Team:BCCS-Bristol/Calendar-Notebook/9 July 2008
From 2008.igem.org
(→Swimming agar assay with aspartic acid) |
|||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{| align="center" | {| align="center" | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| | | | ||
[[Image:BCCS-080709-inoculation model swimming agar assay with aspartate.jpg | 250px]] | [[Image:BCCS-080709-inoculation model swimming agar assay with aspartate.jpg | 250px]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| align="center" | ||
| + | |+'''Inoculatin model''' | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 17:27, 7 August 2008
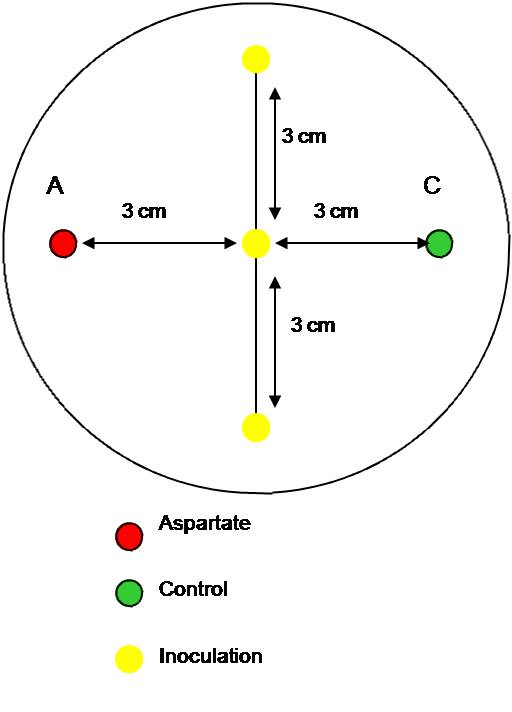
Swimming agar assay with aspartic acid
We conducted a second swimming agar assay with E. coli MG1655. This time, we added paper discs that were soaked with a L-aspartic acid solution. We wanted to observe whether the bacteria are attracted by the amino acid. We tested again different parameters:
- agar concentrations of 0.15 %, 0.3 % and 0.5 %
- incubation temperatures of 25 oC, 30 oC and 37 oC
- inoculations depths of "on the surface", "under the surface" and "deep in the medium"
- aspartic acid concentrations of 0.2 %, 0.1 % and 0.01 %
Photos of swiming agar were taken and travelled distances measured. 0.3% agar was found to be the best for an overnight culture and a temperature of 37oC was too high, since the swarms spread over the whole plate. All plates showed swarm spread at different levels giving inner and outer rings. Unfortunately, we observed no different movement/growth towards the L-aspartic acid compared with the control (water). It was assumed that this is due to the low concentration, but it wasn't possible to made a 0.4 % solution.
 "
"