Team:Princeton/Results
From 2008.igem.org
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|[[Image:Results1_Princeton.jpg|500px]] | |[[Image:Results1_Princeton.jpg|500px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
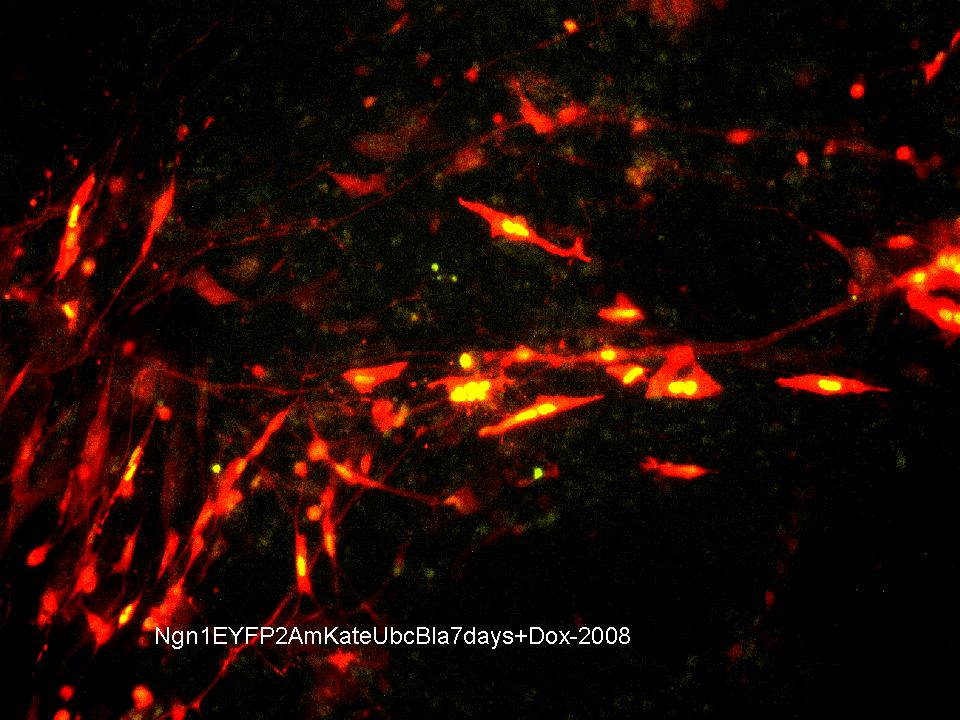
| - | + | Mouse embryonic stem cells (round and unspeciallized at day 0) that have been infected with the Lentiviral plasmid pLV-Ngn1-EYFP-2A-mKate-Ubc-Bla imaged 7 days after exposure to Doxycyclin. The yellow that is observed in the nucleus of the cells indicates the expression of the fluorescent protein EYFP and its attached transcription factor Ngn1, a cell fate regulator that drives the differentiation of stem cells into neurons. The lack of yellow in some of the cells indicates that Ngn1 is no longer being transcribed. The red observed in the cell body and its extensions indicates the expression of cytosolic fluorescent protein mKate as well as its attached Ubc promoter and blastomycin selection. Together these fluorescent proteins show that the plasmid has been incorporated into the host's genetic material and is being expressed. Furthermore, the circular cell bodies with long thin extensions leading to other cell bodies, and the web-like appearance of these extensions are both part of the phenotype expected from a neural precursor as well as mature neurons. (This is really cool.) | |
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
|[[Image:Results2_Princeton.jpg|500px]] | |[[Image:Results2_Princeton.jpg|500px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
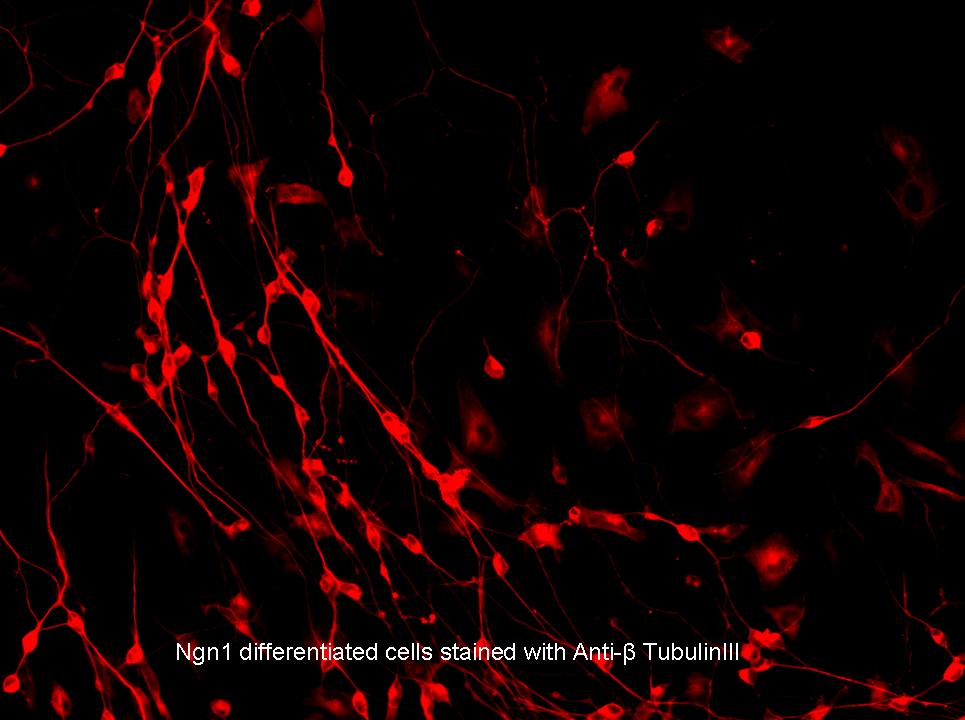
| + | Mouse embryonic stem cells (round and unspecialized at day 0) that have been infected with the Lentiviral plasmid pLV-Ngn1-EYFP-2A-mKate-Ubc-Bla imaged approximately 6 days after exposure to Doxycyclin and stained with anti-B-tubulinIII. The red observed in these cells indicate the presence of B-tubulinIII, which is a protein specific to neural progenitor cells, indicating that the stem cells have successfully been differentiated into neural precursors. | ||
Revision as of 03:10, 30 October 2008
PRINCETON IGEM 2008
| Home | Project Overview | Project Details | Experiments | Results | Notebook |
|---|
| Parts Submitted to the Registry | Modeling | The Team | Gallery |
|---|
|
Mouse embryonic stem cells (round and unspeciallized at day 0) that have been infected with the Lentiviral plasmid pLV-Ngn1-EYFP-2A-mKate-Ubc-Bla imaged 7 days after exposure to Doxycyclin. The yellow that is observed in the nucleus of the cells indicates the expression of the fluorescent protein EYFP and its attached transcription factor Ngn1, a cell fate regulator that drives the differentiation of stem cells into neurons. The lack of yellow in some of the cells indicates that Ngn1 is no longer being transcribed. The red observed in the cell body and its extensions indicates the expression of cytosolic fluorescent protein mKate as well as its attached Ubc promoter and blastomycin selection. Together these fluorescent proteins show that the plasmid has been incorporated into the host's genetic material and is being expressed. Furthermore, the circular cell bodies with long thin extensions leading to other cell bodies, and the web-like appearance of these extensions are both part of the phenotype expected from a neural precursor as well as mature neurons. (This is really cool.)
|
Mouse embryonic stem cells (round and unspecialized at day 0) that have been infected with the Lentiviral plasmid pLV-Ngn1-EYFP-2A-mKate-Ubc-Bla imaged approximately 6 days after exposure to Doxycyclin and stained with anti-B-tubulinIII. The red observed in these cells indicate the presence of B-tubulinIII, which is a protein specific to neural progenitor cells, indicating that the stem cells have successfully been differentiated into neural precursors.
 "
"