Team:Brown/Project/Analysis
From 2008.igem.org
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
* Multiple "salt tests" were performed to determine the sensitivity of our apparatus. Initially, we created NaCl salt solutions of different concentrations and measured the resistance of each solution (Figure 4) with our final resistance apparatus (details in the "Testing" page). Salt solutions of different concentrations were placed in various wells of 6 well plates and resistance readings of each solution were taken for 60 seconds, with 10 readings per second. | * Multiple "salt tests" were performed to determine the sensitivity of our apparatus. Initially, we created NaCl salt solutions of different concentrations and measured the resistance of each solution (Figure 4) with our final resistance apparatus (details in the "Testing" page). Salt solutions of different concentrations were placed in various wells of 6 well plates and resistance readings of each solution were taken for 60 seconds, with 10 readings per second. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
Next, we wanted to test whether our system was sensitive enough to detect the change in ionic concentration that would occur after cell lysis occurs. The concentration of ions in M9 minimal media was calculated to be 0.006M salt. When cells lyse and their ions are released into solution, the final solution should have a total ionic concentration of 0.00605M salt (Calculations in lab notebook --/--) NaCl solution of these two concentrations were created and their resistances were measured with our system. Figure 5 shows that our system was not sensitive enough to measure the change in ionic concentration that would occur after lysis. | Next, we wanted to test whether our system was sensitive enough to detect the change in ionic concentration that would occur after cell lysis occurs. The concentration of ions in M9 minimal media was calculated to be 0.006M salt. When cells lyse and their ions are released into solution, the final solution should have a total ionic concentration of 0.00605M salt (Calculations in lab notebook --/--) NaCl solution of these two concentrations were created and their resistances were measured with our system. Figure 5 shows that our system was not sensitive enough to measure the change in ionic concentration that would occur after lysis. | ||
Revision as of 23:11, 29 October 2008
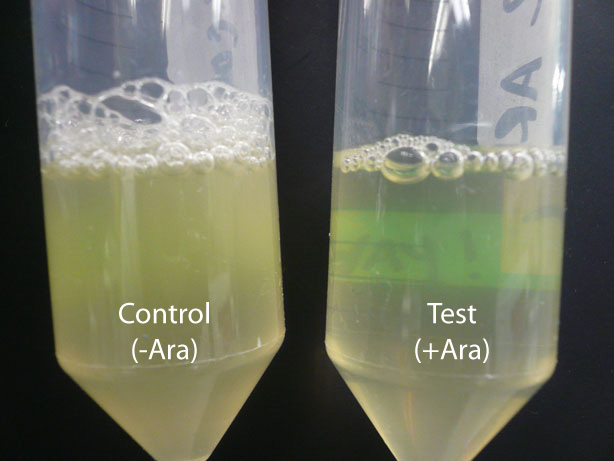
Optical DensityIn order to test the mechanism of the SRRz lysis cassette, we took optical density measurements as cell lysis occurred. The construct we used for testing was contained on the pVJ4 plasmid. This plasmid was obtained from the Mekalanos lab at HMS and contained the SRRz gene cassette in a pBAD18 plasmid. Initially we introduced arabinose to the culture of cells, allowed the cultures to sit at room temperature for several hours and measured the optical density before and after the cells lysed. The results are displayed in Figure 1. It was observed that when cells lysis occurred, the solution of lysing cells cleared after a few hours, providing qualitative evidence that lysis occurred (Figure 2). Next, we wanted to test the amount of time required for lysis to occur. We added 0.2% by volume of an arabinose stock solution to cell cultures and measured the optical densities of the cultures at discrete time points. The following graphs exhibit optical density trends during gene expression and resulting cell lysis and cell wall degradation. Figure 3a shows a test measuring optical density and correlates that data to a predicted change in resistance that should occur as the cells lyse. Figure 3B shows another test of change in optical density over time.
NaCl Testing
Next, we wanted to test whether our system was sensitive enough to detect the change in ionic concentration that would occur after cell lysis occurs. The concentration of ions in M9 minimal media was calculated to be 0.006M salt. When cells lyse and their ions are released into solution, the final solution should have a total ionic concentration of 0.00605M salt (Calculations in lab notebook --/--) NaCl solution of these two concentrations were created and their resistances were measured with our system. Figure 5 shows that our system was not sensitive enough to measure the change in ionic concentration that would occur after lysis.
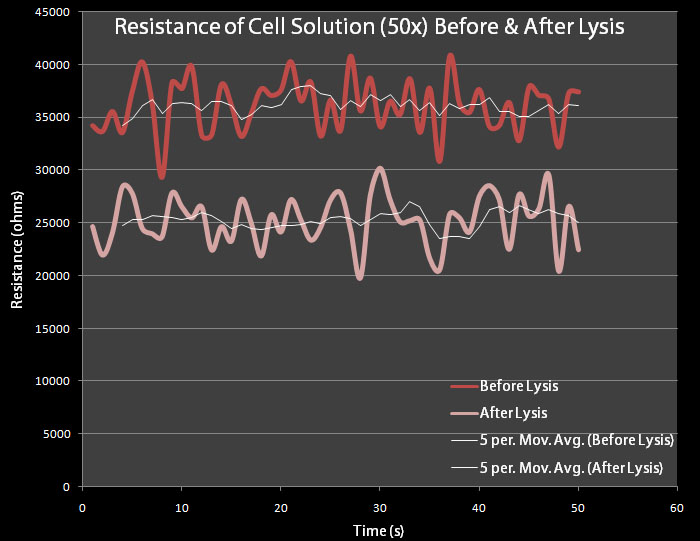
Resistance TestingEngineered E. coli bacteria cells containing the pVJ4 plasmid were grown into the stationary phase and then diluted to the mid-log phase. The control cells contain plasmid pRG1 which contains the cell lysis cassette under the Lac promoter. The test cells contain the pVJ4 plasmid. 500 mL dilutions of both pRG1 and pVJ4 were made in LB Lennox and then centrifuged. The giant pellets were resuspended in 10mL of M9 Minimal Media. 0.2% arabinose was added to the pVJ4 culture with a 50% Arabinose Solution Our resistance apparatus recorded measurements overnight. Figure 6 shows the resistance readings before lysis and after lysis. As expected there is a decrease in resistance.
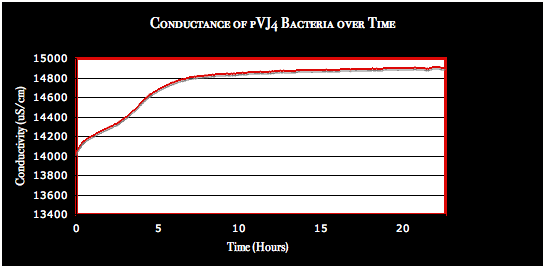
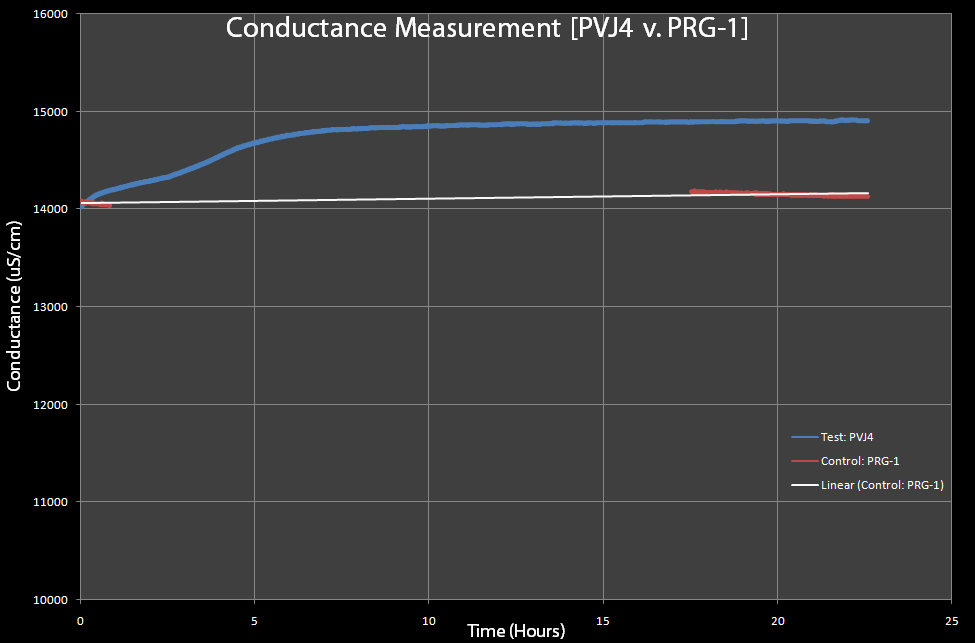
Conductivity Testing
|
 "
"