Team:USTC/Component
From 2008.igem.org
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
===The cell density of the colony on the plate=== | ===The cell density of the colony on the plate=== | ||
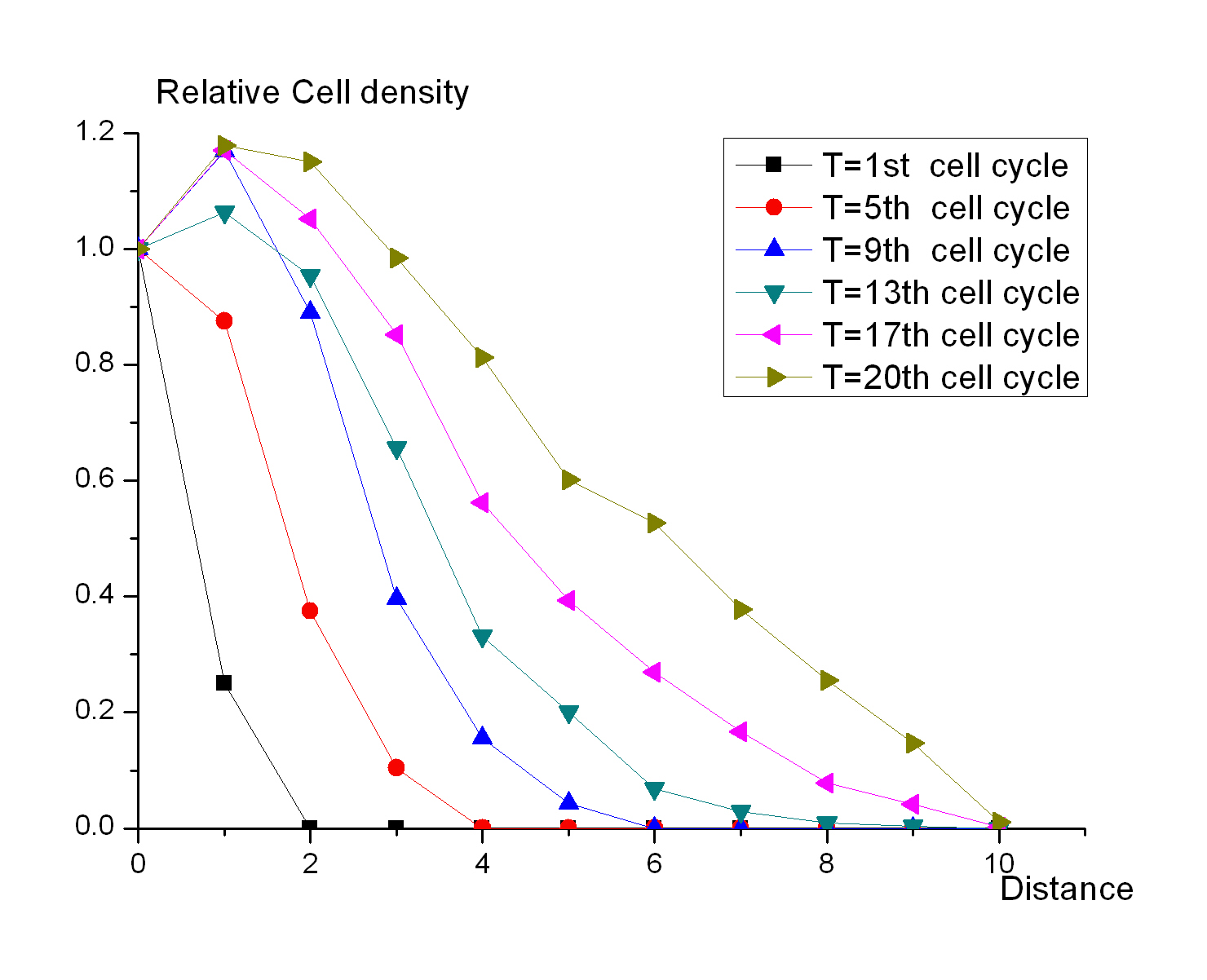
[[Image:USTC_cell_density.jpg|right|thumb|200px|Fig 1 .The changes of cell relative density related to the distance at different time points]] | [[Image:USTC_cell_density.jpg|right|thumb|200px|Fig 1 .The changes of cell relative density related to the distance at different time points]] | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
Cell Automata is employed to mimic the states of a colony growing on the plate. The first seed is placed on the center of the table. Each seed has a child in the next generation, and the child seed is randomly putted into the grid next to its parent. It is the simplest simulation, but it can suggest how the bacteria grow on the plate when the resources are affluent. Fig 1 shows the changes of cell relative density related to the distance at different time points.And the result shows that 1) the colony can be divided into two parts, the central region and the peripheral region, according to the density of cells; 2) the central region will expand during the growth of the colony; 3) the ratio of the highest density in the peripheral region to that in the central region is small enough to be discriminated by the concentration of small molecules. | Cell Automata is employed to mimic the states of a colony growing on the plate. The first seed is placed on the center of the table. Each seed has a child in the next generation, and the child seed is randomly putted into the grid next to its parent. It is the simplest simulation, but it can suggest how the bacteria grow on the plate when the resources are affluent. Fig 1 shows the changes of cell relative density related to the distance at different time points.And the result shows that 1) the colony can be divided into two parts, the central region and the peripheral region, according to the density of cells; 2) the central region will expand during the growth of the colony; 3) the ratio of the highest density in the peripheral region to that in the central region is small enough to be discriminated by the concentration of small molecules. | ||
| + | <br><br><br> | ||
== Report Component== | == Report Component== | ||
asdfasdfasdf | asdfasdfasdf | ||
Revision as of 14:03, 28 October 2008
| Home | The Team | The Project | Components | Parts Submitted to the Registry | Notebook |
|---|
Contents |
Components
Differetiate Component
We design a time-dependent gene regulation system to construct a self-organized system. The RhlL/RhlR system is employed to report the cell-population density. The sender cell will appear first when the density reaches a certain level. And it will tell other cells around it to be the receiver cells by sending the ligands to environment. After receiving the ligands, the Cre recombinase will be expressed to eliminate the function of sending ligands. In this way, a positional differentiation will be done.
The cell density of the colony on the plate
Cell Automata is employed to mimic the states of a colony growing on the plate. The first seed is placed on the center of the table. Each seed has a child in the next generation, and the child seed is randomly putted into the grid next to its parent. It is the simplest simulation, but it can suggest how the bacteria grow on the plate when the resources are affluent. Fig 1 shows the changes of cell relative density related to the distance at different time points.And the result shows that 1) the colony can be divided into two parts, the central region and the peripheral region, according to the density of cells; 2) the central region will expand during the growth of the colony; 3) the ratio of the highest density in the peripheral region to that in the central region is small enough to be discriminated by the concentration of small molecules.
Report Component
asdfasdfasdf
 "
"