additional health benefit at no additional cost.
-->The resveratrol is produced in a ready-to-consume format!
-->Dark and anaerobic conditions required for fermentation improve resveratrol stability.
The Rice 2008 Synthetic BiOWLogists
| Home | The Team | The Project | Parts Submitted to the Registry | Notebook |
|---|
 "
"